When working with electrical systems, precise and consistent wiring is paramount for safety and functionality. Terminal blocks, essential components for organizing and connecting wires, often incorporate color coding to simplify this process. This introduction will explore the significance of these color codes, focusing on the two most widely recognized international standards: IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association).
Understanding the specific color conventions set forth by IEC and NEMA for terminal blocks is crucial for electricians, engineers, and technicians worldwide. Adhering to these standards ensures clarity, reduces the risk of wiring errors, and facilitates easier troubleshooting and maintenance across diverse electrical installations.
What Is Terminal Block Color Code?
The Terminal Block Color Code refers to the standardized system of using specific colors for terminal blocks to indicate the function or purpose of the wires connected to them. This visual coding system helps electricians and technicians quickly identify different circuits, such as protective earth (ground), neutral, live phases, or specific control signals.
Adhering to these color codes, which often follow international standards like IEC or national standards like NEMA, improves safety, simplifies wiring, aids in troubleshooting, and ensures consistency across various electrical installations.
Colored Terminal Blocks Benefits
Colored terminal blocks offer significant benefits in electrical wiring and panel building. They greatly enhance clarity and safety by providing immediate visual identification of different circuit functions. This reduces the likelihood of wiring errors, which can be costly and dangerous.
- Improved Safety: Quickly distinguish between protective earth, neutral, and live phases, minimizing accidental contact with energized circuits.
- Reduced Wiring Errors: The clear visual cues help prevent misconnections, leading to more reliable and functional systems.
- Faster Troubleshooting: When issues arise, identifying the correct circuit is expedited, significantly cutting down on diagnostic and repair time.
- Enhanced Organization: Creates a neat and logical wiring layout, making future modifications or expansions simpler and more efficient.
- Compliance with Standards: Many color codes adhere to international (IEC) or national (NEMA) electrical standards, ensuring global compatibility and best practices.
Terminal Block Color Code List
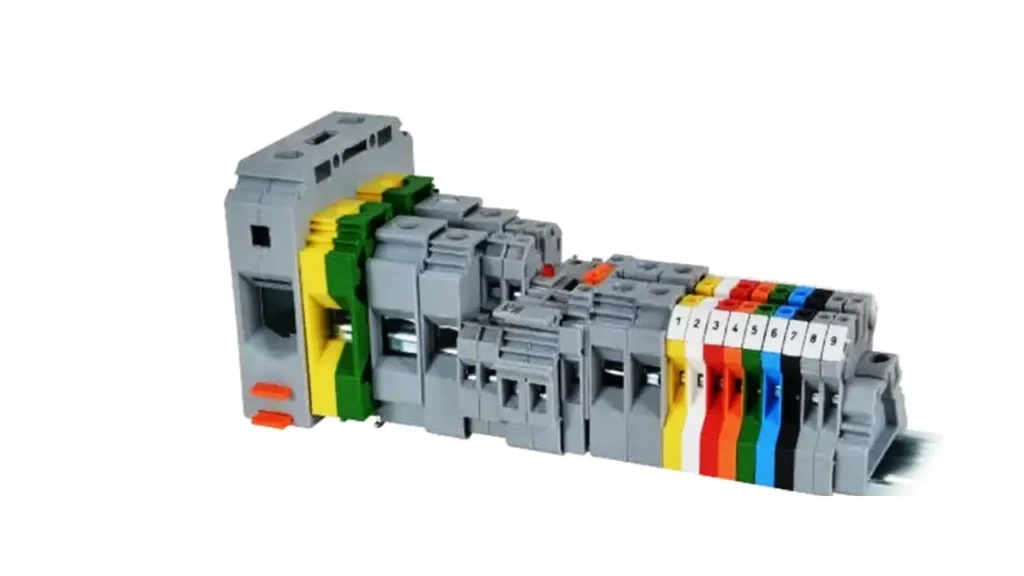

The Terminal Block Color Code is a crucial system that provides a visual guide for electrical wiring, enhancing safety, simplifying troubleshooting, and improving overall organization within electrical panels and systems. By assigning specific colors to different functions, it allows for quick identification of circuit types, reducing errors and streamlining maintenance processes.
Protective Earth (PE) – Green/Yellow
This color combination is universally recognized for protective earth connections. Its purpose is to provide a safe path for fault currents, protecting personnel from electric shock and preventing damage to equipment. This color ensures that grounding wires are immediately distinguishable.
Neutral (N) – Blue
The color blue typically signifies the neutral conductor. The neutral wire provides the return path for current in an AC circuit under normal operating conditions. Clear identification of the neutral line is critical for proper circuit operation and safe maintenance procedures.
Line/Phase Conductors (L1, L2, L3) – Brown, Black, Grey (IEC) / Black, Red, Blue (NEMA)
These colors are used for the live or phase conductors in a multi-phase system. Their specific assignment can vary between IEC and NEMA standards. Correctly identifying each phase is vital for balanced load distribution and ensuring proper motor rotation.
DC Power – Red (+), Blue/White/Black (-)
For DC power applications, red is commonly used for the positive (+) terminal, while blue, white, or black typically represents the negative (-) terminal. This clear distinction is essential for preventing polarity reversals that could damage sensitive electronic components.
Special Functions – Various Colors
Beyond the primary power and ground connections, various other colors can be used for specific functions. These might include orange for interlock circuits, purple for control signals, or yellow for auxiliary circuits. These custom assignments enhance clarity in complex systems.
