You might wonder, what is cfm and why does it matter in your workspace or home? CFM, or cubic feet per minute, tells you how much air moves through a space every minute. When you measure cfm, you can manage airflow to keep things comfortable and efficient.
Studies show that accurate cfm measurement helps you control building pressurization, which cuts down on wasted energy and improves indoor air quality. Whether you want to protect equipment in an engine room or keep a warehouse comfortable, learning the right steps to measure airflow makes a big difference.
Cfm Key Takeaways
- CFM means cubic feet per minute and measures how much air moves through a space every minute.
- Knowing the right CFM helps keep your space comfortable, safe, and energy efficient.
- You can calculate CFM by measuring air velocity and duct area or by using room volume and air changes per hour.
- Using tools like anemometers, pressure transmitters, and flow hoods helps you measure airflow accurately.
- Regular maintenance like cleaning filters and checking vents keeps airflow steady and protects your equipment.
What is CFM
Cubic Feet per Minute
When you hear people talk about what is cfm, they mean cubic feet per minute. This is a simple way to measure how much air moves through a space every minute. Imagine you have a big box. If you fill it with air and then empty it out in one minute, that’s one cubic foot per minute. In hvac, you use cfm to figure out how much air flows through ducts, rooms, or even inside an electrical cabinet.
CFM is more than just a number. It tells you the true cfm, or the real amount of air moving at any moment. Standard cfm, sometimes called scfm, uses set conditions—like 70°F and sea level pressure—so you can compare different systems. You calculate cfm by multiplying the air velocity (in feet per minute) by the area the air moves through (in square feet). This helps you find the total cfm for any space, whether it’s a small control cabinet or a huge warehouse.
Tip: Knowing the true cfm helps you pick the right fan or air conditioner for your space. If you want to keep your equipment cool and safe, you need to know how much air you need to move.
CFM in Airflow Systems
You see cfm everywhere in hvac systems. It’s the key to making sure air flows the way you want. In a home, you might need 1,000 to 2,000 cfm to keep things comfortable. In a factory or engine room, you could need 20,000 cfm or more. The right cfm keeps air fresh, removes heat, and stops hot or cold spots from forming.
In hvac, cfm helps you size your equipment. For example, a 3-ton air conditioner usually needs about 1,200 cfm. If you have a generator room or a machine shop, you need to calculate the true cfm to make sure your hvac system can handle the load. This is also true for electrical cabinets and main control panels. If you don’t get the airflow right, your equipment can overheat or fail.
- CFM keeps air moving in the right direction.
- It balances temperature and humidity.
- It helps your hvac system run efficiently and saves energy.
When you measure cfm, you make sure your space—whether it’s a warehouse, factory, or electrical enclosure—gets the airflow it needs. That’s why understanding what is cfm is so important for anyone working with hvac systems.
Recommended products
CFM Importance

Airflow and Comfort
When you think about comfort in your workspace or home, airflow plays a huge role. The right cfm keeps the air fresh and helps you feel better throughout the day. If you have proper ventilation, you can avoid stuffy rooms and headaches. You also lower the risk of Sick Building Syndrome, which can make people feel tired or sick.
- CFM measures how much fresh air enters your space every minute.
- Higher cfm per person means you dilute pollutants like CO2, dust, and even germs.
- Good ventilation standards, like those from ASHRAE, recommend at least 15 cfm of outdoor air per person to keep air quality high.
- More air changes per hour (ACH) help remove odors and control humidity, making your environment more comfortable.
- Harvard research shows that better ventilation can boost your thinking skills by over 60%.
If you work in a factory, engine room, or even a control cabinet, you need to meet airflow requirements to keep everyone safe and comfortable. The right cfm helps you exchange air quickly, which is key for both health and comfort.
Tip: Always match your cfm to the size and use of your space. Too little airflow leads to stuffy air, while too much can waste energy and cause drafts.
System Efficiency

Your hvac system works best when you optimize cfm. When you get the true cfm right, your system heats or cools spaces faster and uses less energy. Proper airflow helps your hvac system avoid problems like uneven temperatures or high humidity.
