Welcome to our comprehensive guide on electrical junction box rules! Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for ensuring the safety and functionality of any electrical system, whether in residential or commercial settings. Proper installation and wiring within junction boxes are not just best practices; they are legally mandated requirements designed to prevent electrical hazards like fires and shocks.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the essential electrical junction box rules you need to know to achieve code compliance. We’ll break down key aspects such as proper box sizing, wiring methods within the box, secure connections, and accessibility requirements. By mastering these rules, you’ll be well-equipped to handle electrical projects safely and effectively, protecting yourself and your property.
What Are Electrical Junction Box Rules



Understanding electrical junction box rules is crucial for anyone working with electrical wiring, whether you’re a seasoned electrician or a DIY enthusiast.
These rules for box junctions, primarily outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC), are designed to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards.
Let’s break down some of the most important aspects.
Junction Box Sizing and Fill Calculations
One of the most critical aspects of electrical junction box rules is determining the correct size of the junction box. This isn’t just about fitting the wires in; it’s about preventing overheating and ensuring safe current flow. The NEC provides specific calculations to determine the minimum volume of a box based on the number and size of conductors it will contain.
These calculations involve counting conductors, including those passing through the box without being spliced, and assigning a volume allowance to each based on its gauge. Devices like switches and receptacles also count towards the box fill. It’s essential to follow these calculations precisely. Overfilling a junction box can lead to dangerous conditions, including insulation breakdown, short circuits, and fires.
Proper Installation and Accessibility
Beyond sizing, the way a junction box is installed is equally important. The NEC has strict rules about how boxes must be mounted, supported, and made accessible. These rules are in place to ensure that connections remain secure and that electricians can inspect and maintain the wiring in the future.
Junction boxes must be securely fastened to a structural element of the building, such as framing members. They cannot be supported solely by the wiring. Furthermore, all junction boxes must be accessible without removing permanent parts of the building structure or finish. This accessibility is vital for troubleshooting, repairs, and future modifications to the electrical system.
Wiring Connections and Securing Conductors
The rules governing how wires are connected within a junction box are also very detailed. These junction box rules aim to ensure reliable electrical connections and prevent loose wires, which can cause arcing, overheating, and fire hazards.
All connections within a junction box must be made using approved methods, such as wire connectors (wire nuts), terminal screws, or other listed devices. Simply twisting wires together is not an acceptable or safe practice. Additionally, conductors must be secured to the junction box to prevent stress on the connections. This is typically achieved using cable clamps or conduit connectors.
Junction Box Covers
A seemingly simple but absolutely essential rule involves junction box covers. The NEC mandates that all junction boxes must be covered. This might seem obvious, but it’s a critical safety measure.
Covers serve several important purposes. They protect the wiring and connections inside the box from physical damage, prevent accidental contact with live conductors, and contain any sparks or arcing that might occur. The covers must be appropriate for the box type and securely fastened. Using the correct cover is not just a code requirement; it’s a fundamental safety practice.
What Electrical Junction Box Rules Contain

Electrical junction boxes are essential components of any electrical system, acting as protective enclosures for wire connections. They ensure safety by containing sparks or faults and preventing accidental contact with live wires.
Understanding the rules governing their installation and use is crucial for any electrical work, whether you’re a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast. These junction box regulations, often found in electrical codes, dictate the proper selection, installation, and maintenance of junction boxes to guarantee a safe and functional electrical system.
Box Fill Capacity
The National Electrical Code (NEC) specifies the maximum number of wires allowed in an electrical junction box based on its size. This “box fill capacity” is calculated by considering the volume of the box and the volume of each conductor, device (like switches or receptacles), and internal cable clamp.
Overfilling a junction box can lead to overheating and potentially dangerous situations. Therefore, carefully calculating the box fill and selecting an appropriately sized box for the intended number of conductors and devices is paramount for safe electrical installations.
Proper Installation
Electrical codes outline specific requirements for the installation of junction boxes to ensure their structural integrity and accessibility. This includes securely mounting the box to a structural member, such as a stud or joist, and ensuring it is readily accessible for inspection and maintenance.
Concealed junction boxes, those hidden behind walls or ceilings without provisions for access, are generally prohibited. Proper installation not only ensures the longevity of the electrical system but also facilitates future troubleshooting and repairs.
Conductor Connections
Within a junction box, all electrical connections must be made securely and protected with appropriate connectors or termination methods. Wire nuts are commonly used to join conductors of the same gauge and material, ensuring a reliable electrical path.
It’s crucial to properly tighten these connections to prevent loose wires, which can lead to arcing, overheating, and even electrical fires. The NEC also specifies requirements for grounding and bonding within junction boxes to provide a safe path for fault currents.
Accessibility and Identification
Electrical junction boxes must remain accessible after installation to allow for inspection, testing, and maintenance. This means they should not be permanently covered by drywall, insulation, or other building materials without a removable access panel.
Additionally, it’s often required to identify junction boxes, especially in complex electrical systems, to facilitate tracing circuits and locating specific connections. Proper accessibility and identification contribute significantly to the safety and maintainability of an electrical installation.
