R513A refrigerant offers a safer, eco-friendly alternative to R134a in 2025. With lower GWP, zero ozone depletion, and easy retrofitting, it’s ideal for modern commercial and industrial cooling systems.

You may wonder what makes r513a refrigerant important in 2025. R513a refrigerant combines HFO-1234yf and HFC-134a in an azeotropic blend. You get a low global warming potential and zero ozone depletion, which means it is safer for the environment. Many medium temperature systems now use it to replace older refrigerants like R134a. Its A1 safety rating shows you can rely on it for safe operation in commercial and industrial settings.
Key Takeaways
- R513A refrigerant blends HFO-1234yf and HFC-134a to offer low global warming potential and zero ozone depletion, making it environmentally safer than older refrigerants like R134a.
- You can often replace R134a with R513A in existing cooling systems with minimal changes, mainly adjusting the refrigerant charge and checking lubricant compatibility.
- R513A provides similar or better cooling performance than R134a, with higher cooling capacity, lower discharge temperatures, and stable operation in commercial and industrial applications.
- This refrigerant has an A1 safety rating, meaning it is non-flammable and non-toxic, which makes it a safe choice for many cooling systems including automotive and industrial uses.
- Using R513A helps meet many 2025 environmental regulations by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but you should always verify local rules and system compatibility before switching.
R513A Refrigerant

Composition and Properties
You will find that r513a refrigerant is a blend of two chemicals: HFO-1234yf and HFC-134a. The exact ratio is about 89% HFO-1234yf and 11% HFC-134a by mass. This blend creates a refrigerant with a low global warming potential and no ozone depletion. You can use it in many cooling systems that once used R134a.
R513a refrigerant is considered azeotropic or nearly azeotropic. This means it acts almost like a pure refrigerant. You do not have to worry about temperature glide, which can make some blends harder to handle. Because of this, you can use r513a refrigerant as a drop-in replacement in many existing cooling systems. You will also notice that it has an A1 safety classification. This means it is non-flammable and non-toxic, so you can use it safely in commercial and industrial cooling systems.
Here is a table showing some key thermodynamic properties of r513a refrigerant:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | -29.2 °C |
| Critical Temperature | 96.5 °C |
| Critical Pressure | 3766 kPa (546.2 psia) |
Tip: The azeotropic nature of r513a refrigerant makes it easier to handle and more stable in operation compared to non-azeotropic blends. You can expect reliable performance in your cooling systems.
How It Works
You will see r513a refrigerant working inside vapor-compression cooling systems. These systems use a cycle that moves heat from one place to another. The refrigerant absorbs heat as it evaporates and releases heat as it condenses. You can use r513a refrigerant in the same way as R134a, often without changing your equipment.
When you use r513a refrigerant in your cooling systems, you may notice that it behaves much like R134a. It flows through the compressor, condenser, expansion device, and evaporator. You do not need to make major changes to your system. However, you might need to adjust the charge amount. R513a refrigerant usually requires about 15% more mass flow per unit of cooling capacity compared to R134a. This means you may need to add a bit more refrigerant to get the same cooling effect.
You should also pay attention to how r513a refrigerant interacts with lubricants in your system. The more volatile part of the blend can leave the oil faster, which may change how well the compressor is lubricated. This can affect the durability of your cooling systems. Still, most users find that r513a refrigerant offers stable performance and is easy to use as a replacement for R134a.
Note: You can use r513a refrigerant as a drop-in replacement for R134a in many cooling systems. This makes it a popular choice for meeting new environmental rules in 2025.
