You might wonder how to step down dc voltage for your next project. The easiest way is to use a buck converter or a step down transformer. You can power microcontrollers, LED lights, portable power banks, and even motors in robotics by learning how to step down dc voltage. Many beginners ask how to step down dc voltage for solar setups or automotive gadgets. If you want to know how to step down dc voltage safely, just follow basic steps and use reliable parts. Linkwell offers trusted electrical solutions for anyone who wants to learn how to step down dc voltage.
- Powering microcontrollers and development boards
- LED lighting projects
- Portable power solutions
- Automotive gadgets
- Robotics
- Solar power systems
Key Takeaways
- Use buck converters for small electronics. They efficiently lower voltage for devices like microcontrollers and LED lights.
- Choose step down transformers for larger systems. They provide stable voltage for industrial panels and heavy equipment.
- Gather essential components before starting. Use quality parts and safety gear to ensure a reliable and safe circuit.
- Test your circuit with a multimeter. This helps you verify voltage levels and troubleshoot common issues quickly.
- Trust Linkwell for reliable solutions. Their products and expert support can guide you in your voltage regulation projects.
How to Step Down DC Voltage
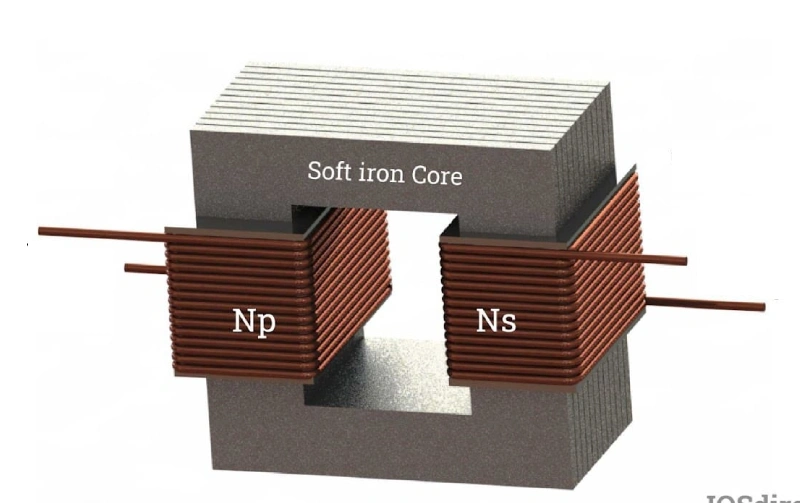
Stepping down dc voltage sounds complicated, but you can do it with just a few basic tools. You have two main choices: dc-to-dc converters like buck converters, or step down transformers. Each method works best for different situations. Let’s break down what you need to know.
Common Methods for Beginners
You’ll find two popular ways to step down dc voltage in beginner projects. The first is using dc-to-dc converters. These converters change one dc voltage to another, making them perfect for electronics. The second method is using step down transformers, which are great for larger setups or industrial panels.
Here’s a quick look at the most common methods:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Power Supply | Simple circuit configuration, inexpensive dc output | Generates heat, less efficient |
| Switching Power Supply | Higher efficiency, reduced heat generation | More complex design, potential noise |
You’ll probably use switching power supplies more often. These include dc-to-dc converters like buck converters. They work efficiently and keep your electronics cool.
Tip: If you want a reliable step down transformer for your project, Linkwell Electric offers high-quality options. Their transformers come with fast delivery and top ratings from customers worldwide.
When to Use a Buck Converter
You should reach for a buck converter when you need to lower dc voltage for small electronics. Buck converters are a type of dc-to-dc converter. They work well if your power source gives you more voltage than your device needs. For example, you might have a 12V battery but need only 5V for your microcontroller.
Buck converters are super flexible. You can use them in these situations:
- Adjust voltage levels for projects that need specific voltages.
- Protect sensitive components from too much voltage.
- Power microcontrollers, sensors, and LED strips.
- Get a stable 5V 1A output for most beginner electronics.
- Use battery sources from 6V to 50V for different projects.
- Build both analog and digital circuits.
Most buck converters handle input voltages from 5V to 55V and can step down to as low as 1.2V. You’ll find them in robotics, solar setups, and portable gadgets. They’re easy to use and don’t take up much space.
When to Use a Step Down Transformer
Step down transformers work best when you need to lower dc voltage for bigger systems. You’ll see them in control cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels. If you want to power heavy equipment or need stable voltage for a whole system, transformers are the way to go.
Linkwell Electric makes step down transformers that are safe and reliable. Customers rate Linkwell with a perfect 5.0 out of 5.0 for quality and delivery speed. Their transformers handle common voltage conversions like 220V to 110V or 480V to 240V. You can even get custom designs for special needs.
Here’s a quick comparison of voltage ranges:
| Component | Voltage Range |
|---|---|
| Buck Converter | 1.2V to 55V |
| Input Voltage | 5V to 55V |
| Step Down Transformer | 100V to 480V |
If you want to protect sensitive equipment and keep your system running smoothly, a step down transformer from Linkwell is a smart choice. You get stable voltage, less power loss, and longer equipment life.
