Three Phase to One Phase Transformers play a crucial role in power distribution. They efficiently convert three-phase power, commonly used for transmission, into single-phase power, which is essential for residential and some commercial applications. This transformation ensures a stable and reliable power supply for diverse electrical needs.
Understanding how these transformers integrate into the power grid is vital. They bridge the gap between high-voltage, three-phase networks and the single-phase systems that power our homes and smaller businesses, highlighting their significance in the overall electricity delivery infrastructure.
What is Three Phase Transformer?
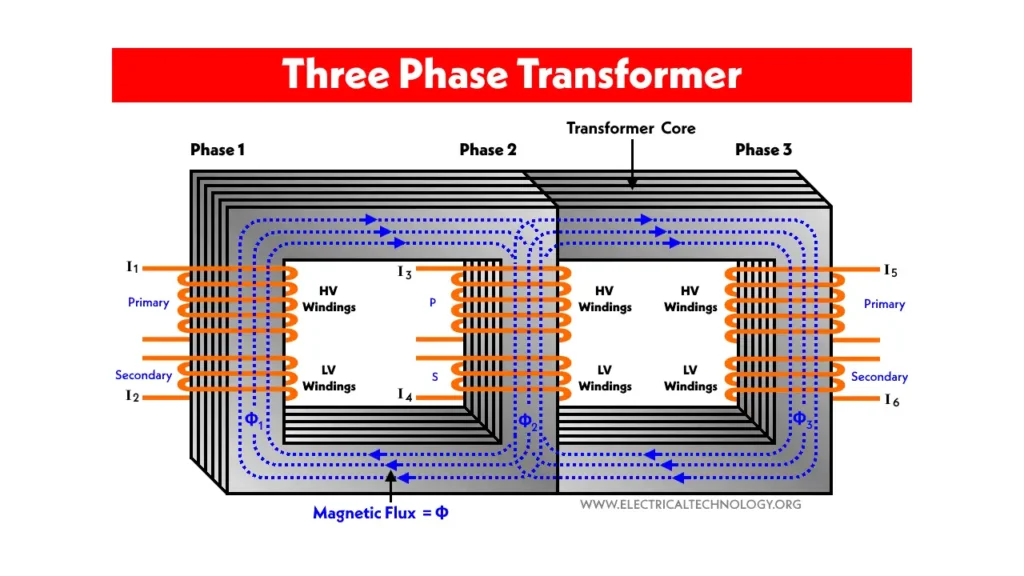
A three-phase transformer is an electrical device designed to transform voltage levels in a three-phase power system. Instead of using three separate single-phase transformers, a three-phase transformer combines the magnetic circuits for all three phases into a single core. This integrated design makes them more compact, cost-effective, and lighter for a given power rating compared to using three individual single-phase units.
Operating on the principle of electromagnetic induction, when a three-phase AC supply is connected to the primary windings, it creates alternating magnetic fluxes in the core, which in turn induce corresponding voltages in the secondary windings, allowing for voltage step-up or step-down as required for various industrial, commercial, and power distribution applications.
What is One Phase Transformer?