Environmental Impact
GWP and ODP
When you choose a refrigerant for your system, you need to consider its global warming potential, or gwp. This value shows how much a refrigerant can contribute to climate change compared to carbon dioxide. R513A refrigerant has a gwp of about 572, which is much lower than R134a’s gwp of 1300. You can see this difference in the table below:
| Refrigerant | GWP Value | Relative GWP Reduction vs R134a | Flammability Class | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R134a | 1300 | N/A | A1 (non-flammable) | Widely used, high GWP |
| R513A | ~572 | 56% reduction | A1 (non-flammable) | Short-term alternative, azeotropic mixture of R134a/R1234yf |
| R1234ze(E) | <150 | >88% reduction | A2L (mildly flammable) | Long-term alternative, pure refrigerant |
| R516A | <150 | >88% reduction | A2L (mildly flammable) | Long-term alternative, mixture of R1234yf/R134a/R152a |
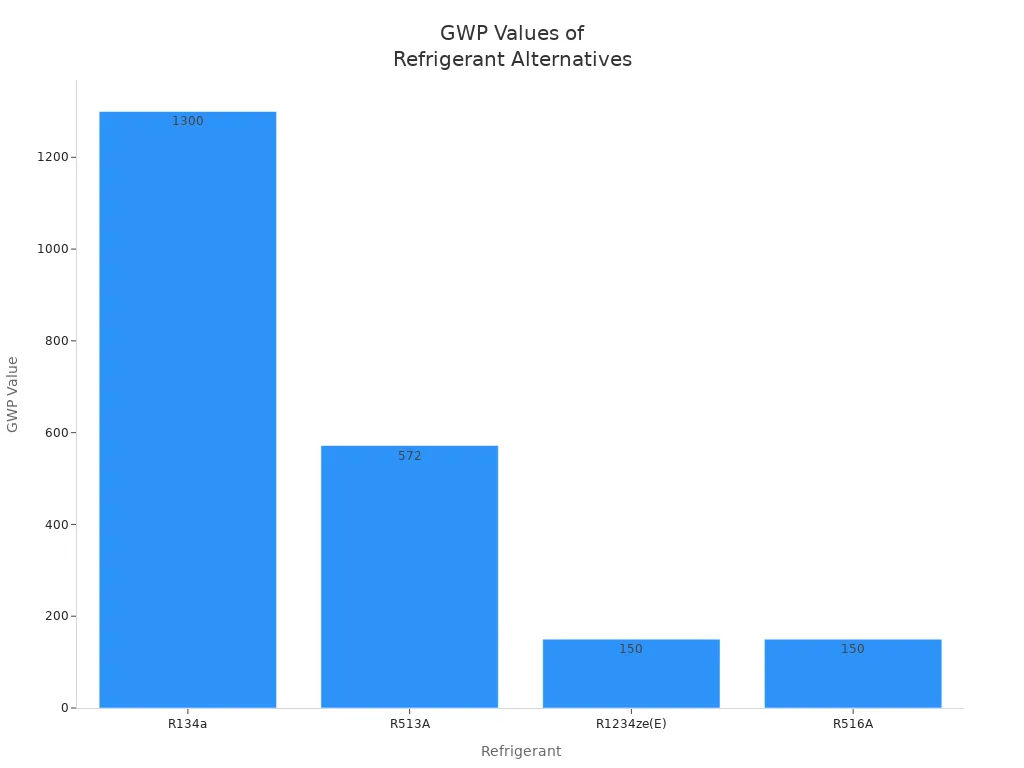
You will notice that R513A refrigerant offers a 56% gwp reduction compared to R134a. This helps you achieve reduced environmental impact in your operations. R513A refrigerant also has an ozone depletion potential (ODP) of zero. This means it does not harm the ozone layer, unlike older refrigerants such as R22 and R12. You support sustainability when you select a refrigerant with low gwp and zero ODP.
