Choosing the right transformer is crucial for efficient and safe power distribution. Two primary types dominate the market: dry-type and oil-filled transformers. While both serve the fundamental purpose of voltage transformation, their construction, cooling mechanisms, and applications differ significantly. Understanding these distinctions is key to selecting the optimal solution for your specific needs and environment.
This blog delves into a detailed comparison of dry-type and oil-filled transformers. We’ll explore their core differences in design, safety features, environmental impact, maintenance requirements, and typical use cases. By highlighting these distinctions, we aim to provide you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision for your power infrastructure.
What is Dry Type Transformer
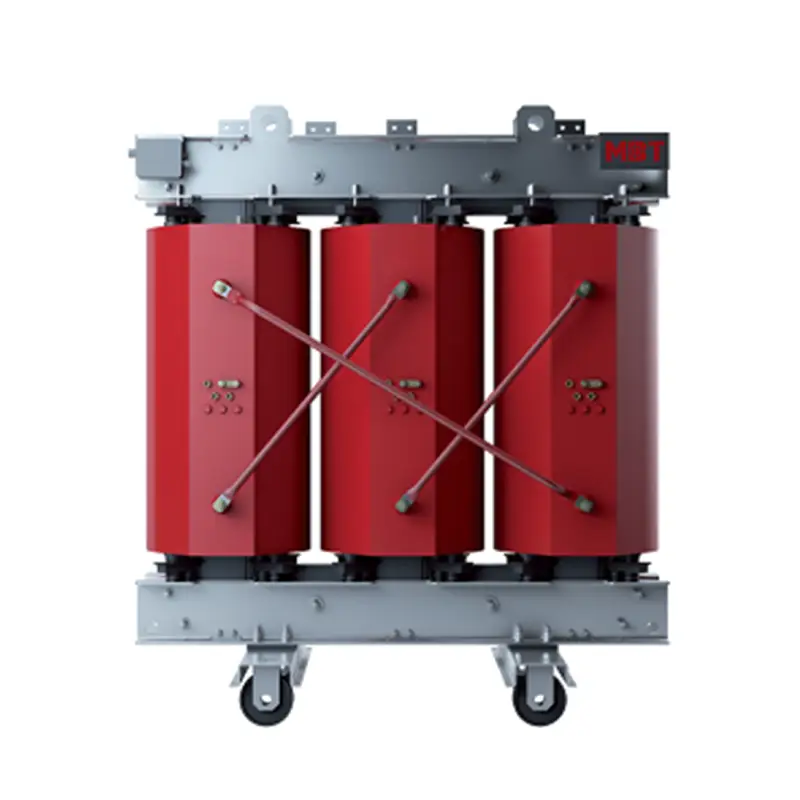

A dry-type transformer is an electrical transformer that uses air or a non-flammable solid insulating material, such as epoxy resin, as the primary insulation medium for its windings, rather than relying on oil or other liquids.
This design eliminates the risk of oil leaks and reduces flammability concerns, making them suitable for indoor and environmentally sensitive applications. While typically having a lower cooling capacity compared to liquid-filled transformers, they offer benefits like reduced maintenance and enhanced safety in specific environments.
Dry Type Transformer Benefits
Dry-type transformers offer a compelling array of benefits, primarily centered around enhanced safety and environmental responsibility, coupled with reduced maintenance needs. Their design eliminates the risks associated with flammable liquids, making them ideal for indoor and sensitive environments. Furthermore, their simplified maintenance routines contribute to lower operational costs and increased uptime.
- Enhanced Safety: No flammable or toxic liquids, significantly reducing fire and explosion hazards.
- Environmentally Friendly: Eliminates the risk of oil leaks and the need for fluid disposal.
- Reduced Maintenance: Lower upkeep requirements compared to liquid-filled transformers, primarily involving visual inspections and cleaning.
- Indoor Suitability: Safe for use in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and other indoor environments.
- Lower Installation Costs: Often simpler installation without the need for fire suppression systems or oil containment.
- Improved Reliability: Robust designs with less potential for leaks or fluid-related issues.