Note: For most beginner projects, dc-to-dc converters like buck converters are easier to set up. If you’re working with larger panels or need industrial-grade solutions, Linkwell’s step down transformers are your best bet.
Step-Down Regulators and Buck Converters
What Is a Step-Down Regulator
You might hear people talk about step-down regulators when working with dc circuits. These regulators help you lower the dc voltage from a higher level to a safer, usable level for your devices. Step-down regulators compare the output voltage to a reference voltage. If the output drops below the set point, the regulator switches on and lets power flow. The inductor stores energy during this time. When the output voltage goes above the set level, the switch turns off. The inductor then releases its energy to the load. The regulator repeats this process to keep the voltage steady.
Step-down regulators come in two main types: linear regulators and switching regulators. Linear regulators are simple and quiet. Switching regulators, like buck converters, work more efficiently and handle bigger voltage drops.
How a Buck Converter Works
Buck converters are a popular type of switching regulator. You use them when you need to step down dc voltage for electronics. Buck converters work in two phases. When the switch is on, current flows from the input through the switch and inductor to the load. The inductor stores energy. When the switch turns off, the inductor releases its stored energy. Current keeps flowing to the load through a diode or a synchronous switch.
Here are the main parts inside a buck converter:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Switch (MOSFET) | Controls energy transfer |
| Inductor | Stores energy and smooths current |
| Diode/Switch | Provides current path when switch is off |
| Output Capacitor | Filters voltage and reduces ripple |
| Controller IC | Monitors and regulates output voltage |
Buck converters give you high efficiency and stable dc voltage. You can use them for microcontrollers, LED strips, and robotics projects.
Choosing the Right Solution
You might wonder which regulator to pick for your project. Buck converters work best for high current needs or when you need to drop dc voltage by a large amount. Linear regulators are better for low noise and small voltage drops. If you want to balance noise and heat, you can use both types in one design.
Here are some tips to help you choose:
- Use buck converters for high power and big voltage changes.
- Pick linear regulators for sensitive circuits that need low noise.
- Think about your voltage drop and current demand before you decide.
Linkwell Electric has years of experience with electrical solutions. You can trust their products for safe and reliable dc voltage control. Their step-down regulators and transformers meet strict quality standards and work in many industries. If you need help picking the right regulator, Linkwell can guide you.
Tip: Always check your device’s voltage and current needs before choosing a regulator. This helps you avoid damage and keeps your project running smoothly.
Components and Tools You Need
When you start working with dc voltage, you want to make sure you have the right tools and parts. You can build a simple dc step-down circuit with just a few components. Let’s break down what you need and where to find the best gear.
Essential Parts List
You need several key items for a basic dc step-down setup. You’ll use a buck converter to lower the dc voltage for most electronics. If you want to handle bigger loads or industrial panels, you’ll need a step down transformer. Here’s a quick look at the main components and their roles in your dc circuit:
| Component | Role in Circuit |
|---|---|
| Inductors | Store energy and control current flow in the circuit |
| Capacitors | Smooth output voltage and filter noise |
| Diodes | Allow current to flow in one direction, essential for rectification |
You also need wires, connectors, and a power supply that matches your dc input. If you want to boost your project’s reliability, pick quality parts. You can add a fuse for extra protection. Don’t forget a multimeter to check your dc voltage before and after you step it down.
Sourcing Linkwell Step Down Transformers
You want to get your step down transformer from a trusted source. Linkwell Electrics stands out for cabinet transformers, customization, and fast delivery. You can find their products online and get support for your dc projects. Here’s a table with top sources for step down transformers:
| Manufacturer | Location | Specialty/Experience | Contact Info |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linkwell Electrics | Global | Cabinet transformers, customization, fast delivery | linkwellelectrics.com |
| Triad Magnetics | USA | Industrial, commercial, over 50 years experience | Phone: 951-277-0757 |
| Altran Corp. | USA | Custom, industrial, commercial transformers | Phone: 815-455-5650 |
| SNC Manufacturing | USA | Durable, industrial transformers | Phone: 800-558-3325 |
| Lenco Electronics | USA | High-quality, custom transformers | Phone: 815-344-2900 |
You can boost your confidence by choosing Linkwell for your dc needs. Their transformers work well in control cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels. You get reliable performance and quick support.
Safety Equipment
Safety matters when you work with dc voltage. You want to protect yourself and your equipment. Grab insulated gloves and safety glasses before you start. Use a fuse in your circuit to prevent overload. You can boost your safety by checking all connections twice. Always turn off the power before you touch any wires. If you want to work with higher dc voltages, use a voltage tester to check for live wires.
Tip: You can boost your project’s safety and performance by using certified parts from trusted brands like Linkwell. Their step down transformers meet strict standards for dc applications.
You can build a safe and reliable dc step-down circuit with the right tools and parts. You boost your skills every time you finish a project. If you want help picking components, you can reach out to Linkwell for advice.
