In many industrial environments, the air we breathe is far from clean. Manufacturing processes, chemical handling, and even general operations can introduce a multitude of airborne contaminants, from dust and fumes to bacteria and hazardous particles. Ensuring clean air isn’t just about comfort; it’s critical for worker health, product integrity, and operational efficiency.
This is where the HEPA filter fan steps in as a game-changer for industrial ventilation systems. But what exactly is a HEPA filter, and how does combining it with a powerful fan create an indispensable tool for achieving pristine air quality in demanding industrial settings? We’ll explore how this technology powers a healthier, safer, and more productive environment.
What is a HEPA Filter?
A HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter is a specialized mechanical air filter designed to capture an extremely high percentage of airborne particles. To be classified as a true HEPA filter by U.S. Department of Energy standards, it must remove at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 micrometers (µm) in diameter.
This 0.3 µm size is crucial because it represents the “most penetrating particle size” (MPPS), meaning particles both larger and smaller than this are trapped with even greater efficiency.
HEPA filters achieve this by forcing air through a dense mat of randomly arranged fibers, which trap particles through a combination of impaction, interception, and diffusion, effectively removing dust, pollen, mold spores, bacteria, and even some viruses from the air.
What is HEPA Filter Made of?
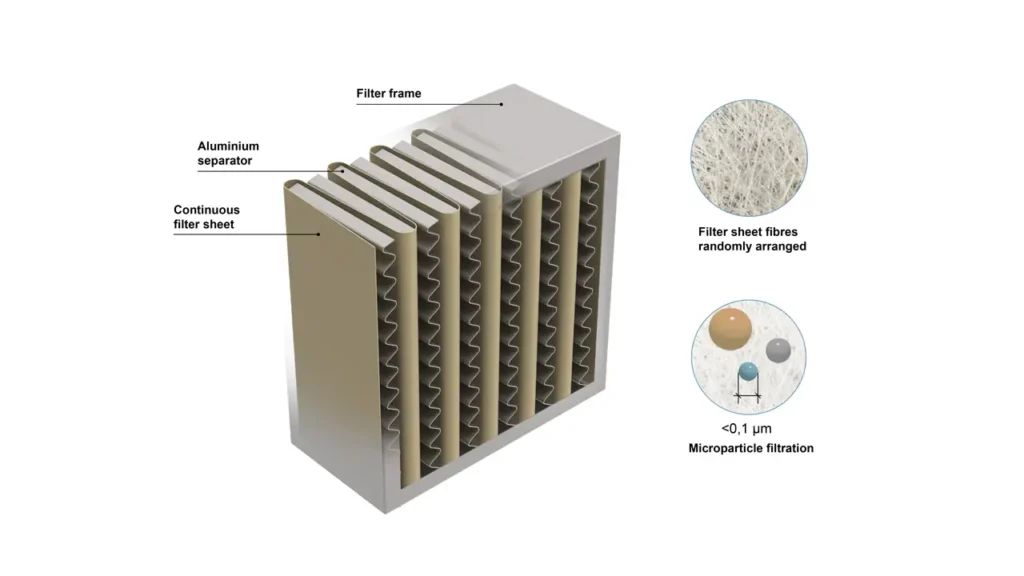
HEPA filters are primarily constructed from a mat of randomly arranged fibers, designed to create a complex labyrinth that traps airborne particles. The most common material used for these fibers is borosilicate glass fiber, which is extremely fine and forms a dense, interwoven network.
This intricate structure is then pleated to significantly increase the surface area available for filtration within a compact space, maximizing the filter’s capacity to hold captured particles.
- Borosilicate Glass Fibers: The primary material, chosen for its extremely fine diameter and ability to create a dense, highly effective filtering medium.
- Acrylic or Polyester Binders: These are often used to hold the glass fibers together, providing structural integrity to the filter media.
- Aluminum or Cardboard Frame: The filter media is typically housed within a sturdy frame, usually made of aluminum or cardboard, which provides support and allows for easy installation into air purification systems.
- Adhesives/Sealants: Glues or sealants are used to secure the pleated media within the frame, preventing air from bypassing the filter through gaps.
- Gasket Material: A gasket (e.g., foam or rubber) is often applied around the frame to ensure a tight seal when installed, preventing air leakage and maximizing filtration efficiency.
