HVAC transformers are crucial for powering the low-voltage control circuits in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, typically stepping down line voltage to 24VAC. Testing these transformers is essential for diagnosing HVAC system malfunctions, as a faulty transformer can disrupt the operation of thermostats, relays, and other vital control components. This guide will outline the steps to safely and effectively test an HVAC transformer using basic electrical testing equipment.
By following these procedures, technicians and homeowners can determine if the transformer is functioning correctly or needs replacement, helping to pinpoint the cause of HVAC control system issues. Proper testing ensures accurate diagnosis and facilitates efficient repairs, restoring the comfort and functionality of the heating and cooling system.
What is HAVC
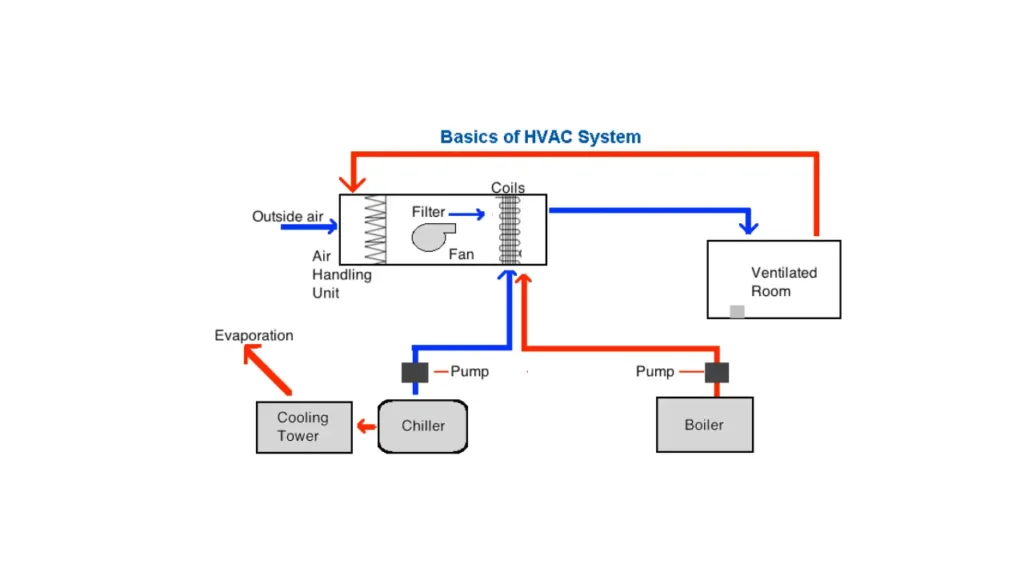
In the electric industry, HVAC in the context of transformers typically refers to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning applications. These transformers are specifically designed to provide the necessary voltage and power for the control circuits and sometimes even the motors within HVAC systems.
The purpose of an HVAC transformer is to step down the main power supply voltage (e.g., 120V or 240V in the US) to a lower, safer voltage (commonly 24V AC) required to operate the control components of heating and cooling systems. This lower voltage powers thermostats, relays, contactors, and other control elements that regulate the operation of the HVAC equipment.
HVAC transformers are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient functioning of heating and cooling systems in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. They act as a vital interface between the building’s electrical supply and the often more sensitive and lower-voltage control circuitry of the HVAC units.
The Importance of Testing Your HVAC Transformer
Testing your HVAC transformer is a vital step in maintaining the functionality and safety of your heating and cooling system. This small but crucial component steps down the main household voltage to a lower voltage, typically 24VAC, which powers the thermostat and other low-voltage control components. Regular checks or testing when experiencing HVAC issues can help identify a failing transformer before it causes more significant problems or complete system failure.
The importance of testing your HVAC transformer can be highlighted by the following points:
- Ensuring System Operation: A faulty transformer will prevent the low-voltage control circuit from functioning, leading to a non-responsive thermostat and a non-operational heating or cooling system. Testing helps pinpoint if the transformer is the cause of the system malfunction.
- Preventing Further Damage: A malfunctioning transformer can sometimes send erratic or insufficient voltage to other sensitive components like the control board or blower motor. Identifying and replacing a bad transformer promptly can prevent damage to these more expensive parts.
- Safety: A failing transformer can overheat or short circuit, potentially creating a fire hazard. Testing can help identify these dangerous conditions before they escalate.
- Troubleshooting Efficiency: Testing the transformer is a key step in systematically diagnosing HVAC problems. It helps narrow down the potential causes, saving time and effort in the repair process.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and replacing a faulty transformer early can prevent more costly repairs that might arise if the issue is left unaddressed and damages other components.
