In the industry of heating technology, innovation continuously seeks to improve efficiency, safety, and versatility. Among the advancements, PTC heaters have emerged as a distinctive solution, offering a unique approach to warmth that sets them apart from traditional heating elements. Their inherent properties make them a compelling choice for a wide array of applications.
This ultimate guide will comprehensively explore what PTC heaters are, delving into the fascinating science behind their self-regulating capabilities. We will uncover their numerous benefits, from enhanced safety to energy efficiency, and examine their diverse applications across various industries, providing you with a complete understanding of this smart heating technology.
What Does PTC Mean on a Heater?
On a heater, “PTC” stands for Positive Temperature Coefficient. This refers to the special ceramic material used as the heating element. The unique property of PTC materials is that their electrical resistance increases as their temperature rises.
This self-regulating characteristic is a key advantage of PTC heaters: as the element gets hotter, its resistance goes up, which in turn reduces the amount of current flowing through it and limits the heat output. This inherent safety feature prevents overheating and allows the heater to maintain a stable temperature without needing complex external controls.
What is a PTC Heater?
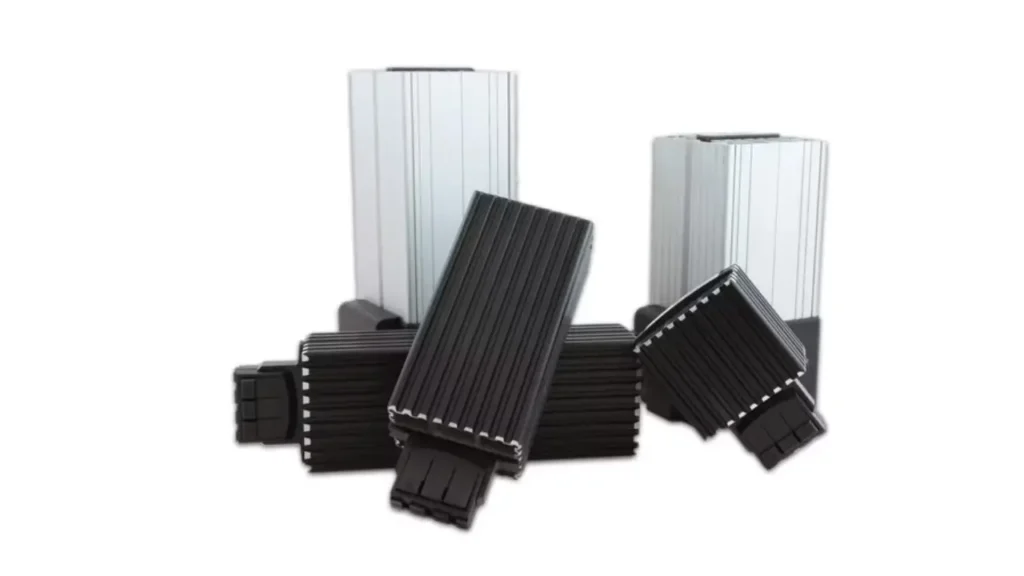

A PTC heater is an electric heating device that utilizes a unique ceramic material with a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) as its core heating element. The distinguishing feature of PTC ceramic is that its electrical resistance increases significantly as its temperature rises.
This inherent property allows PTC heaters to be self-regulating, meaning they automatically limit their own temperature and prevent overheating without the need for additional thermostats or complex control circuitry.
When cold, their resistance is low, allowing more current to flow and heat quickly; as they warm up, their resistance increases, reducing current flow and maintaining a stable, safe operating temperature. This makes them inherently safe, energy-efficient, and highly versatile for various applications.
What is a PTC Heating Element?