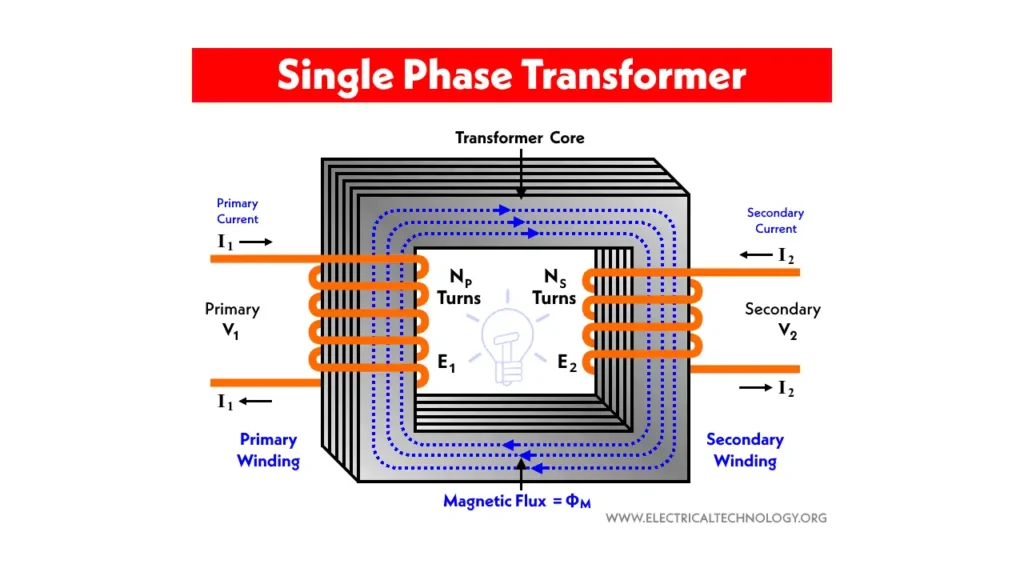
A single-phase transformer is an electromagnetic device used to change the voltage level of a single-phase alternating current (AC) supply. It consists of two windings, a primary and a secondary, wound around a common magnetic core.
When an AC voltage is applied to the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic flux in the core, which, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, induces an AC voltage in the secondary winding. The ratio of the voltages in the primary and secondary windings is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of turns in each winding, allowing the transformer to step up or step down the voltage as needed for various applications, primarily in residential and light commercial power distribution.
Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer
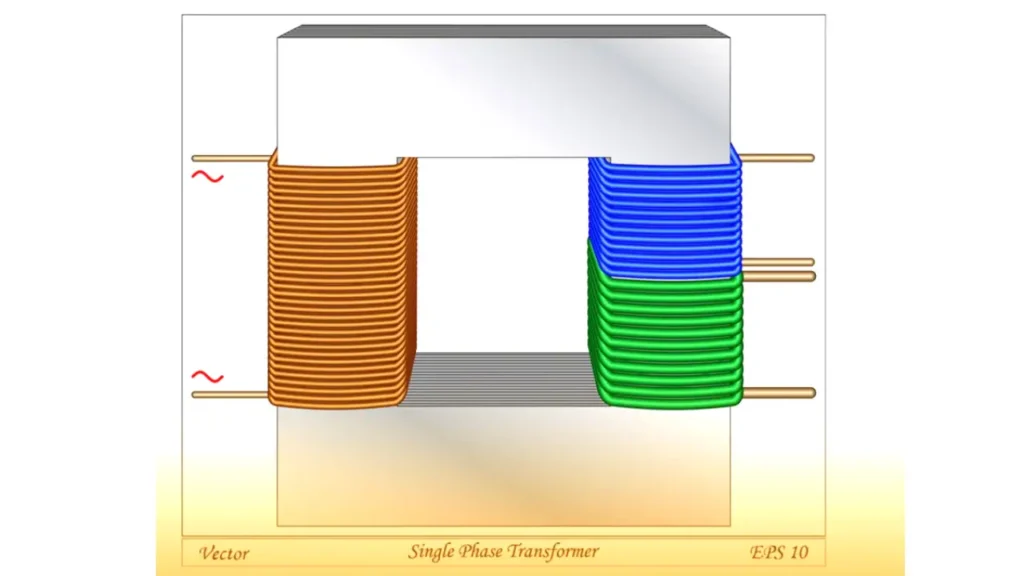
While a standard transformer cannot directly convert single-phase power into three-phase power, specialized devices known as phase converters are used to achieve this. These are not true transformers in the traditional sense but rather systems that manipulate the single-phase input to create a simulated three-phase output.
These converters often employ rotating machinery (rotary phase converters) or static electronic components (static phase converters and variable frequency drives) to generate the additional phases.
These phase converters find applications where three-phase equipment needs to be operated in locations with only single-phase power availability. However, it’s important to note that the generated three-phase power might not be perfectly balanced, and the power capacity might be derated compared to a true three-phase source. Common types of phase converters include:
- Rotary Phase Converters: Utilize a three-phase induction motor running as an idler to generate the third phase.