Assembly and Testing Guide
Setting Up Your Workspace
You want your workspace to be safe and organized before you start. Grab a circuit schematic to guide your design. Place your components close together to keep high-frequency current paths short. This helps reduce noise and electromagnetic interference. Use wide traces for power and ground connections if you’re working on a printed circuit board. Beginners often use a perfboard or stripboard. Make sure you lay out your components neatly. Double-check that your workspace is dry and free of clutter. Wear safety glasses and insulated gloves for extra protection.
Tip: Always check for exposed wires and loose connections before you begin. This simple step can prevent short circuits and keep your project safe.
Wiring the Circuit
Let’s wire a basic buck converter circuit. Follow these steps:
- Gather all the materials you need for your circuit.
- Connect the IN+ terminal to the positive wire from your power source.
- Connect the IN- terminal to the ground wire from your power source.
- Attach the OUT+ terminal to the positive voltage input of your device.
- Attach the OUT- terminal to the ground of your device.
- Use a screwdriver to adjust the trimmer until you reach the desired voltage.
If you’re using a step down transformer, connect the primary side to your input voltage and the secondary side to your output terminals. Always check the polarity before you power up. Tighten all screws and make sure wires are fully inserted into terminal blocks.
| Common Assembly Errors | How to Avoid Them |
|---|---|
| Loose connections | Tighten screws and check wires |
| Exposed wires | Trim and cover all bare wires |
| Ignoring polarity | Double-check before powering on |
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing your circuit is easy if you follow a few steps. Use a multimeter to check the output voltage before you connect your device. An oscilloscope helps you see voltage ripple and noise. Try a variable load device to test how your circuit handles different currents. You can also use a variable DC power supply to change the input voltage and see how your circuit responds.
Before you power on, verify the zero energy state of your circuit. Use a lock-out/tag-out system if you’re working with high voltage. Check for dangerous voltage with your multimeter before touching any conductors.
If your circuit does not produce the expected voltage, follow these troubleshooting steps:
- Make sure your multimeter and test leads are rated for the voltage you expect.
- Measure the input voltage and confirm it matches your power source.
- Measure the output voltage and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Note: Most problems come from loose connections, exposed wires, or incorrect polarity. Fix these issues and your circuit should work as expected.
You can now enjoy a safe and reliable step-down DC circuit. If you need help, reach out to Linkwell for expert support.
Conclusion
You’ve made it to the end of your beginner’s guide to stepping down DC voltage. Now you know how to choose between a buck converter and a step down transformer for your project. You can power microcontrollers, LED lights, and even bigger equipment with the right setup. Safety always comes first, so grab your gloves and double-check your connections before you start.
Let’s recap what you’ve learned:
- You can use a buck converter for small electronics and portable devices.
- You should pick a step down transformer for larger panels or industrial systems.
- You need to gather the right components and safety gear before you build.
- You can test your circuit with a multimeter and fix common issues quickly.
- You can trust Linkwell for reliable transformers and expert support.
Remember, voltage regulation keeps your devices safe and running smoothly. If you use quality parts, you’ll avoid problems and extend the life of your equipment.
Here’s a quick table to help you decide which method fits your needs:
| Project Type | Best Solution | Why Choose It? |
|---|---|---|
| Small electronics | Buck Converter | Easy setup, compact size |
| Industrial panels | Step Down Transformer | Stable voltage, high power |
| Custom requirements | Linkwell Solutions | Expert advice, customization |
You don’t have to figure it all out alone. If you want help picking the right transformer or need a custom solution, reach out to Linkwell. Their team answers questions fast and helps you get the best results. You can experiment with confidence and learn more as you go.
Ready to start your next project? You’ve got the knowledge, the tools, and a trusted partner in Linkwell. Go ahead and build something great!
You’ve learned how to step down DC voltage safely and pick the right method for your project. Always use quality products like Linkwell step down transformers. Check out the key takeaways below:
| Key Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Utilize Integrated Protection Functions | Use built-in protection for safer circuits. |
| Understand Types of Protection | Know input, output, and temperature protection to avoid risks. |
| Recognize Hazards | Watch out for high voltages and currents, especially with AC-DC conversion. |
Want to learn more? Explore voltage dividers, buck converters, and MIT’s Power Electronics course. If you need help or a custom solution, reach out to Linkwell. Stay curious and experiment safely!
FAQ
How do I know which method to use for stepping down DC voltage?
You should check your project’s power needs. Use a buck converter for small electronics. Pick a step down transformer for bigger systems. If you’re unsure, ask Linkwell for advice.
Can I use a buck converter with batteries?
Yes! Buck converters work great with battery power. You can step down voltage from 12V, 24V, or even 48V batteries to run microcontrollers, sensors, or LED strips.
What safety steps should I follow when wiring DC circuits?
Always wear insulated gloves and safety glasses. Double-check connections before turning on power. Use a fuse for extra protection. Never touch live wires.
What if my circuit doesn’t output the correct voltage?
- Check all connections.
- Measure input and output voltages with a multimeter.
- Adjust the buck converter’s trimmer if needed.
- Contact Linkwell for troubleshooting help.