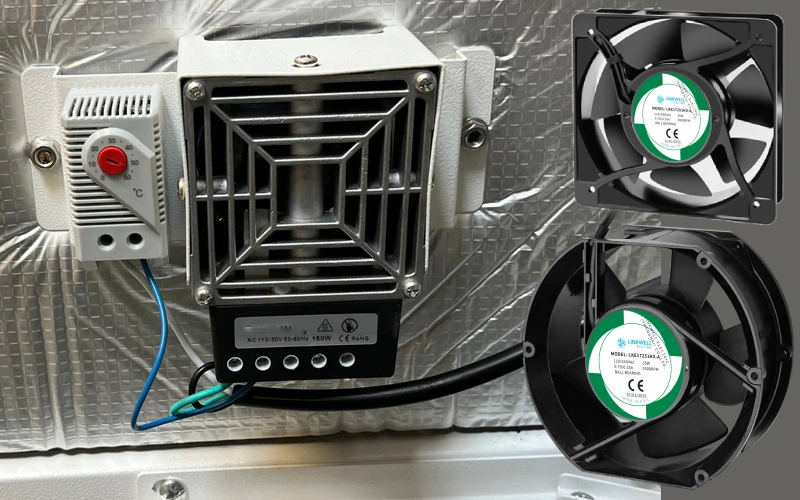
Choosing the right fan can feel tricky, but focusing on a few important factors makes it easier. You’ll want to look at airflow (CFM), static pressure, size, noise, power, reliability, and cost. Different jobs and spaces need different solutions, so think about your specific environment. Here’s a quick look at what matters most:
| Parameter | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Airflow (CFM) | How much air the fan moves |
| Static Pressure | How well the fan pushes air against resistance |
| Size | The fan’s dimensions and fit in your setup |
| Noise | How loud the fan runs |
| Power | The energy the fan uses |
| Reliability | How long and well the fan lasts |
| Cost | Your budget for the fan |
Keep these parameters fan in mind as you explore your options.
Key Takeaways
- Understand key parameters like airflow (CFM) and static pressure. These factors determine how well a fan moves air and overcomes resistance.
- Consider noise levels when selecting a fan. Low noise ratings are important for quiet environments, ensuring comfort and productivity.
- Evaluate the size and material of the fan. Ensure it fits your space and is made from durable materials to withstand your environment.
- Define your requirements based on your specific environment. Assess factors like heat, humidity, and space constraints to choose the right fan.
- Use performance curves to match fan specifications to your needs. This helps you avoid mistakes and ensures optimal fan selection.
Key Parameters Fan Selection
Airflow and Static Pressure
When you select a fan, you want to know how much air it can move and how well it can push air through obstacles. Airflow tells you the volume of air a fan moves, usually measured in cfm. Static pressure shows how much resistance the fan can handle, like filters or tight spaces. You’ll often see static pressure measured in inches of water column, inches of mercury, or Pascals.
| Unit of Measurement | Description |
|---|---|
| Inches of Water Column (inWC) | Measures static force in airflow systems, indicating pressure exerted by a one-inch high column of water. |
| Inches of Mercury (inHg) | Used in HVAC systems to measure force, quantifying pressure from a one-inch tall column of mercury. |
| Pascals (Pa) | A unit of pressure that quantifies static force encountered by air in a network. |
The relationship between cfm and static pressure is important. As cfm goes up, static pressure usually goes down. In an open enclosure, you get maximum cfm and low static pressure. In a closed space, static pressure rises and cfm drops. Linkwell’s Computer Chassis Fan and Axial Fan handle both high cfm and static pressure, making them great for different cabinet setups.
Noise, Power, and Reliability
Noise matters, especially if you work in a quiet office or a control room. Fans with low noise ratings keep your space comfortable. Power tells you how much energy the fan uses. Larger fans or those working against high static pressure will use more power. Reliable fans last longer and need less maintenance. Common causes of failure include lubrication issues, imbalance, or motor problems. Linkwell fans use quality bearings and strong materials, so you get long service life and fewer breakdowns.
Tip: Always check the reliability ratings and power specs before you select a fan. Linkwell’s DC Fan series offers advanced control and long-lasting performance, even in tough environments.
