When deciding between single-phase and three-phase transformers, it’s crucial to understand the differences in power delivery. A single-phase transformer uses two wires to carry power, making it ideal for smaller applications like homes or small businesses.
In contrast, a three-phase transformer utilizes three wires, providing more efficient power transfer for larger applications, such as industrial machines or large commercial buildings.
The main distinction lies in how each system distributes power; three-phase transformers offer higher stability and can handle heavier loads with less fluctuation in voltage.
What is Single Phase Transformer
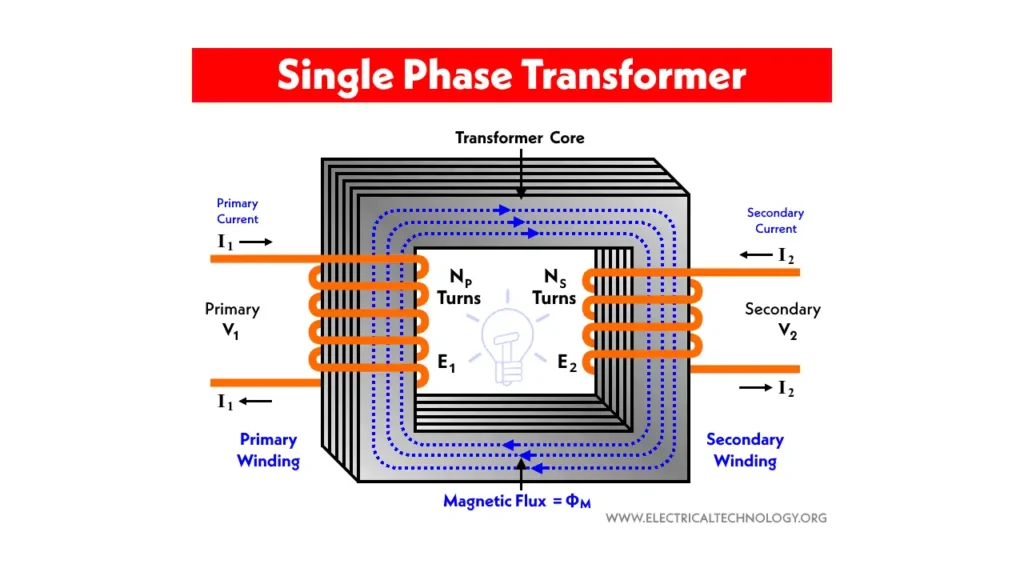
A single-phase transformer is a type of electrical transformer that uses two conductors—one for the live wire and one for the neutral. It is designed to supply power to smaller loads, typically in residential settings or small businesses. Single-phase transformers are simple and cost-effective, providing a stable voltage for low-demand applications.
In operation, a single-phase transformer operates by transferring electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. It is ideal for powering household appliances, lighting, and heating systems, where the demand for electricity is relatively low and does not require the more complex power systems seen in larger industrial setups.
What is Three Phase Transformer?