How to Test HVAC Transformer?

Testing an HVAC transformer is a crucial step in troubleshooting issues with your heating and cooling system’s controls. This typically involves checking the voltage output to ensure it’s providing the necessary power for the low-voltage components. By systematically testing the transformer, you can determine if it’s functioning correctly or if it needs to be replaced.
Here is the detailed guide about how to test HVAC transformer with multimeter in the following:
Tools Needed:
- Multimeter (capable of measuring AC voltage)
- Screwdriver (appropriate for accessing terminals)
- Safety glasses
Step 1: Visual Inspection and Safety Precautions
Begin by visually inspecting the HVAC transformer for any obvious signs of damage. Look for cracks, swelling, burn marks, or loose wiring. A strong burnt odor emanating from the transformer is also a clear indication of a problem. Before proceeding with any electrical testing, always turn off the main power supply to the HVAC unit at the breaker box. This is a critical safety measure to prevent electrical shock. Ensure the power is completely off before touching any wires or terminals.
Once the power is safely disconnected, carefully access the transformer terminals. This usually involves removing a cover on the HVAC unit’s control box. Take note of the wiring connections before disconnecting any wires for testing, or better yet, take a photo for reference. Ensure your hands and tools are dry. If you observe any of the aforementioned physical damage, it’s generally recommended to replace the transformer without further electrical testing, as internal damage is likely.
Step 2: Testing the Primary Voltage
The primary side of the HVAC transformer is connected to the higher voltage power supply (e.g., 120V or 240V). To test the primary voltage, you will need to carefully apply power back to the HVAC unit while taking extreme caution not to touch any live wires or components. Set your multimeter to the AC voltage setting and select a range appropriate for the expected primary voltage.
Place the multimeter probes across the primary terminals of the transformer. The reading should be close to the expected input voltage. If there is no voltage reading on the primary side, the issue lies upstream of the transformer, such as a tripped breaker, a disconnected wire, or a faulty power supply to the unit. If the primary voltage is present and correct, the problem may be on the secondary side or within the transformer itself. Immediately turn off the power to the HVAC unit after completing this test.
Step 3: Testing the Secondary Voltage
The secondary side of the HVAC transformer provides the lower voltage (typically 24V AC) for the control circuit. With the power to the HVAC unit safely turned off, locate the secondary terminals of the transformer. Set your multimeter to the AC voltage setting and select a low voltage range (e.g., 50V AC).
Place the multimeter probes across the secondary terminals of the transformer. If the transformer is functioning correctly, you should read the expected low voltage (e.g., around 24V AC). A reading significantly lower than expected or zero indicates a potential problem with the transformer, such as a blown internal fuse (if equipped), a faulty winding, or complete failure. If you obtain the correct secondary voltage, the issue likely lies elsewhere in the control circuit, such as a faulty thermostat, wiring problem, or a defective control component.
How to Check if a HVAC Transformer is Bad?
Testing your HVAC transformer is a crucial step in diagnosing heating and cooling system malfunctions, as this component provides the low-voltage power for the control circuit.
Identifying a bad transformer early can prevent further damage to other components and ensure the safety of your system. You can check for several telltale signs and perform basic electrical tests to determine its condition.
Here’s how to check if an HVAC transformer is bad:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the transformer for any physical damage such as cracks, swelling, burn marks, or melted components.3 Look for loose or disconnected wires. A strong burnt odor is a significant indicator of internal failure. If any visual damage is apparent, it’s often best to replace the transformer.
- Humming or Vibration: A slight hum from an operating transformer is normal.4 However, a drastically increased humming sound or noticeable vibration can indicate a problem, such as internal faults or loose windings. This symptom warrants further investigation.
- Tripped Circuit Breaker or Blown Fuses: If the circuit breaker supplying power to the HVAC system frequently trips or the low-voltage fuses (if present) blow repeatedly, a faulty transformer drawing excessive current could be the cause.5 However, other issues can also lead to this, so further testing of the transformer itself is necessary.
- Lack of System Power: If your thermostat is unresponsive and the HVAC system doesn’t turn on at all, a bad transformer that is not providing the necessary low-voltage power to the control board could be the culprit. However, always verify the main power supply to the unit first.
To confirm if the HVAC transformer is bad, you’ll need to perform electrical tests using a multimeter:
- Primary Voltage Test: With the main power to the HVAC unit turned on (exercise extreme caution), use a multimeter set to AC voltage to check the voltage across the primary terminals of the transformer. This should match the voltage of your home’s power supply (e.g., 120V or 240V). If there’s no voltage here, the problem lies upstream of the transformer. Turn off the power immediately after this test.