- Quiet Operation: Generally operate with lower noise levels compared to some liquid-filled transformers.
Recommended products
What is Oil-filled Type Transformer
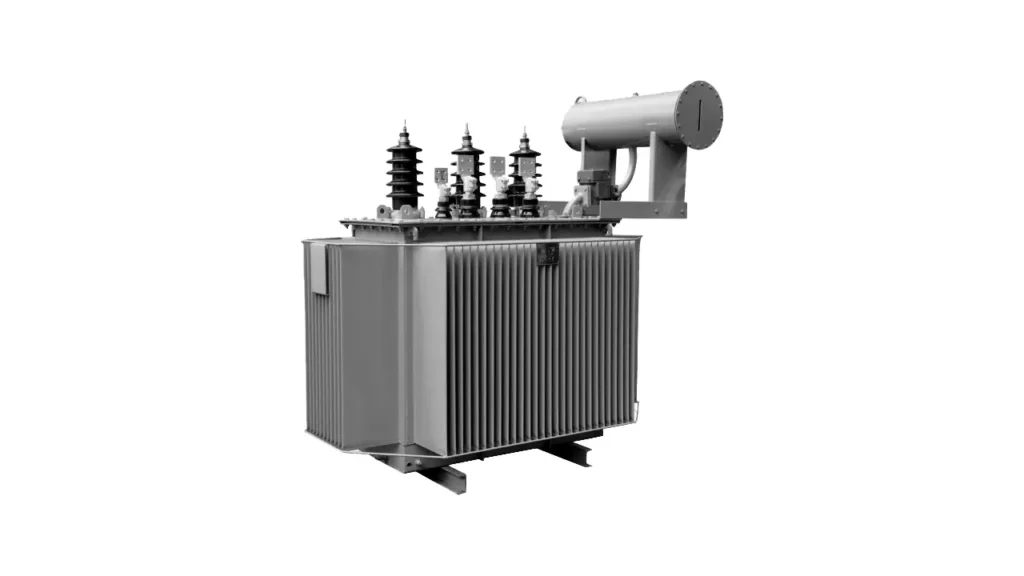

An oil-filled transformer is an electrical transformer that uses oil, typically mineral oil or sometimes synthetic fluids, as its primary insulating and cooling medium. The core and windings of the transformer are immersed in this oil-filled tank, which helps to dissipate the heat generated during operation and provides electrical insulation between the internal components and the grounded tank. This efficient cooling capability allows oil-filled transformers to handle higher power ratings and voltages, making them commonly used in outdoor substations and for large industrial applications.
Oil-filled Type Transformer Benefits
Oil-filled type transformers offer significant advantages, particularly in high-power and high-voltage applications where their efficient cooling capabilities and robust insulation are crucial. Their design allows for a more compact footprint compared to dry-type transformers of similar ratings, and they often exhibit a higher overload capacity due to the effective heat dissipation provided by the oil. This makes them a reliable and cost-effective solution for large-scale power distribution and industrial needs.
- High Power and Voltage Ratings: Well-suited for applications requiring substantial power transfer and high voltage levels.
- Efficient Cooling: The oil provides excellent heat dissipation, allowing for higher load capacities and prolonged operation.
- Compact Size (for high ratings): Can be smaller and lighter than dry-type transformers for comparable high power outputs.
- High Overload Capacity: The efficient cooling system enables them to handle temporary overloads more effectively.
- Lower Initial Cost (for high ratings): Often more economical for large-scale power distribution compared to dry-type alternatives.
- Effective Insulation: The oil provides excellent electrical insulation, contributing to reliable operation at high voltages.
- Quiet Operation (compared to some dry-types with forced air): Can operate more quietly than dry-types that rely on fans for cooling.