How Does a HEPA Filter Work?
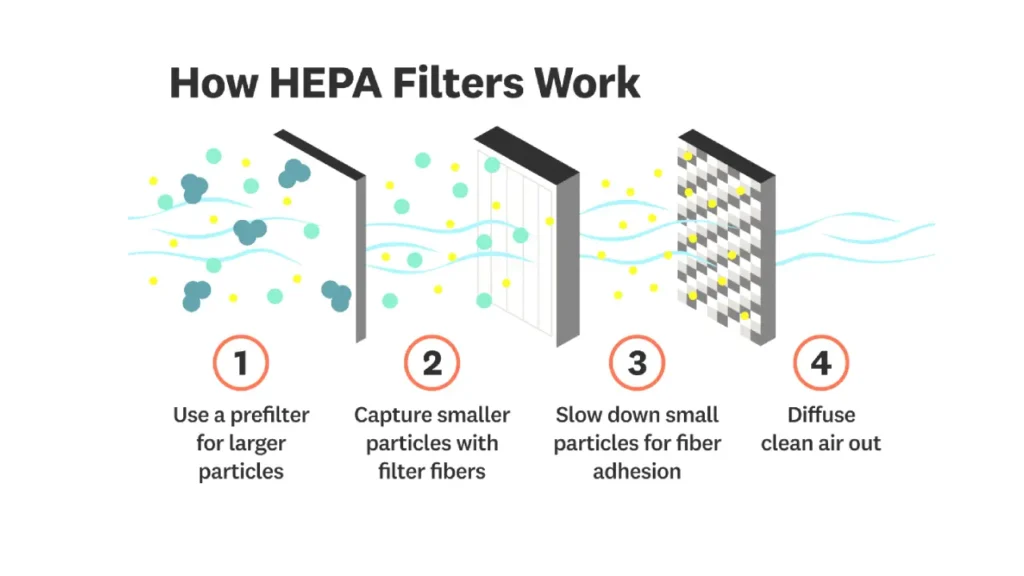
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are crucial for improving air quality by effectively removing a wide range of airborne contaminants. They achieve this high level of filtration through a meticulously engineered, multi-stage process that targets particles of varying sizes, ensuring that the air exiting the filter is significantly cleaner.
- 1. Use a prefilter for larger particles: Initial filtration often involves a prefilter that traps larger particles, such as dust, pollen, and pet dander. This protects the finer HEPA media and extends its lifespan.
- 2. Capture smaller particles with filter fibers: The core of a HEPA filter is a dense mat of randomly arranged fibers, typically made of fiberglass. As air passes through this intricate web, smaller particles are captured through a combination of mechanisms, including interception (particles touching a fiber), impaction (larger particles colliding with a fiber due to inertia), and diffusion (ultrafine particles randomly colliding with fibers due to Brownian motion).
- 3. Slow down small particles for fiber adhesion: The tortuous path through the filter media slows down even very small particles, increasing their contact time with the fibers and making it more likely for them to adhere.
- 4. Diffuse clean air out: Once the air has passed through the dense filter media and had the vast majority of particles removed, clean air is diffused out of the filter.
Types of HEPA Filters
HEPA filters come in various forms, each designed to meet specific filtration needs while adhering to the core principles of high-efficiency particulate air purification.
True HEPA Filters
True HEPA filters are the standard for high-efficiency air purification, capable of capturing at least 99.97% of airborne particles that are 0.3 micrometers in size. This specific particle size (0.3 microns) is considered the most penetrating particle size (MPPS) for HEPA filters, meaning it’s the most difficult size to capture.
True HEPA filters achieve this high efficiency through a dense arrangement of fine fibers, trapping particles through interception, impaction, and diffusion, making them ideal for individuals with allergies, asthma, or those seeking superior air quality.
HEPA-Type Filters
HEPA-type filters offer a lower level of filtration compared to true HEPA filters. While they may capture a significant percentage of airborne particles, they do not meet the stringent 99.97% efficiency standard for 0.3-micron particles.
These filters are often less dense and may be made from different materials, resulting in a slightly less effective capture rate for very fine particles. They can be a more affordable option for general air purification but may not be sufficient for individuals with severe sensitivities or those requiring the highest level of particle removal.