- Static Phase Converters: Employ capacitors and inductors to create an approximate third phase, often suitable for resistive loads or starting three-phase motors.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): While primarily used for motor speed control, some VFDs can take a single-phase input and generate a three-phase output.
240v Single Phase to 208v Three Phase Transformer
It’s important to clarify that a standard transformer cannot directly convert 240V single-phase input into a balanced 208V three-phase output. Transformers operate based on electromagnetic induction between isolated windings with a fixed turns ratio, and they don’t inherently change the number of phases. To obtain a three-phase supply from a single-phase source, a phase converter is required, which is not a traditional transformer.
However, a three-phase transformer with a 240V delta primary and a 208V wye secondary can accept a three-phase 240V input and step it down to a 208V three-phase output.
If your scenario involves having only a 240V single-phase supply and needing a 208V three-phase output, you would typically need to employ a phase converter. These devices come in different types, each with its own characteristics and suitability for various loads:
- Rotary Phase Converters: These use a three-phase motor as an idler to generate the third phase, providing a relatively balanced three-phase output suitable for many motor loads.
- Static Phase Converters: These use capacitors to create an approximate third phase and are often used for starting three-phase motors, but the output might not be suitable for all three-phase equipment.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Some VFDs can take a single-phase input and generate a controlled three-phase output, offering speed control in addition to phase conversion.
How to Connect Single-Phase Transformer to Three-Phase?
Connecting a single-phase transformer directly to a three-phase system is not a standard or efficient method for power transformation. Single-phase transformers are designed for single-phase circuits and lack the necessary windings and connections to properly interface with a three-phase supply. Attempting a direct connection can lead to imbalance, overheating, and potential damage to the transformer and the system.
Understanding the Limitations
Single-phase transformers have only a primary and a secondary winding, intended for a single alternating current. Three-phase systems, on the other hand, utilize three distinct AC voltages that are phase-shifted by 120 electrical degrees. Directly connecting a single-phase transformer to any two lines of a three-phase system will only utilize a portion of the available power and won’t create the balanced three-phase transformation needed for most three-phase loads.
Exploring Alternative Solutions
Instead of direct connection, achieving a three-phase to single-phase transformation typically involves using a bank of three identical single-phase transformers.
These can be connected in various configurations, such as delta-wye or wye-delta, on the three-phase side to step down or step up the voltage, and the single-phase output is taken from one of the secondary windings. Alternatively, specialized Scott-T transformers can be used for a more balanced conversion between three-phase and two-phase systems, from which a single phase can be derived.
Considerations for Implementation
When using a bank of single-phase transformers for three-phase to single-phase conversion, it’s crucial to ensure that all three transformers have the same voltage and power ratings. The chosen connection configuration will depend on the specific voltage transformation requirements and the nature of the single-phase load. Proper fusing and circuit protection are essential to safeguard the transformers and the electrical system from faults.
Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer Converter
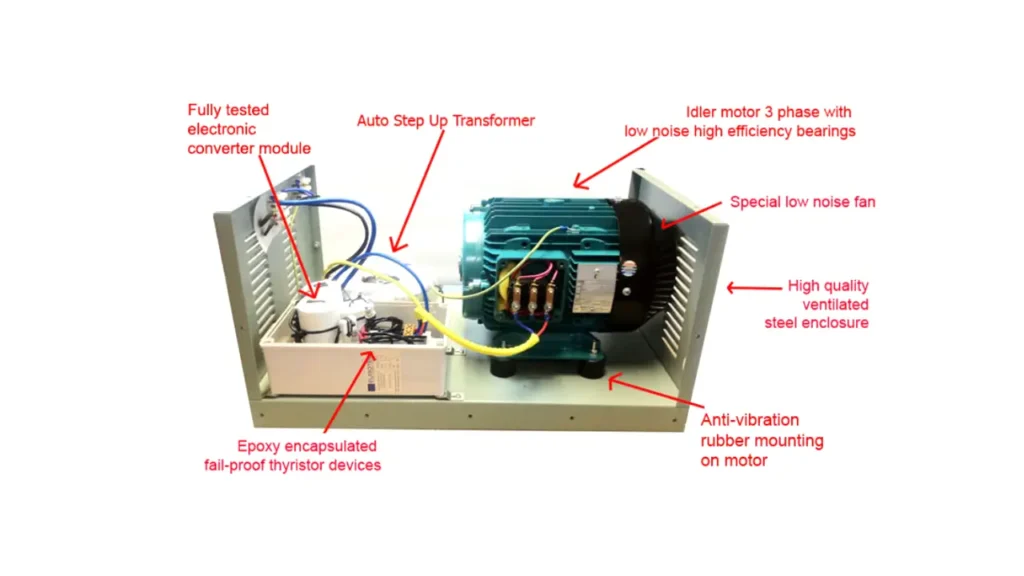
While a transformer itself cannot change the number of phases, a “Single Phase to Three Phase Transformer Converter” typically refers to a device or system designed to produce a three-phase output from a single-phase input. These are not traditional transformers but rather phase converters. They manipulate the single-phase power to generate the necessary voltage waveforms that simulate a three-phase system.
These converters come in various types, each with its own method of creating the additional phases. Rotary phase converters use a rotating motor-generator setup, while static phase converters employ capacitors to create a third phase primarily for starting motors. Digital or solid-state phase converters use electronic circuitry to synthesize a more balanced three-phase output. The choice of converter depends on the specific application, the type of load (resistive or inductive), and the required power quality.
Can a Transformer Go From 3-Phase to Single-Phase?
Yes, a three-phase transformer can be used to supply a single-phase load. This is typically achieved by connecting the single-phase load across two of the terminals on the secondary side of the three-phase transformer.
In this configuration, the transformer effectively acts as two single-phase transformers connected in series or parallel, depending on the internal winding connections (delta or wye).
However, it’s important to understand that when a three-phase transformer supplies a single-phase load, the load will be unevenly distributed across the three phases of the transformer. This can lead to an imbalance in the currents drawn from the three-phase supply, potentially causing inefficiencies and increased losses within the transformer and the supply system.
While feasible for smaller single-phase loads, it’s generally not the most efficient or balanced way to supply significant single-phase power from a three-phase source. Specialized three-phase to single-phase transformers are designed to mitigate these imbalances to some extent.
Can a Transformer Convert Single Phase to Three Phase?
No, a standard transformer, by itself, cannot directly convert single-phase electrical power into three-phase power. A transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction between two or more coils linked by a magnetic core.
The change in voltage is determined by the turns ratio of these coils, but the number of phases remains the same across the transformation. A single-phase transformer has windings designed to work with a single alternating current, and it lacks the necessary components and winding configurations to generate the phase-shifted voltages characteristic of a three-phase system.
To obtain three-phase power from a single-phase source, specialized devices known as phase converters are required. These are not true transformers but rather electrical systems that manipulate the single-phase input to create a simulated three-phase output.
These converters typically utilize rotating machinery (rotary phase converters) or static electronic components (static phase converters) to generate the additional phases. While they allow the operation of three-phase equipment on a single-phase supply, the resulting three-phase power might not be perfectly balanced in voltage and current.
Conclusion
Three Phase to One Phase Transformer: The Role in Power Distribution Systems plays a crucial part in efficiently supplying single-phase loads from three-phase networks. Their ability to step down voltage and isolate circuits makes them indispensable for various applications, ensuring reliable power delivery. Understanding their function is key to designing effective power distribution systems.
For businesses seeking dependable and high-quality wholesale phase transformers, Linkwell Electrics offers a comprehensive range to meet diverse needs. Their expertise and product selection can ensure you find the perfect solution for your power distribution requirements.
Contact Linkwell Electrics today to explore their wholesale options and secure the three-phase to one-phase transformers your projects demand.