Dry Type Transformer vs Oil Filled
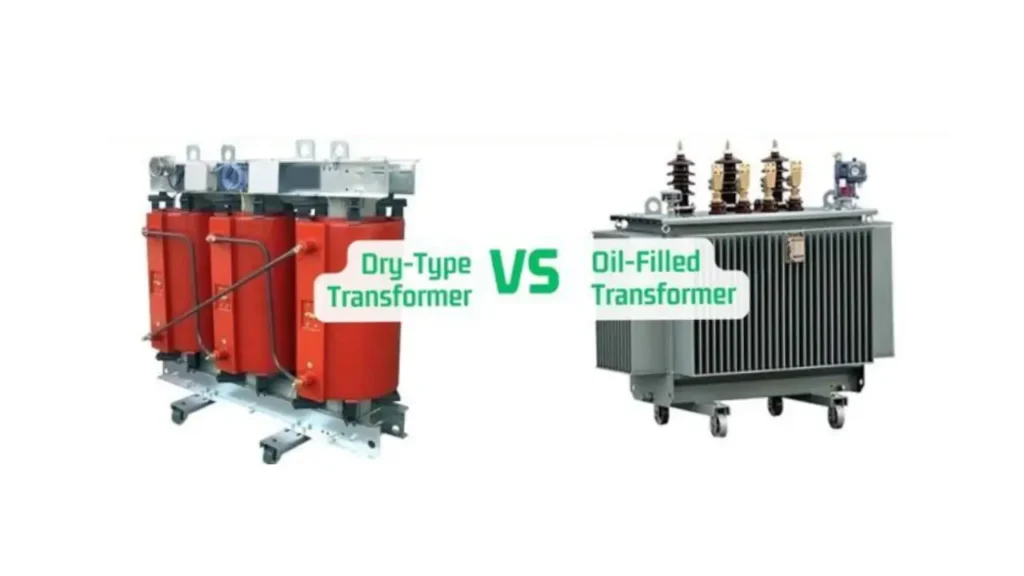
Choosing the right transformer for your application hinges on understanding the fundamental differences between dry-type and oil-filled designs. Both serve the essential function of voltage transformation, but their construction, cooling mechanisms, and suitability vary significantly, impacting safety, environmental considerations, maintenance, and cost.
Let’s delve into the difference between dry and oil type transformer in the following:
Cooling and Insulation
Dry-type transformers primarily rely on air or solid insulation materials like epoxy resin for both cooling and electrical insulation. The windings are either open to the air or encapsulated in resin, allowing heat to dissipate through natural convection or forced air cooling in larger units. This design inherently eliminates the risk of fluid leaks and reduces fire hazards, making them suitable for indoor and environmentally sensitive areas where oil-filled transformers pose a greater risk.
Oil-filled transformers, in contrast, immerse their core and windings in a tank filled with insulating oil. This oil serves a dual purpose: it acts as a dielectric insulator, preventing electrical breakdown, and as a coolant, dissipating heat generated during operation. The oil circulates through the transformer, often with the assistance of cooling fins or radiators, to transfer heat away from the windings and core. This efficient cooling method allows oil-filled transformers to handle higher power ratings and voltages more effectively than similarly sized dry-type units.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Dry-type transformers offer significant safety advantages, particularly in indoor applications. The absence of oil eliminates the potential for flammable liquid spills and reduces the risk of fire. Furthermore, they do not produce toxic gases under arcing conditions in the same way that some oil-filled transformers might. This inherent safety makes them preferable in environments with stringent fire safety regulations and where human contact is more likely.
Oil-filled transformers present a greater environmental concern due to the potential for oil leaks, which can contaminate soil and water. While modern insulating oils are less hazardous than older types, containment measures and spill prevention plans are often necessary. Additionally, the flammability of the oil necessitates fire suppression systems in many installations. However, advancements in biodegradable insulating fluids are emerging to mitigate some of these environmental concerns.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Dry-type transformers generally require less maintenance compared to oil-filled units. The absence of oil eliminates the need for regular fluid level checks, oil sampling, and potential oil replacement or reconditioning. Maintenance primarily involves periodic visual inspections for dust accumulation and ensuring proper ventilation. This lower maintenance requirement can lead to reduced operational costs and downtime.