Medical-Grade HEPA Filters
Medical-grade HEPA filters, also known as absolute filters or ULPA (Ultra-Low Particulate Air) filters in some contexts, exceed the performance of true HEPA filters. These filters are designed to capture an even higher percentage of particles, often up to 99.999% of particles as small as 0.12 micrometers.
They are constructed with even finer fibers and a more elaborate pleating process to maximize surface area and trapping capability. Medical-grade HEPA filters are typically used in critical environments such as hospitals, cleanrooms, and laboratories where airborne contaminants must be meticulously controlled to prevent contamination and ensure sterility.
HEPA Filter Uses

HEPA filters play a vital role in numerous applications, effectively capturing a wide array of airborne contaminants to improve air quality and protect health. Their high efficiency makes them indispensable in diverse environments.
Residential Settings
In homes, HEPA filters are commonly found in air purifiers and vacuum cleaners. They significantly reduce indoor air pollutants such as dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, and even smoke particles. For individuals suffering from allergies or asthma, HEPA filters provide substantial relief by creating an allergen-reduced environment, allowing for easier breathing and a better quality of life. They contribute to overall healthier indoor air.
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare environments heavily rely on HEPA filters for infection control. These filters are crucial in operating rooms, isolation rooms, and patient areas to remove airborne bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, thereby minimizing the spread of airborne diseases and ensuring a sterile environment. Their ability to capture microscopic contaminants is paramount in preventing healthcare-associated infections.
Industrial and Commercial Environments
HEPA filters are essential in industries requiring strict contamination control, such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and biotechnology. Cleanrooms, where even the smallest particles can compromise product quality, depend on HEPA filtration to maintain ultra-clean conditions. In commercial buildings, HEPA filters integrated into HVAC systems help improve overall indoor air quality for occupants, contributing to a healthier and more productive workspace.
Automotive and Aviation
HEPA filters are increasingly being incorporated into vehicle cabin air filters to protect drivers and passengers from external pollutants like exhaust fumes, pollen, and dust. In aviation, HEPA filters are standard in commercial aircraft cabins, ensuring that recirculated air is thoroughly cleaned and free of airborne contaminants, contributing to passenger comfort and health during flights.
How to Choose HEPA Filters
Choosing the right HEPA filter is essential for effective air purification, as various factors influence performance and suitability for specific needs. It’s crucial to understand the different ratings and features to make an informed decision and ensure optimal air quality.
- True HEPA vs. HEPA-Type: Always look for “True HEPA” certification, which guarantees the filter captures 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. “HEPA-type” or “HEPA-like” filters do not meet these stringent standards and offer lower efficiency.
- Filter Size and Compatibility: Ensure the filter’s dimensions precisely match your air purifier, HVAC system, or vacuum cleaner. An ill-fitting filter will allow air to bypass the media, reducing effectiveness.
- Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR): For air purifiers, the CADR rating indicates how quickly the device can clean a room of smoke, pollen, and dust. A higher CADR is better for larger rooms.
- Additional Filter Layers: Many HEPA filters are combined with pre-filters (to capture larger particles and extend HEPA life) and activated carbon filters (to remove odors and VOCs). Consider these additions based on your specific air quality concerns.
- Maintenance and Replacement Costs: Factor in the lifespan of the filter and the cost and availability of replacements. Regular replacement is crucial for maintaining optimal filtration efficiency.
- Certifications: Look for certifications like EN 1822 (European Standard) or ISO 29463, which provide rigorous testing and classification of HEPA filters, indicating their efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HEPA filter fans are indispensable tools for achieving and maintaining pristine air quality in industrial settings. Their ability to capture microscopic airborne particles, from common dust to harmful pathogens, makes them a critical component in ensuring product integrity, worker safety, and regulatory compliance across diverse sectors. Investing in these advanced filtration systems is a proactive step towards creating healthier, more efficient, and contaminant-free environments.
The importance of integrating reliable HEPA filtration into your industrial ventilation systems cannot be overstated. By consistently delivering clean air, these solutions safeguard sensitive processes, prevent costly contamination, and contribute significantly to operational excellence and overall well-being within your facility.
For robust and HEPA fan filters, consider Linkwell Electrics. As a trusted manufacturer from China, Linkwell Electrics offers a wide range of wholesale fan filters designed to meet the rigorous demands of industrial applications, providing the performance and reliability you need for your clean air projects.