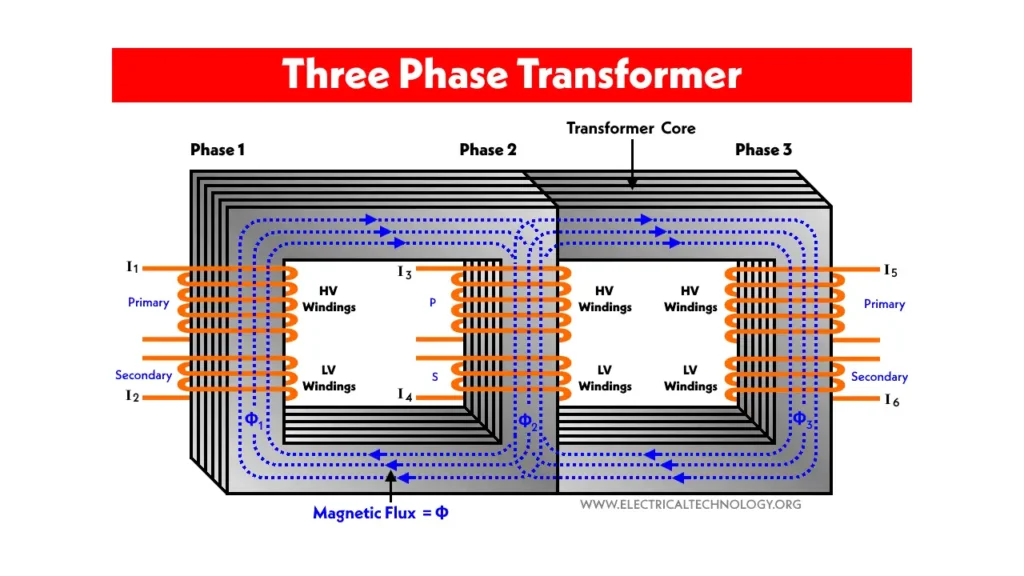
A three-phase transformer is an electrical device that supplies power using three alternating currents, each offset by 120 degrees. This configuration allows for a more efficient and continuous flow of electricity, making it ideal for high-demand applications. Unlike single-phase transformers, three-phase transformers use three conductors, providing a balanced and stable power supply that is suitable for large-scale operations.
Three-phase transformers are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where there is a need to power large machinery, heavy equipment, or entire buildings. By distributing power evenly across three phases, they reduce the risk of power surges and voltage fluctuations, ensuring smoother and more reliable operation.
Single Phase vs Three Phase Transformer
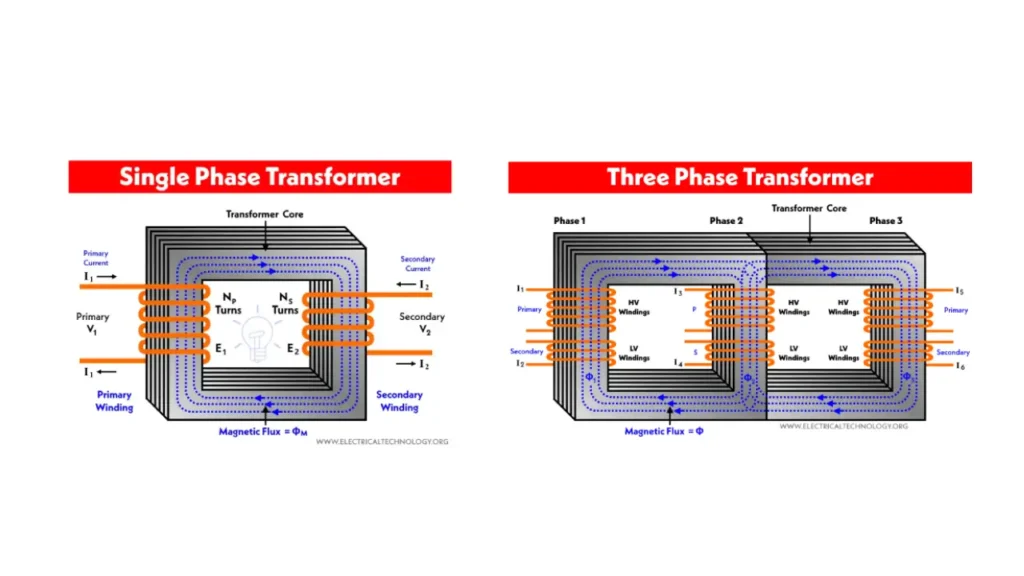
When choosing between a single-phase and a three-phase transformer, it’s important to consider the specific power needs of your application. While both types are designed to transfer electrical energy, they differ significantly in terms of power capacity, efficiency, and ideal use cases.
Understanding difference between single phase transformer and three phase transformer is also important for your electronic project.
Single Phase Transformer
Features
A single-phase transformer operates with two conductors—one for live current and one for neutral—providing power to lower-demand applications. Its design is relatively simple compared to three-phase transformers, making it a cost-effective solution for smaller systems. Typically, single-phase transformers are lighter, smaller in size, and easier to maintain. These transformers are capable of providing steady power for small devices, but their maximum capacity is limited by their two-wire system, making them unsuitable for high-demand environments.