Regulatory Compliance
You must follow strict rules when you use refrigerants in 2025. Many regions have set gwp limits to protect the environment. In the European Union, new regulations ban self-contained systems with refrigerants that have a gwp of 150 or higher starting January 2025. R513A refrigerant, with a gwp of 629, falls above this limit for some uses. The United States and Canada have set their own gwp limits at 700 and 750, so you can still use R513A refrigerant in many applications there.
| Regulation Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| EU Regulation (EU) 2024/573 | From 1 Jan 2025, self-contained systems with refrigerants having GWP ≥ 150 are prohibited; F-gases with GWP ≥ 2500 prohibited from 1 Jan 2025 |
| Multipack Centralised Systems | Since 1 Jan 2022, systems ≥ 40 kW with F-gases GWP ≥ 150 are prohibited, with some derogations |
| R513A GWP | 629 (GWP100), thus restricted under these rules for certain applications |
| EU REACH Proposal | Potential restrictions on PFAS substances including F-gases like R513A, decision expected in 2025 |
| US and Canada Regulations | Stepwise GWP limits of 700 (US) and 750 (Canada) from 2025, showing global trend towards lower GWP refrigerants |
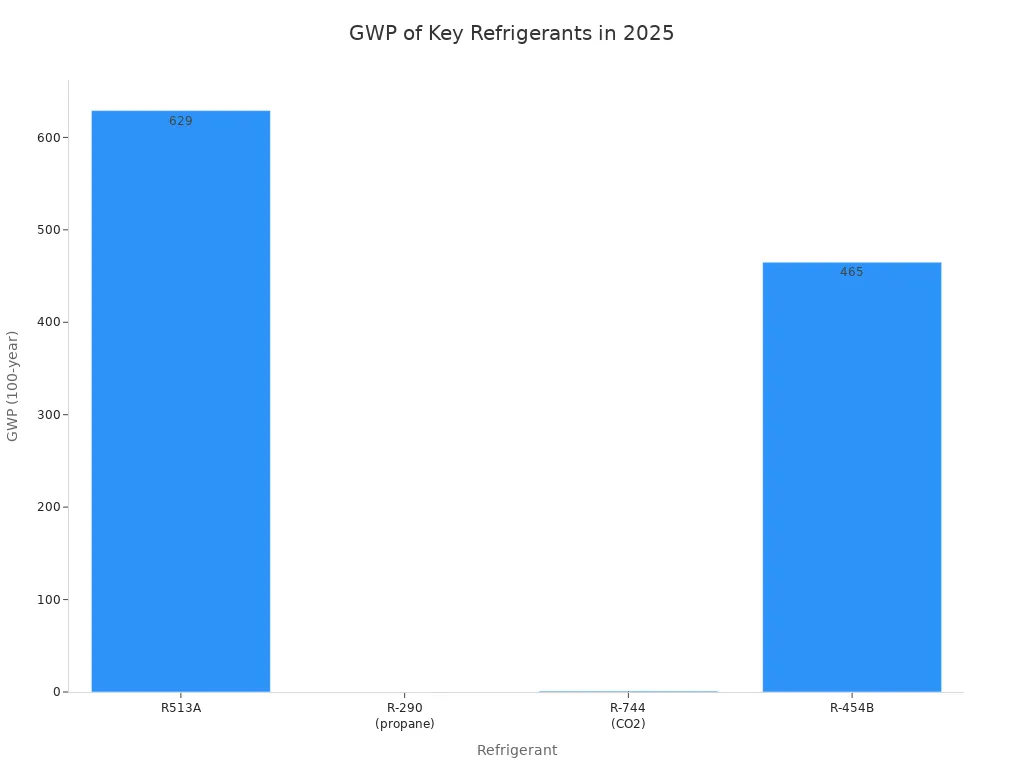
You can use R513A refrigerant to meet EPA SNAP and EU F-Gas rules in many cases. The EPA lists R513A refrigerant as an acceptable substitute for several cooling applications. This helps you comply with laws that aim to lower gwp and protect the ozone layer. As rules continue to change, you should always check if your refrigerant meets the latest requirements.
Tip: By choosing R513A refrigerant, you help your company meet current regulations and prepare for future changes in gwp limits.