- Secondary Voltage Test: With the main power to the HVAC unit turned off, locate the low-voltage secondary terminals (typically two wires). Set your multimeter to AC voltage (low range, e.g., 50V). Carefully turn the main power to the HVAC unit on again (with extreme caution) and measure the voltage across these secondary terminals. A healthy transformer should output the specified low voltage (usually around 24VAC). A reading significantly lower than expected or zero indicates a likely failure of the transformer. Turn off the power immediately after this test.
- Continuity Test (Power Off): With the main power off, disconnect the wires from the transformer terminals. Use the resistance (ohms) setting on your multimeter to check the continuity of both the primary and secondary windings. An infinite resistance reading indicates an open winding, meaning the transformer is bad. A very low resistance reading could suggest a short circuit within the winding.
Most Common Cause of Transformer Failure

The most common cause of transformer failure is overheating, which can stem from a variety of factors. When a transformer operates at excessively high temperatures, the insulation materials surrounding the windings break down at an accelerated rate.
This degradation compromises the transformer’s ability to electrically isolate its components, leading to internal faults and eventual failure. Overheating can be a gradual process or occur rapidly depending on the underlying cause.
Several factors contribute to transformer overheating. Overloading the transformer beyond its rated capacity is a frequent culprit, as it causes excessive current flow and increased heat generation.
Inadequate cooling, whether due to blocked ventilation, malfunctioning cooling fans (in dry-type transformers), or insufficient oil levels or blocked cooling circuits (in liquid-filled transformers), prevents proper heat dissipation. Other contributing factors include high ambient temperatures, sustained overvoltage, excessive harmonic content in the power supply, and even loose connections that create localized hot spots.
Here’s a breakdown of common causes leading to overheating and subsequent failure:
- Overloading: Exceeding the transformer’s VA rating.
- Inadequate Cooling: Blocked ventilation or faulty cooling systems.
- High Ambient Temperature: Operating in environments exceeding the transformer’s thermal limits.
- Sustained Overvoltage: Applying voltage higher than the transformer’s rating.
- Harmonic Distortion: Excessive non-sinusoidal currents causing increased losses.
- Loose Connections: Creating resistance and localized heating.
FAQ
What tools are needed to test an HVAC transformer?
You need a digital multimeter, insulated probes, and basic safety gear. A multimeter allows you to measure input voltage, output voltage, and continuity, which are essential for diagnosing transformer performance accurately and safely.
How do you check if an HVAC transformer is receiving power?
Set the multimeter to AC voltage and measure across the primary terminals. If the reading matches the rated input voltage, the transformer is receiving power. No voltage usually indicates wiring issues, blown fuses, or upstream power problems.
How do you test the output voltage of an HVAC transformer?
Measure the secondary terminals with the multimeter set to AC voltage. A healthy transformer should deliver its rated output, typically 24V. A significantly lower or zero reading suggests internal failure or excessive load conditions.
What does a continuity test tell you about a transformer?
A continuity test checks whether the transformer windings are intact. No continuity indicates an open winding, meaning the transformer is defective. This test is done with power disconnected to avoid equipment damage or personal injury.
Can a transformer show voltage but still be faulty?
Yes. A transformer may show correct no-load voltage but fail under load. Overheating, buzzing sounds, or voltage drops when connected often indicate internal insulation breakdown or shorted windings affecting real operating performance.
When should an HVAC transformer be replaced instead of repaired?
Replace the transformer if windings are open, insulation is damaged, or output voltage is unstable under load. Replacement is usually safer and more cost-effective than repair, especially in commercial HVAC systems requiring long-term reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, testing an HVAC transformer is a straightforward process involving visual inspection and voltage checks to ensure it’s providing the correct output voltage for the control circuit. Confirming the primary voltage input and verifying the stepped-down secondary voltage are crucial steps in diagnosing potential issues. If the output is incorrect or absent, the transformer may need replacement.
Regular testing can prevent system malfunctions and ensure the reliable operation of your HVAC unit. Identifying a faulty transformer early can save time and prevent further damage to other components. For businesses needing replacement transformers, Linkwell Electrics offers a range of wholesale control transformers suitable for HVAC applications.
Sourcing from Linkwell Electrics provides access to quality transformers for your HVAC needs. Proper testing, combined with reliable components, ensures the efficient and safe operation of heating and cooling systems. Contact Linkwell Electrics for your wholesale control transformer inquiries.