Benefits
The key benefit of a single-phase transformer lies in its affordability and ease of installation, which makes it the go-to solution for residential and light commercial uses. It’s also highly reliable for low-energy devices, providing a stable voltage for lights, small motors, and home appliances. Additionally, its simple structure leads to lower maintenance costs, and its compact size allows it to fit easily into residential and small business settings without taking up significant space.
Applications
Single-phase transformers are ideal for powering homes, small businesses, and light commercial applications where the power requirements are not significant. They are commonly used in residential areas for appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and lighting systems. These transformers also serve small commercial establishments like shops and offices, providing reliable and cost-effective power for lighting, HVAC systems, and basic machinery. However, they are not suitable for large machinery or high-power systems typically found in industrial settings.
Three Phase Transformer
Features
A three-phase transformer operates with three conductors, each carrying one phase of the alternating current (AC) power, providing a more consistent and efficient energy supply. The three-phase system works in a staggered manner, ensuring that power is always available, as one phase is always in a different part of the cycle than the others. This setup results in fewer voltage dips and a smoother, continuous power flow. Three-phase transformers are designed for higher capacities, making them ideal for large-scale applications requiring constant power.
Benefits
The primary advantage of a three-phase transformer is its ability to supply high-capacity, stable power. By distributing energy across three separate phases, it minimizes the risk of power fluctuations, providing consistent and reliable voltage levels.
This leads to less wear and tear on machines and appliances. Three-phase systems are also more efficient than single-phase systems, as the power is distributed more evenly, reducing losses and making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Furthermore, they can deliver more power using smaller and lighter conductors, making them more efficient over long distances.
Applications
Three-phase transformers are essential in industrial, commercial, and large-scale applications. They power heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and large commercial buildings that demand a constant, high-volume power supply.
From manufacturing plants to hospitals and office buildings, three-phase transformers ensure that power is evenly distributed, reducing downtime and ensuring smooth operations. They also serve as the backbone for electric grids, providing the necessary energy for public infrastructure. With their ability to handle high-power loads, these transformers are critical in sectors where power reliability is non-negotiable.
Here is the table about the differences between single phase and three phase transformers in the following:
| Feature | Single Phase Transformer | Three Phase Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Single phase (2 conductors) | Three phases (3 conductors) |
| Applications | Homes, small businesses, light appliances | Industrial machinery, large buildings |
| Power Capacity | Lower capacity, suited for light loads | High capacity, suited for heavy machinery |
| Voltage Stability | Can face voltage dips and fluctuations | Provides stable voltage with minimal dips |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for high power needs | More efficient and balanced power supply |
How to Choose Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer?
Choosing between a single-phase and a three-phase transformer depends largely on the power requirements and the type of application. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Power Demand: If your application requires high power, a three-phase transformer is the better choice. It efficiently distributes energy across three phases, making it ideal for heavy-duty machinery or large-scale industrial operations. Single-phase transformers, however, are better suited for smaller power needs.
- Efficiency: Three-phase transformers are generally more efficient than single-phase transformers. They maintain a constant flow of power, minimizing energy loss and reducing the risk of voltage fluctuations. For large operations, this makes them a more reliable and cost-effective choice over time.
- Cost: Single-phase transformers are typically less expensive to purchase and install, making them an economical option for low-power applications. Three-phase transformers, while more expensive upfront, offer long-term savings due to their superior efficiency and capacity.
- Application Size: If your application involves a few low-power devices like home appliances, lighting, or small office equipment, a single-phase transformer will be sufficient. For large commercial buildings, industrial plants, or large machinery, a three-phase transformer is necessary to handle the high power loads efficiently.
Conclusion
A single-phase transformer uses two wires and is ideal for low-power applications, providing a steady supply of electricity for residential and small business use. In contrast, a three-phase transformer operates with three wires, delivering more efficient power and is used for industrial and high-demand applications.
The main difference between the two lies in their power output, with three-phase transformers offering higher efficiency and reliability for larger loads.
For wholesale transformers, consider Linkwell Electrics, a trusted supplier of both single-phase and three-phase options.