Refrigerant Comparison

R513A vs R134a
You may wonder how R513A compares to R134a. Both serve as popular choices for medium temperature cooling, but they differ in several ways. R513A is an azeotropic blend, while R134a is a single-component refrigerant. R513A offers a much lower global warming potential, making it a better choice for the environment. You will also find that R513A has better stability during leaks and a smaller optimal charge size.
Here is a table that highlights the main differences:
| Aspect | R513A | R134a |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Azeotropic blend: 44% R134a + 56% R1234yf | Single component refrigerant |
| Global Warming Potential (GWP) | ~573 | 1300 |
| Environmental Stability | Better during leakage | Less stable during leakage |
| Optimal Refrigerant Charge | Smaller | Larger |
| Performance Characteristics | Slightly better freezing capacity, lower discharge temperature | Standard freezing capacity and discharge temperature |
Tip: Choosing R513A helps you lower your carbon footprint, especially if your system experiences leaks.
Performance and Efficiency
When you look at performance, R513A stands out for its efficiency and cooling power. You can expect a cooling capacity about 4% higher than R134a. The energy efficiency, measured as COP, remains equal. R513A also runs with a lower discharge temperature, which can help your compressor last longer.
| Performance Metric | R513A Compared to R134a |
|---|---|
| Cooling Capacity | 4% higher |
| Energy Efficiency (COP) | Equal |
| Mass Flow | 20% increase |
| Compressor Discharge Pressure | Lower |
You only need to adjust the thermostatic expansion valve when switching to R513A. Most systems do not require major changes. Tests show that annual energy use drops slightly, and the total warming impact falls by about 5%. This makes R513A a practical and efficient refrigerant for modern systems.
Safety
Safety matters when you select a refrigerant. R513A and R134a both have an A1 safety classification, which means they are non-flammable and have low toxicity. You can use R513A in commercial, automotive, and industrial cooling without special safety concerns. Unlike some newer alternatives, R513A does not pose flammability risks.
Here is a chart comparing the safety profiles of common refrigerants:
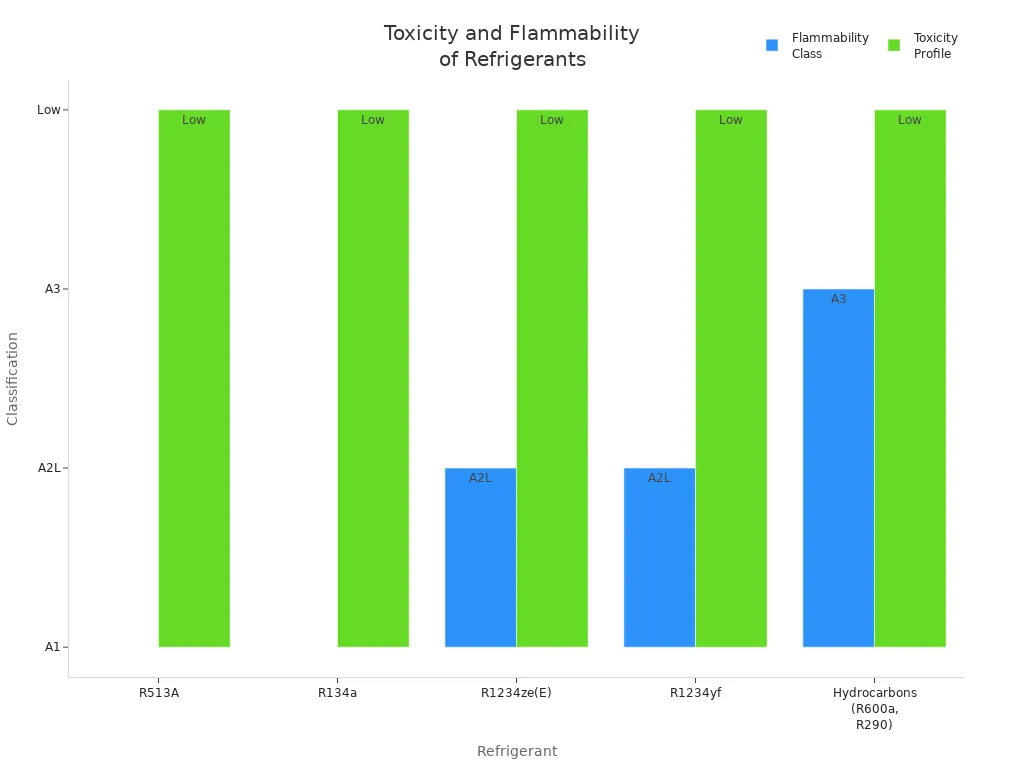
Note: R513A’s non-flammable nature makes it a strong candidate for applications where safety is a top priority.