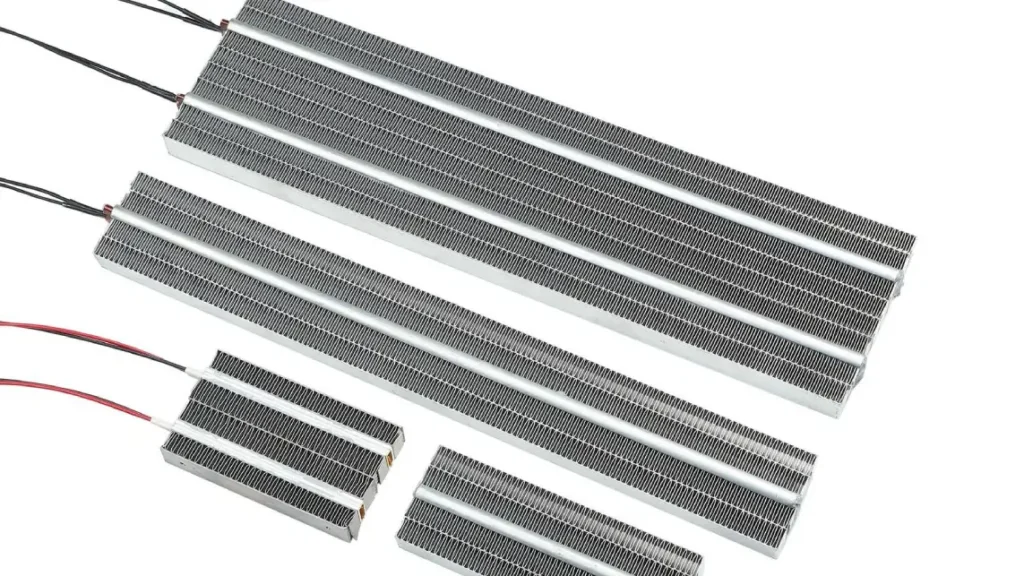

A PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heating element is a type of resistive heater made from specialized ceramic materials that exhibit a unique self-regulating characteristic. Unlike traditional heating elements with a relatively constant resistance, the resistance of a PTC element dramatically increases when its temperature reaches a specific threshold (the Curie temperature).
This inherent property allows the element to maintain a relatively constant maximum temperature without the need for external temperature controls, as its resistance rise limits the current flow and thus the heat output.
Key characteristics of PTC Heating Elements:
- Self-Regulating: They automatically adjust their power output to maintain a constant temperature. As the ambient temperature rises, the PTC’s resistance increases, reducing power consumption and preventing overheating.
- Safety: The self-regulating nature inherently limits the maximum temperature, making them safer as they are less prone to overheating compared to conventional resistive heaters that require external thermostats.
- Energy Efficient: By reducing power consumption once the desired temperature is reached, PTC heaters can be more energy-efficient for certain applications, avoiding continuous full-power operation.
- Rapid Heat-Up: They typically offer a fast heat-up time due to their initial low resistance, which allows for a quick surge of current and rapid temperature increase until the set point is achieved.
- Longevity: Due to the absence of moving parts and self-limiting temperature, PTC heating elements generally have a longer lifespan and are less susceptible to failure from overheating.
What’s PTC Heat System in Heaters?
A PTC heat system in heaters refers to the application of Positive Temperature Coefficient ceramic elements for generating heat. This system leverages the unique property of PTC ceramics where their electrical resistance rapidly increases as their temperature rises.
When the heater is initially cold, the PTC element has low resistance, allowing a high current to flow and quickly generate heat. As the element warms up and approaches its designed temperature, its resistance sharply increases, naturally limiting the current flow and, consequently, its heat output.
This inherent self-regulating mechanism eliminates the need for external thermostats or complex control circuits to prevent overheating, making PTC heat systems remarkably safe, energy-efficient, and durable for various heating applications.
How Does a PTC Heater Work?
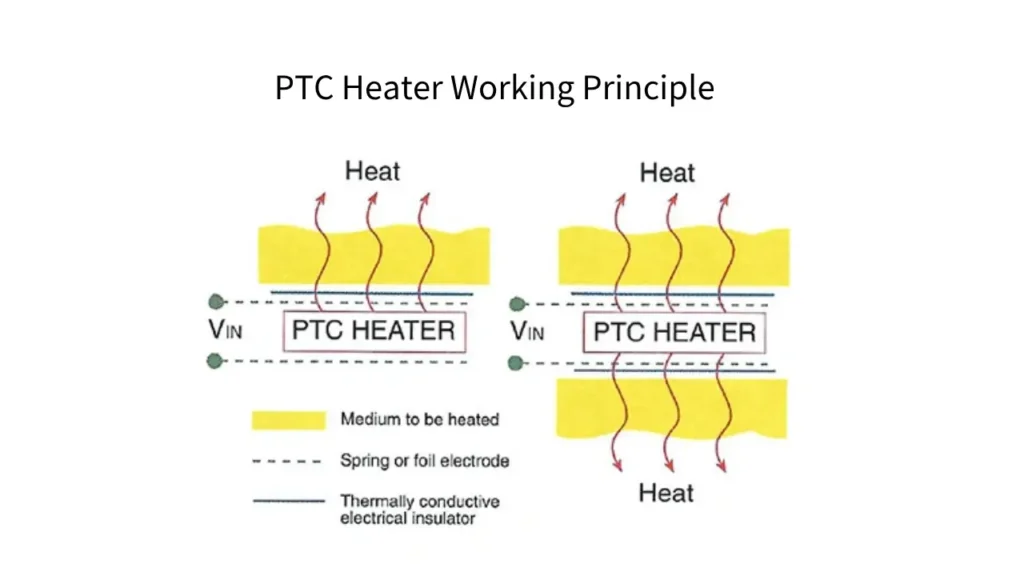
PTC heaters operate on a unique principle derived from their Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic heating elements. This ceramic material exhibits a property where its electrical resistance increases significantly as its temperature rises. This self-regulating characteristic is the core of how a PTC heater functions, allowing it to efficiently and safely generate and maintain heat without complex external controls.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Initial Low Resistance: When the PTC heater is cold (e.g., at room temperature or colder), the PTC ceramic element has a relatively low electrical resistance.