- Optimizing cfm improves heat transfer and dehumidification, stopping mold and moisture.
- Good airflow prevents your compressor from short cycling, which saves energy and reduces wear.
- Variable-speed fans and smart controls let you adjust cfm based on what your space needs.
- Sealing duct leaks and using the right air filters help maintain the correct cfm.
Here’s a quick look at recommended air changes per hour (ACH) for different spaces:
| Room Type / Building | Recommended ACH (1/h) |
|---|---|
| Engine Room | 15 – 20 |
| Generator Room | 15 – 20 |
| Warehouse | 4 – 6 |
| Factory | 8 – 15 |
| Machine Shop | 8 – 15 |
| Electrical Cabinet | 10 – 18 |
| Control Cabinet | 10 – 18 |
Matching your cfm to these standards helps your hvac system run smoothly. You save money, protect your equipment, and keep everyone comfortable. When you plan for proper ventilation and airflow, you make your space safer and more efficient.
Measure CFM

Getting the right cfm in your space starts with knowing how to measure cfm accurately. Whether you work in a warehouse, engine room, or need to keep an electrical cabinet cool, you can follow a few simple steps to measure airflow and make sure your hvac system works at its best.
Calculate the CFM
You can calculate the cfm for any space by following these steps. First, figure out the air velocity and the duct cross-sectional area. Then, use the right formula for your application. Here are the most common ways to calculate cfm:
- Velocity-Area Method
This method works well for ducts and vents.- Measure the air velocity in feet per minute (fpm) using an anemometer or pressure transmitter.
- Find the duct cross-sectional area in square feet. For a rectangular duct, multiply width by height. For a round duct, use the formula:
Area = π × (radius)^2 - Multiply velocity by area to get cfm:
CFM = Velocity (fpm) × Duct Cross-Sectional Area (sq ft)
- Room Volume and Air Changes Method
This method helps when you want to calculate the cfm needed for a whole room, like a warehouse or engine room.- Measure the room’s length, width, and height to get the volume in cubic feet.
- Decide on the number of air changes per hour (ACH) for your space. For example, engine rooms and generator rooms often need 15–20 ACH.
- Use the formula:
CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) ÷ 60
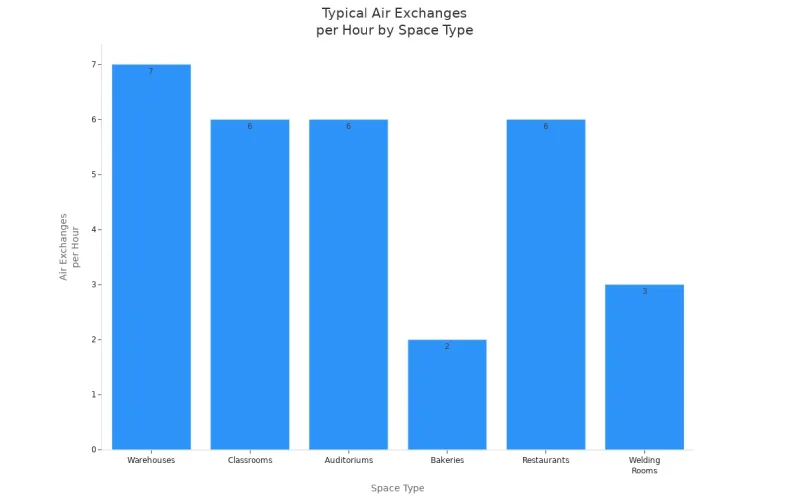
Here’s a quick table to help you match your space type with typical air exchange rates:
| Space Type | Typical Air Exchanges per Hour | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Warehouses | 7 | 4 to 10 |
| Classrooms | 6 | 4 to 8 |
| Auditoriums | 6 | 1 to 20 |
| Bakeries | 2 | 1 to 3 |
| Restaurants | 6 | 2 to 10 |
| Welding Rooms | 3 | 1 to 4 |
If you want a visual comparison, check out this chart showing air exchange rates for different spaces:
Let’s look at an example. Suppose you have a warehouse that measures 100 feet long, 50 feet wide, and 20 feet high. The volume is 100 × 50 × 20 = 100,000 cubic feet. If you want 7 air changes per hour, the calculation is:
CFM = (100,000 × 7) ÷ 60 = 11,667
So, you need about 11,667 cfm to keep the air fresh and safe.