Oil-filled transformers necessitate regular maintenance to ensure the integrity of the insulating oil. This includes monitoring oil levels, testing the dielectric strength and chemical properties of the oil, and potentially filtering or replacing the oil over time. Bushings and cooling system components also require periodic inspection. While this maintenance is crucial for the longevity and reliable operation of oil-filled transformers, it adds to the overall operational costs and requires specialized expertise.
Cost and Application
The initial cost of dry-type transformers can sometimes be higher than comparable oil-filled transformers, especially for larger ratings. However, the lower maintenance costs and reduced need for fire suppression systems can offset this initial investment over the transformer’s lifespan. Dry-type transformers are commonly used in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and industrial facilities where safety and environmental considerations are paramount.
Oil-filled transformers are often more cost-effective for high-power and high-voltage applications, particularly for outdoor substations and large industrial installations. Their superior cooling capabilities allow for more compact designs at higher ratings. While the initial cost might be lower, the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and potential environmental remediation, should be factored into the overall economic assessment.
Chart about difference between dry type and oil type transformer
| Feature | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Filled Transformer |
| Cooling & Insulation | Air or solid insulation | Oil (mineral or synthetic) |
| Safety | Lower fire risk, no oil leaks | Higher fire risk, potential oil leaks |
| Environmental | More eco-friendly, no fluid disposal | Potential for oil contamination |
| Maintenance | Minimal, primarily visual inspections | Regular oil testing and potential treatment |
| Application | Indoor, safety-critical, lower power | Outdoor, high power, high voltage |
| Size & Weight (High Rating) | Larger and heavier | More compact |
| Overload Capacity | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Initial Cost | Can be higher for larger ratings | Often lower for larger ratings |
| Lifespan | Can be long with proper maintenance | Can be long with proper oil maintenance |
Safety Requirements and Environmental Considerations of Dry Type vs Liquid Transformer
Dry-type and liquid-filled transformers present distinct safety and environmental profiles. Dry-types prioritize safety by eliminating flammable and toxic fluids, reducing fire and explosion risks, making them ideal for indoor use despite limited recycling options.
Liquid-filled transformers, while offering efficient cooling, pose environmental concerns due to potential fluid leaks and require stringent fire prevention measures, though they often have better recycling and remanufacturing possibilities, with some alternative fluids offering improved environmental compatibility.
- Safety (Dry-type): Eliminates flammable and toxic fluids, reducing fire and explosion risks, preferred for indoor applications.
- Safety (Liquid-filled): Uses flammable dielectric fluid, requiring strict fire prevention measures, generally less suitable for indoor use.
- Environmental (Dry-type): Produces less waste during operation, but has limited recycling solutions for components.
- Environmental (Liquid-filled): Risk of environmental contamination from fluid leaks, but offers more options for recycling and remanufacturing of components and fluids (with some greener alternatives available).
Dry-Type Transformers Are Filled With Oil to Reduce Overheating
That’s incorrect. Dry-type transformers are specifically designed without the use of oil or any other liquid for insulation and cooling. Instead, they rely on air circulation and the inherent insulating properties of solid materials like epoxy resin, varnish, and specialized insulation papers for cooling and electrical insulation. This design eliminates the risks associated with oil-filled transformers, such as leaks, flammability, and the need for oil handling and disposal.
The absence of oil makes them a safer and more environmentally friendly option for many applications.
Here are some key characteristics of dry-type transformers:
- Air-cooled: Heat generated during operation is dissipated into the surrounding air through natural convection or forced air cooling using fans.
- Solid insulation: Windings are insulated with materials like epoxy resin, varnish, and high-temperature insulation papers.
- Reduced fire risk: The absence of flammable oil significantly reduces the risk of fire.
- Lower maintenance: They generally require less maintenance compared to oil-filled transformers as there is no oil to monitor or maintain.
- Environmentally friendly: No risk of oil leaks or spills, making them a more sustainable choice.