- Rapid Heat-Up: Due to this low resistance, a high current flows through the element when power is applied, causing it to heat up very quickly and efficiently.
- Resistance Increase with Temperature: As the PTC element’s temperature increases and approaches a pre-defined “Curie temperature” (specific to the ceramic composition), its electrical resistance dramatically rises.
- Self-Regulation (Current Reduction): This sharp increase in resistance automatically limits the amount of current that can flow through the element. Less current means less power consumption and, consequently, less heat generation.
- Temperature Stability: The heater reaches and maintains a stable operating temperature without overheating. If the ambient temperature drops, the PTC element cools slightly, its resistance decreases, and it draws more current to generate more heat, thus maintaining the set temperature. Conversely, if the temperature rises, it draws less current.
What are PTC Heaters Used for?
PTC heaters are highly versatile due to their self-regulating and safe operation, finding use in a wide array of applications where precise, reliable, and inherently safe heating is crucial. Their ability to quickly reach a target temperature and then maintain it without external controls makes them ideal for both consumer and industrial products.
Here are some common applications for PTC heaters:
- Automotive Industry: Used extensively for cabin heating in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, as well as for seat heaters, battery thermal management, and defogging/defrosting systems for windows and mirrors.
- Household Appliances: Found in everyday items like hairdryers, ceramic space heaters, electric kettles, coffee makers, clothes dryers, and even instant water heaters, due to their quick heat-up time and safety features.
- Industrial Equipment: Employed in various industrial settings for climate control within electrical enclosures, dehumidifiers, laboratory equipment, and for anti-condensation heating in sensitive machinery or outdoor cabinets.
- Medical Devices: Utilized in applications where precise temperature control and safety are paramount, such as incubators, respiratory devices, and heated therapy pads.
- Consumer Electronics: Integrated into smaller electronic devices that require localized heating, such as surveillance cameras (for anti-fogging), 3D printers, and even certain types of smart toilets.
- Agriculture and Greenhouses: Applied for targeted heating to protect plants from low temperatures and maintain optimal growing environments.
How to Use PTC Heaters
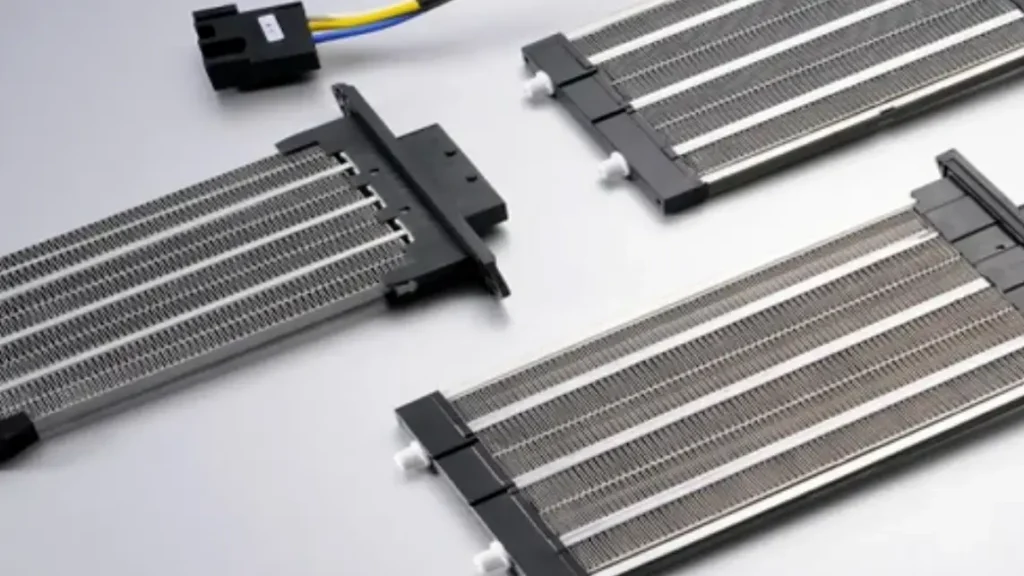

Effectively utilizing PTC heaters involves more than just plugging them in; it requires understanding their unique properties and ensuring proper integration for optimal performance and safety. Due to their self-regulating nature, they simplify many aspects of heater use.