Size, Material, and Mounting
Fan size affects both cfm and static pressure. Bigger fans can move more air but may not fit every space. Materials like mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum impact durability and cost. For example, aluminum is light and resists corrosion, while stainless steel works well in harsh environments. Mounting options let you install the fan easily in your cabinet or enclosure. Linkwell’s Cabinet Fan comes in different sizes and materials, so you can match the right fan to your needs.
When you look at all these parameters fan, you make sure your system gets the right flow rate, cooling, and reliability. Linkwell’s wide range of fans helps you find the perfect fit for your application.
How to Select the Right Fan for Your Application
Choosing the best fan for your setup can feel overwhelming, but you can break it down into three simple steps. Let’s walk through how you can select a fan that matches your needs and delivers the right cooling solution.
Define Requirements and Environment
Start by looking at your environment and what you need the fan to do. Every space is different, so you want to think about more than just moving air. Ask yourself these questions:
- What kind of equipment or area needs cooling?
- How much space do you have for the fan?
- Are there any special conditions, like high heat, humidity, or dust?
- Do you need the fan to run quietly?
- What is your budget for the project?
Here’s a table to help you focus on the most important environmental factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces power costs and helps the environment. Efficient fans lower your bills and carbon footprint. |
| Environmental Conditions | Make sure the fan can handle heat, moisture, or chemicals. This protects your investment and keeps the fan running longer. |
| Noise Levels | Keep your workspace comfortable and meet noise rules. Too much noise can make people tired and less productive. |
| Size and Space Constraints | The fan must fit in your space and be easy to reach for maintenance. |
| Budget Considerations | Think about both the upfront cost and long-term savings. Sometimes a cheaper fan costs more over time due to higher energy use or more repairs. |
You also want to pay attention to things like temperature, humidity, and dust. Here are a few tips:
- Talk to an expert if you’re not sure about the types of dust or chemicals in your space.
- Know the normal temperature range where the fan will run.
- Think about whether sunlight will heat up the area.
- Check if your fan will face dry, hot weather or cold, snowy conditions.
- If your environment changes a lot, pick a fan that can handle different situations.
Calculate Airflow and Static Pressure
Once you know your needs, you can figure out the numbers. This is where you look at airflow (cfm) and static pressure. Airflow tells you how much air the fan moves, while static pressure shows how well it pushes air through filters, coils, or tight spaces.
To get the right numbers, follow these steps:
- Map out all the paths where air will flow.
- List every part that air passes through, like filters, coils, grilles, and dampers.
- Add up the pressure loss for each part.
- Find the highest pressure the fan will need to overcome.
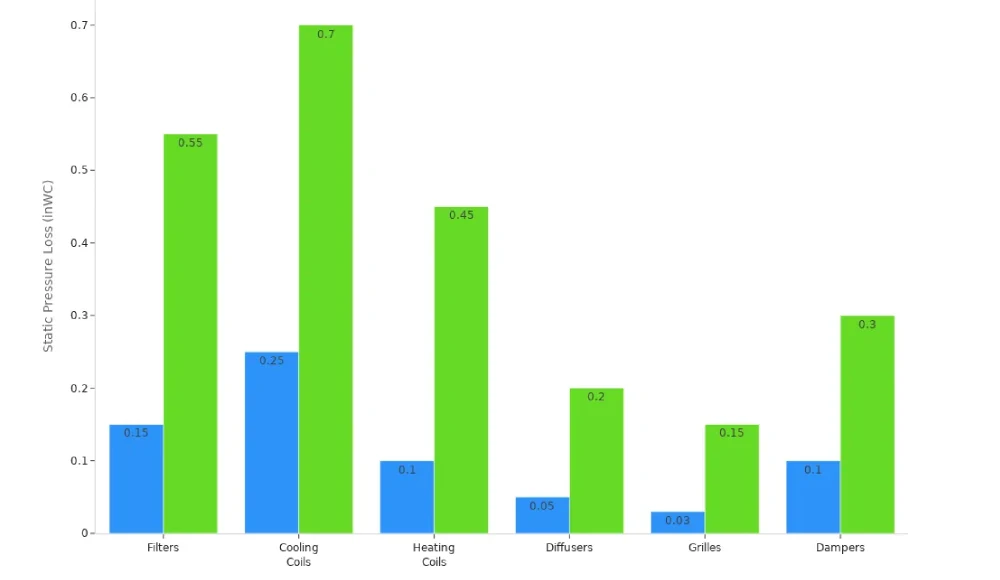
Here’s a table with typical static pressure losses for different parts:
| Component | Typical Range (inWC) | Factors Affecting Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Filters | 0.15-0.55 | MERV rating, dust loading |
| Cooling Coils | 0.25-0.70 | Rows, fins per inch, velocity |
| Heating Coils | 0.10-0.45 | Configuration, velocity |
| Diffusers | 0.05-0.20 | Type, throw distance, volume |
| Grilles | 0.03-0.15 | Free area ratio, velocity |
| Dampers | 0.10-0.30 | Position, blade configuration |
For example, in a server room, you might see static pressure between 0.03″ and 0.07″ WC. If you want to cool servers with a 20°F temperature rise, you’ll need about 158 cfm per kilowatt. Cleanrooms usually keep a positive pressure of 0.03 to 0.05 inches of water gauge.