Electrical Junction Box Regulations
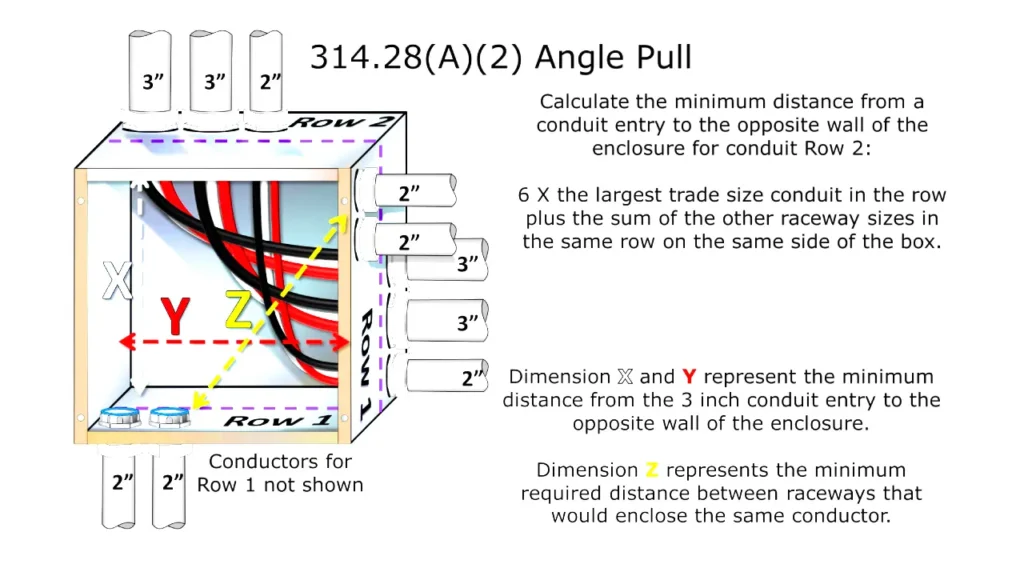
Electrical junction box regulations, primarily outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local electrical codes, establish the standards for the safe installation and use of these critical components.
These junction box regulations are in place to protect people and property from electrical hazards by ensuring that junction boxes are appropriately selected, installed, and maintained. Compliance with these codes is not merely recommended; it is a legal requirement for all electrical work.
National and Local Codes
The foundation of electrical junction box regulations lies within the National Electrical Code (NEC), a comprehensive set of guidelines for electrical installations in the United States. While the NEC provides a national standard, local jurisdictions often adopt and sometimes amend these regulations to suit their specific needs and conditions.
Therefore, it is crucial to consult both the NEC and the local electrical codes applicable to the area where the electrical work is being performed to ensure full compliance. These codes detail everything from box fill capacity to installation methods and material specifications.
Material and Construction Standards
Electrical regulations specify the types of materials and the construction of junction boxes to ensure durability and safety in various environments. Junction boxes must be made of non-combustible materials like metal or high-grade plastic and must be appropriately rated for their intended use, such as damp or hazardous locations.
The construction must provide a complete enclosure for the conductors, protecting them from physical damage and environmental factors like moisture and dust. Furthermore, regulations often require features like secure covers and proper fittings to maintain the integrity of the electrical connections within.
Installation and Accessibility Requirements
Electrical codes have strict rules regarding the installation of junction boxes to ensure both safety and future accessibility. Boxes must be securely mounted and supported, and their installation must not compromise the structural integrity of the building.
A key aspect of these regulations is the requirement for junction boxes to remain accessible without removing any part of the building structure. This accessibility is vital for inspection, maintenance, and troubleshooting, and concealing junction boxes in inaccessible locations is generally prohibited to prevent potential hazards and facilitate necessary electrical work.
Why Box Junction Rules Important
Electrical junction box rules are not just arbitrary guidelines; they are fundamental to ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical systems. Adhering to these regulations minimizes the risk of electrical hazards, protects property from fire, and ensures the long-term reliability of electrical installations. By standardizing practices, these junction box rules create a framework for safe and efficient electrical work, benefiting both professionals and individuals undertaking electrical projects.
Preventing Electrical Hazards
Strict adherence to junction box rules is paramount in preventing a range of electrical hazards. Properly sized and installed boxes prevent overcrowding of wires, which can lead to overheating and insulation damage, ultimately increasing the risk of short circuits and electrical fires.
Secure connections within the box, as mandated by these rules, minimize the chances of loose wires causing arcing and sparking. Furthermore, grounding and bonding requirements within junction boxes provide a safe path for fault currents, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock.
Ensuring Fire Safety
Electrical faults are a leading cause of residential fires, and junction boxes play a critical role in containing these potential hazards. Regulations regarding the use of appropriate box materials, proper installation techniques, and the avoidance of overfilling help to limit the spread of fire should an electrical fault occur within the box. By containing sparks and flames, junction boxes act as a crucial barrier, protecting surrounding building materials and providing valuable time for occupants to evacuate safely.
Maintaining System Reliability
Following junction box rules contributes significantly to the long-term reliability of electrical systems. Proper installation ensures the physical protection of wire connections from damage and environmental factors.
Accessible junction boxes facilitate easier inspection, troubleshooting, and maintenance, allowing for the timely identification and correction of potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By adhering to these standards, electrical systems are more likely to function safely and efficiently over their intended lifespan, reducing the need for costly repairs and replacements.
Conclusion
Adhering to electrical junction box rules is not merely about following guidelines; it’s about ensuring the safety and longevity of your electrical system. Proper installation, appropriate box sizing, and secure wiring practices minimize the risk of electrical hazards like shorts and fires. Understanding and implementing these regulations protects both property and lives.
Navigating the complexities of electrical codes can be challenging. However, compliance is non-negotiable for any electrical work. By prioritizing adherence to junction box rules, you contribute to a reliable and safe electrical infrastructure. This diligence prevents future issues, ensures code compliance, and provides peace of mind.
Looking for a reliable source for code-compliant junction boxes? We offer a wide selection of wholesale electrical junction boxes to meet your project needs. Ensure safety and quality with our dependable products. Contact us today for competitive pricing and a comprehensive catalog!




