If your system generates heat — and most do — proper ventilation isn’t just an afterthought, it’s essential. Whether you’re designing an industrial control panel, an HVAC system, or a small electronics device, selecting the right cooling fan can make or break performance. That means you’re likely choosing between two major types: Axial vs Centrifugal Fan. Both have their strengths, but knowing how and when to use each type is where real expertise lies.
In this guide, we’ll break down the differences, benefits, and best-use scenarios for axial and centrifugal fans. We’ve gathered insights from top-tier sources and added our hands-on experience as manufacturers to give you the most practical, well-rounded resource available. Shop Linkwellelectrics’ full range of AC fans and DC fans is your most worry-free and cost-saving choice.
What Are Axial Fans?

Master the Basics of Axial Fans
Axial fans are perhaps the most common type of fan used in both residential and industrial environments. Their construction includes a central hub with blades attached, rotating around an axis to move air in a direction parallel to the shaft. This configuration results in a high volume of airflow with relatively low pressure.
These fans come in various sub-types, such as propeller fans, tube-axial fans, and vane-axial fans. Each has unique performance characteristics, but all share the fundamental design principle of moving air parallel to the motor shaft. Axial fans are available in both AC and DC power configurations, making them adaptable to different voltage requirements.
Axial Fans Real-World Applications
Axial fans are known for their efficiency in moving large volumes of air. They’re ideal for:
- Ventilating computer server rooms
- Cooling electrical panels
- Air circulation in residential HVAC systems
- Industrial spot cooling for machinery
- Operating as exhaust fans in confined areas
- Electrical Enclosure Ventilation
In one of our recent projects for an electronics manufacturer, axial fans were integrated into power distribution units (PDUs) in server racks. The customer praised the fans for their quiet operation and minimal maintenance, which significantly reduced downtime.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Lightweight and compact
- Cost-effective
- Low energy consumption
- Low noise emission (especially in larger sizes)
Limitations:
- Limited static pressure capacity
- Less effective in ducted systems or systems with high resistance
As per Wikipedia, axial fans are favored in applications where a large amount of air needs to be moved through open spaces. Their simple construction and affordability make them a standard in the cooling industry.
What Are Centrifugal Fans?
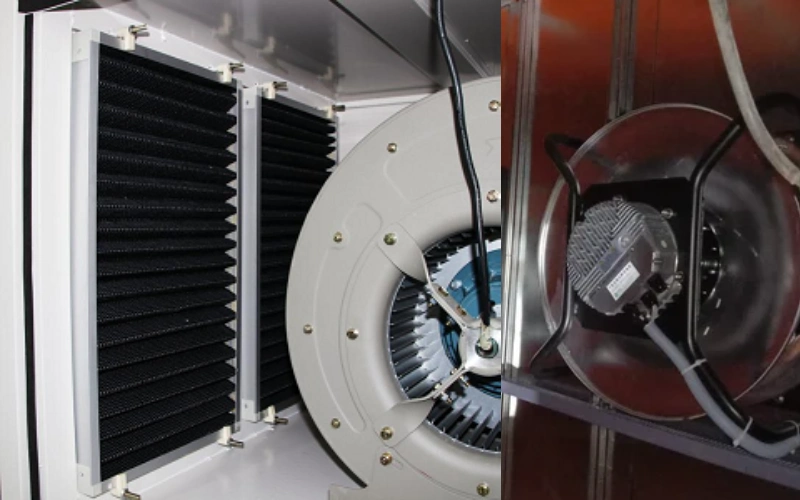
The Engineering Behind Centrifugal Fans
Centrifugal fans, also referred to as blowers or radial fans, operate on a different principle. They intake air along the axis and expel it perpendicularly. The impeller, enclosed within a housing, increases the air pressure and redirects the flow at a 90-degree angle. This design is ideal for applications requiring higher pressure.
Centrifugal fans are commonly categorized by blade orientation: forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial blades. Forward-curved blades are more compact and quieter but less efficient, while backward-curved fans offer higher efficiency and durability. Radial fans are especially robust and suitable for harsh environments.