Tip: Use the equal friction method to keep calculations simple. This method keeps the pressure drop steady along the airflow path, making it easier to size your fan.
Match Parameters to Linkwell Fans
Now that you have your numbers, you can match them to the right fan. Look at the parameters fan like cfm, static pressure, size, and noise level. Compare these to the specs in the manufacturer’s data sheets and performance curves.
Here’s how you can select a fan for different applications using Linkwell’s lineup:
- Computer Chassis Fan: Great for electronics and IT equipment. Delivers high cfm and low noise, perfect for server racks or workstations.
- Axial Fan: Works well in electrical cabinets and telecom enclosures. Handles both airflow and static pressure, and fits tight spaces.
- DC Fan: Ideal for tough environments. Offers advanced control, high air flow efficiency, and long service life. Handles wide temperature swings and high humidity.
- Cabinet Fan: Best for industrial control panels and telecom cabinets. Provides strong flow rate, low noise, and easy installation.
| Specification | Linkwell Product | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | F9 | Meets/exceeds |
| Filtration Grade | ULPA Filter | Meets/exceeds |
| IP Class | IP54, IP55, IP56 | Meets/exceeds |
| Noise Level | 46-50 dB(a) | Acceptable range |
| Operating Temp Range | -30 to +70 °C | Standard range |
Note: Always check the manufacturer’s data sheets and performance curves before you select a fan or select a blower. These charts show how the fan performs at different static pressure and cfm levels. This helps you avoid mistakes and get the best fan selection for your needs.
When you follow these steps, you can select the right fan for your application. You’ll get a cooling solution that matches your environment, fits your space, and keeps your equipment safe.
Fan Selection Tips and Common Mistakes
Evaluate Performance Curves
When you look at fan performance curves, you get a clear picture of how a fan will work in your system. These curves show the relationship between flow rate and static pressure. You want to find the operating point where your system’s airflow resistance matches the fan’s pressure capabilities. Here’s how you can use these curves:
- Find the intersection of your system’s pressure and the fan’s curve.
- Check the fan’s CFM, static pressure, and power at that point.
- Look at the efficiency curve to pick a fan that runs close to peak efficiency.
Performance curves also help you spot problems like clogged filters or closed dampers. If you see a drop in airflow, you can use the curve to troubleshoot.
Tip: Axial fans can show uneven curves and may get noisy or use more power in the stall region. Centrifugal fans have smoother curves and usually run quieter.
Consider Noise and Energy Efficiency
Noise can make a workspace uncomfortable. You can lower fan noise by using aerodynamic inserts, adjusting fan speed, or changing the installation layout. Straight duct runs and bell-mouth intakes help reduce noise by up to 12dB(A). Lowering fan speed by 20% can cut noise by 5dB.