Here is a table summarizing common terminal block color codes:
| Function | IEC Standard Color | NEMA Standard Color (Common) |
| Protective Earth (PE) | Green/Yellow | Green |
| Neutral (N) | Blue | White / Grey |
| Line 1 (L1) / Phase A | Brown | Black |
| Line 2 (L2) / Phase B | Black | Red |
| Line 3 (L3) / Phase C | Grey | Blue |
| DC Positive (+) | Red | Red |
| DC Negative (-) | Blue | Blue / White / Black |
| Interlock/Control | Orange | Orange / Yellow |
What is the Color Code for Terminal Connectors?

The color code for terminal connectors, often interchangeable with terminal blocks, is a standardized system that uses specific colors to denote the function or purpose of the electrical connection. This visual aid is crucial for safety, efficiency, and clarity in electrical installations, allowing for quick identification of wire types and their corresponding roles within a circuit.
Adhering to these codes, typically guided by international (IEC) or national (NEMA) standards, helps to prevent wiring errors, simplify maintenance, and ensure consistent practices across various projects.
- Green/Yellow (or Green): Universally indicates the protective earth (ground) connection, providing a safe path for fault currents.
- Blue (or White/Grey): Commonly used for the neutral conductor, which serves as the return path for current in AC circuits.
- Brown, Black, Grey (IEC) / Black, Red, Blue (NEMA): Designate live or phase conductors in multi-phase systems, with specific colors for each phase.
- Red (+), Blue/White/Black (-): Used for DC power connections, distinguishing positive from negative terminals.
- Various Other Colors (e.g., Orange, Yellow, Purple): Can be used for specialized functions like control signals, interlock circuits, or auxiliary power, often specified by local regulations or project requirements.
IEC Standard
The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards for terminal blocks are a set of globally recognized guidelines that ensure the safety, performance, and interchangeability of these critical electrical components.
These standards are widely adopted, particularly in Europe and many other parts of the world, contrasting with the NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) standards more commonly used in North America.
The most relevant IEC standard for terminal blocks is generally IEC 60947-7, which is subdivided into several parts addressing different types of terminal blocks:
- IEC 60947-7-1: This part specifies requirements for terminal blocks with screw-type or screwless-type clamping units primarily intended for industrial or similar use and1 for copper conductors. It covers general requirements for their electrical and mechanical connection.
- IEC 60947-7-2: Focuses specifically on protective conductor (PE) terminal blocks for copper conductors, outlining their safety requirements.
- IEC 60947-7-3: Addresses safety requirements for fuse terminal blocks.
- IEC 60947-7-4: Deals with PCB (Printed Circuit Board) terminal blocks for copper conductors.
- IEC/TS 60947-7-5: This is a technical specification (TS) that provides requirements for terminal blocks designed for aluminum conductors, or for connecting aluminum to copper conductors.
Adherence to these IEC standards ensures that terminal blocks meet rigorous criteria for voltage and current ratings, conductor sizes (often specified in square millimeters, mm²), mechanical strength, temperature rise, dielectric strength, and resistance to environmental factors. This standardization is crucial for international trade, promoting compatibility and safety across different electrical systems and applications worldwide.
NEMA Standard
The NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) standards are a set of widely recognized specifications and guidelines primarily used in North America for electrical products, including terminal blocks.
Unlike the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, which are globally adopted, NEMA standards are specific to the United States and Canada, though their influence extends to some other countries that follow North American electrical practices.
For terminal blocks, NEMA standards typically focus on aspects such as:
- Ratings: Defining voltage and current ratings, often expressed in volts and amperes.
- Wire Sizes: Specifying acceptable wire gauges, commonly using the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system.
- Construction: Dictating the physical characteristics, materials, and durability of the terminal blocks.
- Testing Procedures: Outlining the methods for testing terminal blocks to ensure they meet performance and safety criteria.
- Environmental Ratings: While NEMA is more famously known for its enclosure ratings (e.g., NEMA 4X for outdoor use), these environmental considerations also implicitly influence the design and material selection for terminal blocks used in such enclosures.
Key differences from IEC standards include the preferred units of measurement (inches and AWG vs. millimeters and mm²), testing methodologies, and some design philosophies. For example, NEMA standards often focus on broad product categories, while IEC standards can be more granular in their specifications for particular types of components.
Adherence to NEMA standards ensures that electrical components, including terminal blocks, are compatible with existing infrastructure and meet the safety and performance requirements prevalent in North American electrical systems. This is crucial for manufacturers, distributors, and installers operating within this market.
Conclusion
Understanding and correctly applying Terminal Block Color Code based on IEC and NEMA standards is paramount for safe and efficient electrical installations. Adhering to these established guidelines minimizes wiring errors, simplifies troubleshooting, and significantly enhances the overall safety of your electrical systems. It fosters clarity and consistency across different projects and regions.
By consistently employing the specified color codes for various functions—such as protective earth, neutral, and phases—engineers and technicians can quickly identify connections. This adherence not only streamlines installation and maintenance processes but also reduces the risk of accidents and equipment damage, leading to more reliable and robust electrical infrastructures.
For all your terminal block needs, ensuring compliance with both IEC and NEMA standards, you can get bulk terminal blocks from Linkwell Electrics. Their products are designed to meet international safety and performance specifications, providing you with reliable components essential for well-organized and secure electrical systems.