R513A Applications

Industrial Cooling Use Applications
You will find R513A used in many industrial cooling systems today. These systems include refrigeration and air-conditioning setups that use both smooth and microfinned tubes. When you use R513A in microfinned tube designs, you get improved heat transfer and lower pressure drops, especially at higher mass flow rates. This means your cooling systems can run more efficiently and use less energy. The table below shows how R513A performs in different industrial cooling setups:
| Industrial Cooling System Aspect | Refrigerant | Tube Type | Performance Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigeration and air-conditioning systems | R513A | Smooth tubes | Similar pressure gradients to R134a; slightly lower heat transfer coefficients (HTCs) |
| Industrial cooling systems | R513A | Microfinned tubes | Equivalent or improved heat transfer performance compared to R134a; lower pressure drops at higher mass fluxes |
| Thermal industry applications | R513A | Microfinned tubes | Enhanced heat transfer coefficients; reduced energy consumption; robust candidate for sustained use |
| Condensation heat transfer | R513A | Microfinned tubes | Matches R134a performance; contributes to lower pressure drops |
Tip: If you want reliable and efficient cooling systems for your industrial needs, R513A offers strong performance and energy savings.
Commercial Refrigeration
You will see R513A widely adopted in commercial refrigeration applications. Many businesses use it in chillers, HVAC units, heat pumps, and other medium-temperature cooling systems. Because R513A is compatible with existing R134a systems, you can retrofit your equipment easily. This helps you maintain cooling capacity and energy efficiency while lowering your environmental impact. In 2025, new US regulations require refrigerants with a GWP below 700 for intermodal refrigerated containers. R513A meets this requirement, making it a preferred choice for refrigerated shipping containers. Companies like MCI have optimized their Star Cool containers for R513A since 2017, showing its proven track record in commercial cooling systems.
Retrofitting and Replacement
You can retrofit your existing R134a cooling systems to use R513A with minimal changes. Most of the time, you only need to adjust the thermostatic expansion valve. You do not have to replace major components like compressors. R513A gives you better or similar performance, with higher cooling capacity and lower discharge temperatures. However, you should check the refrigerant charge and make sure your system uses compatible lubricants, such as POE oils. Proper charge management is important because it affects power use and efficiency. Studies show that R513A retrofits may have a slightly lower coefficient of performance, but the environmental benefits often outweigh this small trade-off. Always monitor your cooling systems after a retrofit to ensure stable operation.
- R513A can replace R134a with minimal system modifications.
- You get higher mass flow rates and slightly increased power use, but overall efficiency remains strong.
- No major component changes are needed.
- Check refrigerant charge and lubricant compatibility for best results.
Automotive Cooling Systems
You will notice that automotive cooling systems are starting to use R513A as a low-GWP alternative. R513A offers similar pressures and temperatures to R134a, so manufacturers can adopt it easily. In automotive air conditioning, R513A requires about 5.9% less refrigerant charge and cools the cabin 21% faster than R134a. However, you may see a slightly lower coefficient of performance and heating capability. The table below compares key performance metrics:
| Performance Metric | R513A Compared to R134a |
|---|---|
| Heating Capability | 2% lower |
| Coefficient of Performance (COP) | 3–9% lower |
| Filling Volume | Less than R134a systems |
Note: R513A is non-toxic and non-flammable, making it a safe choice for automotive cooling systems. While it does not meet the strictest GWP limits, it remains a practical option for vehicles where moderate GWP standards apply.r32 vs r513a refrigerants differences advantages and which one is better,It has always been a hot topic in the air conditioning industry. I hope I can help you solve the problem.