Where Centrifugal Fans Excel
These fans shine in challenging environments and ducted systems. Key applications include:
- Industrial dryers
- Air scrubbers
- HVAC duct systems
- Exhaust systems in commercial kitchens
- Cooling of laptops and compact electronics
One of our clients in the textile industry relies heavily on backward-curved centrifugal fans to remove hot air and lint from industrial dryers. The high-pressure airflow not only enhances efficiency but also ensures a cleaner working environment.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- High static pressure capabilities
- Ideal for ducted systems
- Resistant to particulates and contaminants
- Durable and long-lasting
Limitations:
- Higher energy consumption
- Noisier than axial fans
- Bulkier and heavier design
The ASHRAE Handbook emphasizes the importance of pressure loss considerations in duct systems, highlighting centrifugal fans as optimal choices for applications requiring airflow through complex or restricted pathways.
Key Differences Between Axial and Centrifugal Fans
| Feature | Axial Fans | Centrifugal Fans |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Direction | Parallel to axis | Perpendicular to axis |
| Pressure | Low | High |
| Volume | High | Low to medium |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
| Size and Weight | More compact | Generally bulkier |
| Noise Level | Quieter | Louder |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Durability in Harsh Environments | Moderate | Excellent |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Moderate to high |
Understanding these differences isn’t just academic. It helps designers make critical decisions that affect system longevity, cost-efficiency, and even user satisfaction.
Noise, EMI, and Efficiency Considerations
Noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI) are vital factors when selecting a fan. Axial fans generally produce less noise and EMI, particularly when powered by DC motors. This makes them suitable for use in:
- Hospitals
- Offices
- Consumer electronics
Centrifugal fans, on the other hand, are louder but more robust. While EMI shielding can mitigate issues, noise control may require additional components like silencers or acoustic insulation. Bearings also play a crucial role in noise levels and durability — ball bearings last longer but may be louder than sleeve bearings.
Our internal testing has shown that a 120mm axial fan with fluid dynamic bearings generates only 30 dBA at full speed, whereas a comparable centrifugal fan might exceed 40 dBA.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Smart Control Cabinets
A German manufacturer of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure needed a compact, low-noise cooling solution for their smart control cabinets. After evaluating several options, they selected our 24V DC axial fans. The results were remarkable — a 35% reduction in cabinet temperature and zero EMI complaints in over 1,000 field installations.
Case Study 2: Textile Industry Drying Systems
In India, a textile factory struggled with frequent fan failures in their industrial dryers. Our backward-curved centrifugal fans replaced the old units and offered superior resistance to lint and heat. The new fans lasted 18 months longer on average and saved over $8,000 in annual maintenance costs.
Case Study 3: Medical Diagnostics Equipment
For a high-end diagnostics lab, maintaining noise below 35 dBA was non-negotiable. We custom-engineered a DC axial fan with PWM control and dynamic balancing, achieving a near-silent operation while maintaining consistent airflow. The client commended the precision and reliability.
Expert Insight & Manufacturer Perspective
We’ve been in the cooling solutions industry for over a decade, and here’s what we’ve learned:
- Start fan selection early in the design process. This avoids expensive retrofitting.
- Always consider total cost of ownership, not just the upfront price.
- Prioritize lifecycle testing. The rated lifespan of a fan can vary wildly based on real-world use.
Our engineering team collaborates with clients from prototyping to production. We regularly advise OEMs on optimal fan placement, vibration isolation, and EMI shielding — not just the fan itself, but how it integrates into the system as a whole.
Which Fan Type Should You Choose?
Choosing between axial and centrifugal fans isn’t just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. The right choice ensures not only effective cooling but also better long-term reliability, lower noise, and operational efficiency. Here’s how you can evaluate your needs with 10 key questions — plus our practical take as a fan manufacturer with years of hands-on experience.
What’s the available installation space?
- Axial fans are typically more compact and lightweight, making them a perfect fit for tight spaces, wall-mounts, or devices with shallow enclosures.