Energy efficiency matters for your budget. High-efficiency DC fans use much less electricity than standard AC fans. Check out this table:
| Feature | Standard Fans (AC-motor) | High-Efficiency Fans (DC-motor) |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity Consumption | 100 watts | 30-40 watts |
| Energy Savings Percentage | N/A | 60-80% less electricity |
| Potential AC Savings | N/A | 12-35% by raising thermostat 4-7°F |
Avoid Sizing and Compatibility Errors
Sizing mistakes can cause big problems. If you pick a fan that’s too big, you get too much airflow, more noise, and possible motor issues. If the fan is too small, you get uneven temperatures and more wear on bearings. Here are common errors and their effects:
| Error Type | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Oversized Fans | Inefficient airflow, increased noise, motor issues, discomfort |
| Undersized Fans | Increased noise, bearing wear, uneven temperature distribution |
| Neglecting Furniture and Clearance | Obstruction, safety hazards, discomfort |
| Ignoring Local Building Codes | Safety hazards, code violations, electrical issues |
To avoid these mistakes, measure your space, check the volume of air to move, and consider the layout. If you’re unsure, Linkwell’s team can help with custom solutions and expert support.
Note: Always double-check measurements and system requirements before you buy a fan.
Linkwell Fan Solutions for Industry Needs
Computer Chassis Fan Applications
You want your electronics to stay cool and run smoothly, right? Linkwell’s computer chassis fans make that happen. These fans fit all sorts of setups, from gaming rigs to data centers. You’ll find 92mm fans in compact builds, keeping GPUs and CPUs at safe temperatures. If you work with 3D printers or NAS devices, 60mm fans deliver the airflow you need in tight spaces. For ultra-small routers or mini PCs, 30mm fans step up with higher RPMs, though you might notice a bit more noise.
- Linkwell fans push a lot of air, which means better cooling for your gear.
- They run quietly, so you can focus on your work or game without distractions.
- Even under heavy loads, these fans keep things cool, often beating industry averages.
Here’s a quick look at how Linkwell fans meet different industry needs:
| Industry | Key Features |
|---|---|
| IT | High air circulation, perfect for data centers and server rooms. |
| Manufacturing | Handles high air volumes and pressure, keeping equipment safe. |
| HVAC | Works for supply, exhaust, and air pollution control. |
Axial, DC, and Cabinet Fan Uses
You’ll see Linkwell’s axial, DC, and cabinet fans in all kinds of industrial environments. Cabinet exhaust fans work best in packed cabinets and tough setups, giving you strong airflow and great efficiency in tight spaces. Axial fans fit open cabinets and basic cooling jobs, offering moderate airflow and solid performance.
| Fan Type | Airflow Strength | Best For | Efficiency in Tight Spaces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cabinet Exhaust Fans | High | Packed cabinets, tough setups | Excellent |
| Axial Fans | Moderate | Open cabinets, basic cooling | Good |
Linkwell’s DC axial fans last over 50,000 hours, so you don’t have to worry about frequent replacements. These fans run 24/7, keeping airflow steady no matter the conditions. Built with ball bearings and quality motors, they stand up to heavy use. You can customize size, voltage, and speed to match your project. Linkwell also supports you with global logistics and technical help, making sure you get the right solution fast.
Tip: Regular cleaning and inspection help your fans last longer. Lubricate bearings and check alignment to keep everything running smoothly.
Linkwell stands out with global quality, innovation, and strong support. You get fans that fit your needs, last a long time, and come with expert help whenever you need it.
Choosing the right fan gets easier when you focus on key parameters like airflow and static pressure. Using a step-by-step approach helps you:
- Boost system performance and match energy goals.
- Improve energy efficiency for a greener setup.
- Make your design more reliable and effective.
You get better results when you match fans to your needs. Linkwell supports you with technical guidance, performance charts, and custom options. Need help? Visit Linkwell’s website or reach out for expert advice.
FAQ
How do you know which fan size fits your cabinet?
Check the space inside your cabinet. Measure the width, height, and depth. Look at the fan’s dimensions in the product specs. If you need help, ask Linkwell’s support team for advice.
What does CFM mean when picking a fan?
CFM stands for cubic feet per minute. It shows how much air your fan moves. Higher CFM means more cooling power. Match the CFM to your equipment’s needs for the best results.
Can you get custom fans for special projects?
Yes! Linkwell offers OEM and ODM services. You can request custom sizes, voltages, airflow, or branding. Just contact their team and share your project details.