You may have questions about R513A refrigerant. Here are answers to the most common ones:
- Is R513A refrigerant safe to use?
You can use R513A safely in most systems. It has an A1 safety classification, which means it is nonflammable and has low toxicity. You do not face the same risks as with ammonia or flammable refrigerants. - How does R513A compare to R134a for the environment?
R513A has a global warming potential (GWP) of about 573. This is much lower than R134a’s GWP of 1430. You help reduce your carbon footprint when you choose R513A. - Can you use R513A as a drop-in replacement for R134a?
Yes, you can often use R513A in systems designed for R134a. You may need to adjust the charge and check lubricant compatibility, but you do not need to replace major components. - Where can you use R513A refrigerant?
You find R513A in mobile air conditioning, heat pumps, commercial and industrial refrigeration, direct expansion cooling, and even ice stadiums. - Does R513A have temperature glide?
No, R513A is an azeotropic blend. You do not need to worry about temperature glide, which makes charging and maintenance easier. - Will R513A be phased out soon?
Regulations keep changing. Some regions may restrict R513A in the future due to its GWP. You should check local rules before making long-term plans. - Are there special handling precautions?
R513A has a slight ether-like odor, which helps you detect leaks. You should avoid inhaling the gas. Always follow safety guidelines.
Tip: You need EPA 608 or 609 certification to buy and handle R513A in the United States.
- Where can you find technical resources?
You can use pressure-temperature (PT) charts for charging and maintenance. These charts help you keep your system running efficiently.
Conclusion
You now understand why R513A refrigerant stands out in 2025. This refrigerant gives you a strong balance between environmental responsibility and reliable performance. You can use it as a replacement for R134a in many cooling systems. Its low global warming potential and zero ozone depletion help you meet strict environmental rules. The A1 safety rating means you can trust it in commercial, industrial, and automotive applications.
R513A helps you reduce your carbon footprint while keeping your systems efficient and safe.
Before you switch to R513A, you should know about some important trade-offs:
- R513A can show about 24% lower energy efficiency ratio (EER) than R134a in water chillers with piston-type compressors and minichannel condensers.
- The vapor density at the compressor suction is higher, which increases the mass flow rate by around 15%.
- Higher mass flow can lead to more pressure drops in refrigerant lines and a higher compressor compression ratio.
- Reciprocating compressors may see about 8% lower isentropic and mechanical efficiencies.
- Performance changes with compressor type. Rotary compressors in small systems can get up to 5% higher coefficient of performance (COP) and more cooling capacity.
- The benefits or drawbacks depend on your system’s design, compressor type, and operating conditions.
You should always evaluate your system before making the switch. R513A works best when you match it to the right equipment and conditions. If you want to future-proof your cooling systems, talk to a qualified professional. They can help you check compatibility and make sure you meet all regulations.
Choosing R513A means you support a cleaner environment and prepare your business for the future.
You gain several benefits when you choose R513A refrigerant for your cooling systems:
- R513A has a much lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) than older refrigerants, helping you meet 2025 environmental rules.
- You can retrofit existing R134a equipment with R513A, making the switch easier.
- The refrigerant is non-flammable and non-toxic, so you get a safer system.
- R513A keeps your cooling performance high while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
For best results, talk with a professional to check system compatibility and select equipment designed for low-GWP refrigerants. This step helps you future-proof your investment.
You may have questions about R513A refrigerant. Here are answers to the most common ones:
- Is R513A refrigerant safe to use?