Dry Type vs Liquid Transformer Maintenance
Maintaining dry-type transformers is generally a simpler process compared to their liquid-filled counterparts, primarily involving visual inspections and cleaning. The frequency of these inspections depends on the transformer’s operational intensity, with more frequent use necessitating more regular checks for dust and debris accumulation on windings, grilles, and coils. Cleaning is typically performed using compressed air, a vacuum, or a blower to ensure proper ventilation and cooling. Additionally, inspecting for loose electrical connections is a crucial aspect of dry-type transformer maintenance.
While the maintenance of dry-type transformers is straightforward, potential challenges can arise from their limitations in size and voltage ratings, which can make them more susceptible to overheating under overload conditions. Despite this, the overall maintenance demands are lower than those of liquid-filled transformers.
Many manufacturers, like Linkwell Transformers with their five-year warranty and repair services, offer support to ensure the long-term and efficient operation of dry-type units, assisting with both proactive maintenance and addressing any operational issues that may occur.
Liquid-filled transformers, due to their oil-based cooling and insulation system, require a more comprehensive maintenance regime. Similar to dry-type transformers, inspecting and tightening electrical connections is necessary.
However, the key difference lies in the need to monitor and maintain the insulating fluid. This includes regularly checking the liquid levels and gauges, as well as inspecting for any signs of leaks, with zero pressure potentially indicating a significant issue.
Furthermore, periodic sampling and testing of the transformer oil are essential to assess its condition, including dissolved gas analysis (DGA) to determine moisture content, fire and flashpoints, contamination, and dielectric strength, potentially requiring filtration or replacement of the fluid if it falls outside acceptable parameters.
How to Choose Dry Type and Oil Type Transformer
Choosing between dry-type and oil-filled transformers requires a careful evaluation of several key factors to match the transformer’s characteristics with the specific application requirements and environmental conditions.
Consider safety as a primary concern, favoring dry-type for indoor or densely populated areas due to the absence of flammable oil. Evaluate the power and voltage demands, as oil-filled transformers are generally more suitable for high-capacity and high-voltage applications due to their superior cooling.
- Safety Requirements: Prioritize dry-type transformers for indoor, safety-critical environments like hospitals and schools due to the absence of flammable oil. For outdoor or remote locations where fire risk can be managed, oil-filled types may be acceptable.
- Power and Voltage Needs: For high power demands (typically above 2500 kVA) and high voltage applications, oil-filled transformers generally offer a more economical and efficient solution. Dry-type transformers are often preferred for lower to medium power ratings.
- Environmental Considerations: If environmental impact is a major concern, dry-type transformers are the better choice due to the lack of potential oil leaks. However, consider the recyclability of both types in the long term.
- Maintenance Requirements: Dry-type transformers require less routine maintenance, mainly visual inspections and cleaning. Oil-filled transformers necessitate regular oil testing and potential servicing, which adds to operational costs.
- Installation Location: Indoor installations often favor dry-type transformers due to safety regulations and reduced fire hazards. Outdoor substations and industrial sites commonly utilize oil-filled transformers.
- Budget: While the initial cost of dry-type transformers can be higher for larger ratings, their lower maintenance costs might lead to long-term savings. Oil-filled transformers often have a lower upfront cost for high-power applications but higher maintenance expenses.
- Load Characteristics: Consider the type of load. Oil-filled transformers generally handle overloads better due to their superior cooling. For specific loads with harmonics, specialized dry-type (K-rated) or oil-filled transformers might be necessary.
Conclusion
In the choice between dry-type and oil-filled transformers, key distinctions in cooling, safety, and environmental impact play crucial roles. Dry-type transformers excel in safety and indoor applications with minimal maintenance, while oil-filled transformers often suit high-power outdoor needs, albeit with greater maintenance and environmental considerations. Understanding these trade-offs is vital for selecting the optimal transformer technology for specific requirements.
For businesses seeking a reliable supply of wholesale transformers, Linkwell Electrics offers a comprehensive range encompassing both dry-type and oil-filled solutions. Their expertise and diverse product catalog can help you find the ideal transformer to meet your project’s technical and budgetary needs.
Contact Linkwell Electrics today, your trusted wholesale transformer supplier, to discuss your requirements and secure the right transformers for your power infrastructure projects.