For electrical cabinets and main control panels, you need to measure cfm more precisely. Linkwell’s fan filter units and cabinet air conditioners help you maintain the right airflow in these enclosures. These products pull in cool air, filter out dust, and exhaust warm air, keeping your sensitive electronics safe from overheating and contamination. You can use the same formulas to calculate the cfm needed for your cabinet, then choose the right Linkwell solution based on your results.
Tools for Airflow
You have several tools to measure cfm and airflow measurement in both home and industrial settings. Each tool has its strengths, so you can pick the one that fits your needs best.
- Anemometers
These devices measure air velocity. Vane anemometers use a spinning fan, while hot-wire anemometers use a heated wire to sense airflow. You enter the duct cross-sectional area, and the device calculates cfm for you. Hot-wire anemometers work well in tight spaces and low-flow situations. - Pressure Transmitters (Manometer + Pitot Tube)
This setup measures the pressure difference in a duct. You use the formula:FPM = 4005 × √ΔP
Then, multiply by the duct cross-sectional area to get cfm. This method works well for large ducts and industrial hvac systems. - Capture (Flow) Hoods
These hoods fit over vents or diffusers and measure the total cfm directly. They are great for checking air flow volume at supply or return grilles. You may need to apply a correction factor to account for resistance caused by the hood.
Here’s a table comparing these tools:
| Instrument Type | Measurement Principle | Accuracy Factors and Limitations | Measurement Range (FPM) | Notes on CFM Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vane Anemometer | Measures air velocity via rotating vane | Accuracy affected by vane angle, minimum velocity needed, orientation | 50 to 6000 | Requires input of vent area; provides velocity measurement only |
| Hot-Wire Anemometer | Measures airflow based on heat transfer | Limited to ambient temperature, suitable for low-flow, small probe size allows tight space measurement | 0 to 10,000 | Measures velocity; cfm calculated with area input; more common due to wider range |
| Pressure Transmitter | Measures differential pressure to infer velocity | Accuracy depends on precise pressure measurement and correct conversion formulas; indirect velocity measurement | N/A | Converts pressure difference to velocity and then to cfm; requires careful setup and calculation |
| Capture (Flow) Hood | Direct volume measurement at grilles/diffusers | Introduces flow resistance affecting accuracy; requires correction factor from duct traverses to adjust readings | N/A | Provides direct cfm measurement; correction factor needed to compensate for flow resistance caused by hood |
In 2025, you’ll find even more advanced tools for airflow measurement. Many hvac technicians now use Bluetooth-enabled cfm meters, wireless sensors, and smart devices that connect to building automation systems. These tools give you real-time data and help you measure cfm quickly and accurately.
When you need to maintain proper airflow in electrical enclosures, Linkwell’s fan filter units and cabinet air conditioners offer practical solutions. These products keep air moving, filter out dust and moisture, and help you measure cfm with confidence. You can choose models with digital displays or thermostat integration for even better control.
Always match your cfm measurement method to your space. For a large warehouse or factory, use a flow hood or pressure transmitter. For a control cabinet or electrical panel, a hot-wire anemometer and Linkwell’s fan filter unit make a great team.
By following these steps to measure cfm, you can keep your hvac system running smoothly, protect your equipment, and create a safer, more comfortable environment.
Troubleshooting Airflow
Common Issues
You might notice that your ventilation system does not always deliver the airflow you expect. Many things can go wrong, especially in busy places like engine rooms, generator rooms, warehouses, or inside electrical cabinets. Here are some of the most common airflow problems you may face:
- Blocked vents and registers – Furniture, boxes, or closed vents can stop air from moving freely.
- Clogged filters – Dirty or old filters restrict airflow and can even damage your equipment.
- Leaky or blocked ducts – Cracks, dust, or debris in ducts reduce airflow and waste energy.