You can use R513A safely in most systems. It has an A1 safety classification, which means it is nonflammable and has low toxicity. You do not face the same risks as with ammonia or flammable refrigerants. - How does R513A compare to R134a for the environment?
R513A has a global warming potential (GWP) of about 573. This is much lower than R134a’s GWP of 1430. You help reduce your carbon footprint when you choose R513A. - Can you use R513A as a drop-in replacement for R134a?
Yes, you can often use R513A in systems designed for R134a. You may need to adjust the charge and check lubricant compatibility, but you do not need to replace major components. - Where can you use R513A refrigerant?
You find R513A in mobile air conditioning, heat pumps, commercial and industrial refrigeration, direct expansion cooling, and even ice stadiums. - Does R513A have temperature glide?
No, R513A is an azeotropic blend. You do not need to worry about temperature glide, which makes charging and maintenance easier. - Will R513A be phased out soon?
Regulations keep changing. Some regions may restrict R513A in the future due to its GWP. You should check local rules before making long-term plans. - Are there special handling precautions?
R513A has a slight ether-like odor, which helps you detect leaks. You should avoid inhaling the gas. Always follow safety guidelines.
Tip: You need EPA 608 or 609 certification to buy and handle R513A in the United States.
- Where can you find technical resources?
You can use pressure-temperature (PT) charts for charging and maintenance. These charts help you keep your system running efficiently.
Conclusion
You now understand why R513A refrigerant stands out in 2025. This refrigerant gives you a strong balance between environmental responsibility and reliable performance. You can use it as a replacement for R134a in many cooling systems. Its low global warming potential and zero ozone depletion help you meet strict environmental rules. The A1 safety rating means you can trust it in commercial, industrial, and automotive applications.
R513A helps you reduce your carbon footprint while keeping your systems efficient and safe.
Before you switch to R513A, you should know about some important trade-offs:
- R513A can show about 24% lower energy efficiency ratio (EER) than R134a in water chillers with piston-type compressors and minichannel condensers.
- The vapor density at the compressor suction is higher, which increases the mass flow rate by around 15%.
- Higher mass flow can lead to more pressure drops in refrigerant lines and a higher compressor compression ratio.
- Reciprocating compressors may see about 8% lower isentropic and mechanical efficiencies.
- Performance changes with compressor type. Rotary compressors in small systems can get up to 5% higher coefficient of performance (COP) and more cooling capacity.
- The benefits or drawbacks depend on your system’s design, compressor type, and operating conditions.
You should always evaluate your system before making the switch. R513A works best when you match it to the right equipment and conditions. If you want to future-proof your cooling systems, talk to a qualified professional. They can help you check compatibility and make sure you meet all regulations.
Choosing R513A means you support a cleaner environment and prepare your business for the future.
You gain several benefits when you choose R513A refrigerant for your cooling systems:
- R513A has a much lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) than older refrigerants, helping you meet 2025 environmental rules.
- You can retrofit existing R134a equipment with R513A, making the switch easier.
- The refrigerant is non-flammable and non-toxic, so you get a safer system.
- R513A keeps your cooling performance high while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
For best results, talk with a professional to check system compatibility and select equipment designed for low-GWP refrigerants. This step helps you future-proof your investment.
FAQ
What makes R513A refrigerant different from R134a?
You get a lower global warming potential with R513A. It uses a blend of HFO-1234yf and HFC-134a. You can often use it as a direct replacement for R134a in many systems.
Can you mix R513A with other refrigerants?
You should not mix R513A with other refrigerants. Mixing can cause performance issues and may damage your equipment. Always use the correct refrigerant for your system.
How do you handle leaks with R513A?
You can detect leaks by its slight ether-like odor. Use electronic leak detectors for accuracy. Always repair leaks quickly to keep your system efficient and safe.
What lubricants work best with R513A?
You should use polyolester (POE) oils with R513A. These lubricants ensure proper compressor function and long equipment life. Always check your system’s manual for specific oil recommendations.