- Centrifugal fans are bulkier due to the housing and impeller structure. If you’re limited in depth but have vertical clearance, they may still work.
Recommendation: Go axial if space is tight and layout is flat.
Are you dealing with high back pressure?
- Centrifugal fans are designed to handle high static pressure and resistance in the system (ductwork, filters, bends).
- Axial fans struggle in high-resistance environments; performance drops significantly under pressure.
Recommendation: Centrifugal wins for ducted systems and pressure-heavy setups.
Is continuous operation required?
- Both fan types can be designed for 24/7 operation, but:
- Centrifugal fans, especially backward-curved models, tend to have more rugged bearings and enclosures.
- Axial fans may need frequent checks in demanding environments.
Recommendation: For continuous use, choose centrifugal unless axial fans are specifically rated for endurance.
How important is energy efficiency?
- Axial fans generally consume less power for the same airflow volume at low pressure.
- Centrifugal fans use more power but are more efficient under load and in restricted environments.
Recommendation: Axial for energy savings; centrifugal if the system inherently resists airflow.
Will the fan be exposed to dust, chemicals, or moisture?
- Centrifugal fans with sealed housings and industrial-grade coatings offer better protection.
- Axial fans are vulnerable unless you specify IP-rated models.
Recommendation: Choose centrifugal in harsh, dirty, or wet environments.
How critical is low noise in the application?
- Axial fans are generally quieter, especially at lower RPMs and larger sizes.
- Centrifugal fans produce more audible and vibration noise due to pressure output and housing.
Recommendation: Axial fans are better suited for medical, office, or home use.
What’s the budget?
- Axial fans are cheaper to purchase, install, and replace.
- Centrifugal fans cost more due to complex housings and higher material requirements.
Recommendation: Axial fans offer better value for standard use cases.
Is the fan located near EMI-sensitive components?
- DC axial fans generate less electromagnetic interference.
- Centrifugal fans, especially large AC-powered ones, may cause EMI issues unless shielded.
Recommendation: Axial is safer near sensors, RF modules, or microcontrollers.
Will the airflow be through ducts?
- Centrifugal fans excel at maintaining airflow through long, bent, or filtered duct systems.
- Axial fans lose efficiency quickly in ducted environments.
Recommendation: Centrifugal is ideal for ductwork.
Do you need high reliability with minimal maintenance?
- Centrifugal fans are typically more durable in rough settings, with better enclosure integrity.
- Axial fans may be easier to replace but might require more frequent checks.
Recommendation: Centrifugal fans offer lower lifetime maintenance in industrial settings.
Summary Table: Axial vs. Centrifugal Fan Decision Matrix
| Question | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Tight installation space? | Axial Fan | Compact, lightweight, easier to install |
| High back pressure or resistance? | Centrifugal Fan | Handles static pressure better |
| 24/7 continuous operation? | Centrifugal Fan | More rugged construction |
| Focus on energy efficiency? | Axial Fan | Lower power draw in low-pressure environments |
| Harsh environment (dust, moisture)? | Centrifugal Fan | Sealed housing resists contaminants |
| Noise-sensitive application? | Axial Fan | Quieter operation |
| Limited budget? | Axial Fan | More affordable and widely available |
| EMI-sensitive system? | Axial Fan (DC) | Lower electromagnetic interference |
| Ducted airflow system? | Centrifugal Fan | Designed for directional airflow in ducts |
| Low-maintenance requirement? | Centrifugal Fan | Longer life, better performance in industrial environments |
Conclusion: Build Smarter Cooling Systems
Axial and centrifugal fans both have their place in modern thermal management. Your choice ultimately depends on performance needs, environmental demands, and system constraints.
We hope this guide has not only clarified the technical differences but also provided you with actionable insights from both research and our direct industry experience. Bookmark this article for your future projects, share it with your team, and if you need tailored recommendations, our engineering team is here to help.
Looking for high-performance fans? Contact us to explore our full range of AC and DC axial fans, centrifugal blowers, and accessories tailored for industrial, commercial, and consumer-grade applications.