- Improper ductwork size – Ducts that are too big or too small disrupt air pressure and airflow distribution.
- Dirty coils and blowers – Dust on coils or a malfunctioning blower fan lowers airflow and cooling.
- Insufficient return air vents – Not enough return vents means less air gets reconditioned, which hurts ventilation.
- Outdoor unit obstructions – Leaves or debris around outdoor units block airflow and cause overheating.
- Aging equipment – Older HVAC units often lose efficiency and airflow over time.
Inside control cabinets or main control panels, dust buildup and poor airflow can cause electronics to overheat. Linkwell’s fan filter units help solve these problems. They use strong fans and easy-to-replace filters to keep air moving and clean. You can swap filters quickly, so you spend less time on maintenance and keep your equipment safe.
Tips for Accuracy
Getting accurate airflow measurement is key to proper ventilation and system performance. Here are some tips to help you measure airflow the right way:
- Pick the right tool for the job. Use anemometers or flow hoods for large spaces, and thermo-anemometers for tight spots like electrical cabinets.
- Measure at several points, especially near duct walls, to get a true picture of airflow.
- Always calculate the duct or vent area correctly. Use the right formula for round or rectangular shapes.
- Apply correction factors if you have grilles or obstructions in the way.
- Watch out for changes in temperature and humidity. These can affect your airflow readings by changing air density.
- Choose devices with features like backlit displays or data storage to make your job easier in the field.
Linkwell’s fan filter units make it easy to maintain steady airflow in control cabinets. Their tool-free design and modular parts mean you can replace filters or fans without shutting down your system. This keeps your airflow balanced and your electronics protected.
You now know what CFM means and how to measure cubic feet per minute airflow in any space—from engine rooms to electrical cabinets. Accurate CFM measurement keeps your environment comfortable, efficient, and safe. Regular maintenance, like filter changes and airflow checks, extends equipment life and saves money.
| Maintenance Task | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Change filters monthly | Prevents overheating |
| Inspect fans and belts | Maintains airflow |
| Use CFM meters | Ensures accurate results |
- Linkwell’s fan filter units and cabinet air conditioners deliver reliable airflow, with quality you can trust.
- Need help? Reach out to Linkwell for expert support and custom solutions.
Proper airflow management means fewer breakdowns, lower costs, and a healthier workspace.
FAQ
What does CFM stand for in HVAC?
CFM means “cubic feet per minute.” In HVAC, it shows how much air moves through a space each minute. You use CFM to size fans, air conditioners, and ventilation systems for rooms, warehouses, or electrical cabinets.
How do you measure CFM airflow in an engine room or warehouse?
You measure CFM by using a cfm meter, anemometer, or flow hood. First, find the air velocity in feet per minute. Then, multiply it by the duct or vent area in square feet. This gives you the cubic feet per minute airflow.
How do you calculate required CFM for an electrical cabinet?
First, measure the cabinet’s volume in cubic feet. Decide on the needed air changes per hour (ACH), usually 10–18 for control cabinets. Use the formula:CFM = (Cabinet Volume × ACH) ÷ 60
This helps you pick the right fan or cabinet air conditioner.
What tools help you find CFM in industrial spaces?
You can use a vane or hot-wire anemometer, a pressure transmitter, or a capture hood. These tools measure air velocity or volume. For electrical cabinets, a cfm meter and Linkwell’s fan filter unit make airflow measurement simple and accurate.
How do you convert feet per minute to cubic feet per minute?
Multiply the air velocity (feet per minute) by the vent or duct area (square feet).
For example:CFM = Velocity (fpm) × Area (sq ft)
This formula helps you find the airflow in cubic feet per minute for any space.
Conclusion
what is CFM is crucial for managing airflow in any industrial or commercial space. Accurate CFM measurement boosts HVAC efficiency, protects sensitive equipment, and ensures comfort. Whether you’re optimizing ventilation in a warehouse or cooling electrical cabinets, knowing how to calculate and maintain proper CFM helps you reduce energy waste, avoid costly breakdowns, and extend equipment life.
Linkwell provides trusted airflow solutions to keep your systems running smoothly.