1. Understanding Specifications
Before using a PTC heater, thoroughly understand its specifications, including voltage rating, power rating, and temperature coefficient. Ensure the power supply matches the heater’s requirements to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Operating within specified limits guarantees safe and efficient heat generation.
2. Proper Mounting and Airflow
Install the PTC heating element in a location that allows for proper ventilation and clearances. Securely mount the element according to manufacturer instructions, ensuring no obstructions impede airflow around it. Proper airflow is critical for efficient heat transfer and for the PTC element to self-regulate effectively.
3. Electrical Connection
Connect the wiring from the PTC heating element to a compatible power source or control device. Always follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram precisely to ensure correct connections. While PTC heaters are inherently safe, proper electrical connection is crucial to prevent electrical faults and ensure reliable operation.
4. Monitoring and Maintenance
Even with their self-regulating feature, it’s beneficial to monitor the temperature during initial operation to confirm safe and efficient performance. Regularly clean the element to prevent dust buildup, which can affect heat transfer. Periodically inspect for any signs of damage or wear, replacing the unit if necessary to ensure longevity.
Are PTC Heaters Better Than Fan Heaters?
When comparing PTC heaters and traditional fan heaters (which typically use a fixed-resistance coil heating element), several key differences emerge, influencing which might be “better” depending on the application and priorities. It’s important to note that many modern fan heaters actually incorporate PTC ceramic elements, combining the benefits of both technologies. However, for the purpose of this comparison, we’ll consider a “fan heater” to mean one with a traditional, non-PTC coil.
PTC heaters generally stand out for their inherent safety and self-regulating nature. The ceramic element automatically adjusts its power output as it heats up, preventing overheating and significantly reducing fire risk without needing extra thermostats or safety cut-offs.
This self-regulation also contributes to energy efficiency, as the heater only draws the necessary power to maintain temperature. They tend to have a longer lifespan due to less stress on the components and operate more quietly in models without a fan.
Conversely, traditional fan heaters with fixed-resistance coils can often be more affordable upfront. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to quickly push out a large volume of hot air, rapidly warming a room or directed area. However, they rely heavily on external thermostats and safety switches to prevent overheating, as their heating element’s resistance doesn’t self-limit.
PTC heaters can also be noisier due to the constant operation of the fan and may consume more consistent power regardless of whether the target temperature has been reached, potentially leading to higher running costs if not managed effectively.
Why Use PTC Heaters
Our PTC heaters offer compelling advantages over traditional heating elements, making them a preferred choice in numerous applications where safety, efficiency, and reliability are paramount. Their unique material properties provide inherent benefits that address common concerns associated with older heating technologies.
Here are the benefits of PTC heater in the following
- Inherent Safety (Self-Regulation): This is the most significant advantage. PTC heaters automatically limit their own temperature due to their increasing resistance with heat. This eliminates the risk of overheating, preventing fire hazards and component damage without the need for external thermostats or complex control systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Because they self-regulate, PTC heaters draw less power as they approach their optimal temperature, only consuming the energy necessary to maintain the desired heat. This leads to reduced energy waste and lower operating costs compared to resistive heaters that continuously draw full power.
- Fast Heat-Up Time: PTC elements have a low initial resistance when cold, allowing them to draw maximum power and heat up very quickly. This provides rapid warmth on demand, which is highly beneficial in applications like vehicle cabin heating or instant water heaters.
- Durability and Longevity: With no moving parts (except for fans in some designs) and robust ceramic construction, PTC heaters are highly resistant to wear and tear, vibration, and even some mechanical abuse. This results in a longer operational lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements.
- Compact Size and Versatility: PTC elements can be designed into very small and lightweight forms, allowing for integration into a wide variety of products and tight spaces. Their adaptable nature makes them suitable for diverse applications across consumer, industrial, and automotive sectors.
Conclusion
In the world of heating technology, innovation continuously brings forth safer and more efficient solutions. Among these advancements, PTC heaters have emerged as a distinctive and increasingly popular option, known for their unique self-regulating properties and versatile applications. They offer a departure from traditional heating elements, promising enhanced safety and performance.
This ultimate guide will delve into the fascinating world of PTC heaters, explaining the fundamental principles behind their operation. We’ll explore the key advantages that set them apart, from inherent safety features to energy efficiency, and examine the diverse range of applications where these smart heating elements excel.
Join us as we uncover what makes PTC heaters a compelling choice for various heating needs, providing reliable warmth in a surprisingly clever way.