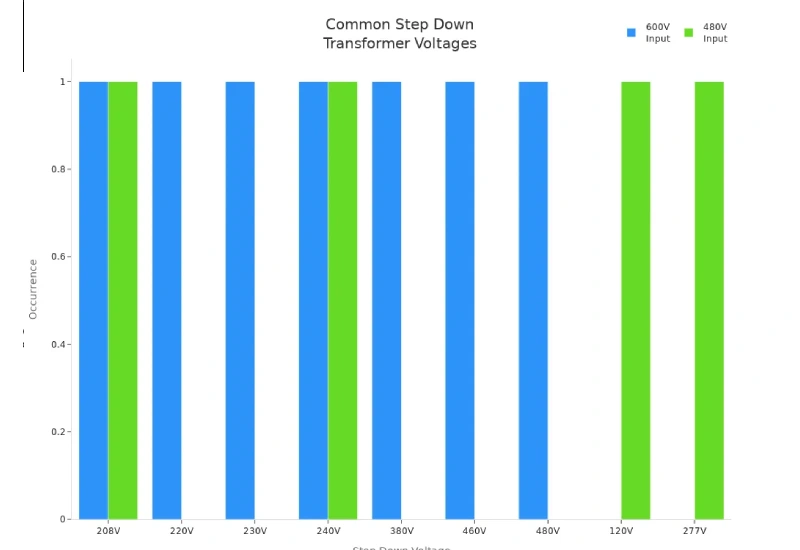
You might wonder, what is a step down transformer? It’s a device that takes high voltage electricity and makes it safer for your equipment by lowering it to a more usable level. If you’re working with control cabinets or low-voltage electrical panels, you’ll use a step down transformer—not the big ones you find in substations. Most industrial and commercial systems rely on this technology, with about 70% of applications using step down transformers. Here’s a quick look at typical voltage conversions:
| Input Voltage | Common Step Down Voltages | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 600V | 208V, 220V, 230V, 240V, 380V, 460V, 480V | Industrial equipment, hydrogen production |
| 480V | 240V, 208V, 120V, 277V | Control systems, auxiliary equipment |
You’ll find Linkwell’s step down transformer working reliably in these settings, helping you power your equipment safely and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- A step down transformer lowers high voltage electricity to safer, usable levels for equipment in control cabinets and industrial panels.
- It works by electromagnetic induction, using coils with different turns to reduce voltage and increase current safely.
- Key parts include copper windings and a laminated steel core, which improve efficiency and durability while reducing energy loss.
- Step down transformers protect equipment by stabilizing voltage, preventing damage, and supporting safe operation in low-voltage settings.
- They save energy and reduce costs by minimizing power loss, making them essential for reliable and efficient industrial and commercial power systems.
What Is a Step Down Transformer

Basic Function
When you ask, “what is a step down transformer,” you’re really asking how you can safely use high-voltage electricity in your everyday equipment. A step down transformer takes electricity at a high voltage and lowers it to a level that your devices can handle. You’ll see this technology everywhere in control cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels—places where you need a low voltage output to keep things running smoothly.
Here’s what a step-down transformer does for you:
- It reduces high transmission voltages, like 480V or 220V, down to safer levels such as 110V or 24V.
- It protects your electrical equipment from damage by regulating voltage and preventing overloads.
- It provides electrical isolation between input and output, which boosts safety for sensitive devices.
- It keeps your power supply stable, so you don’t have to worry about surges or fluctuations.
- It helps minimize energy loss, making your system more efficient.
You won’t find these transformers in substations. Instead, you’ll use them in low-voltage electrical cabinets and panels, where safe and reliable power is essential for your operations.
Tip: If you work with industrial control cabinets or telecom systems, a step down transformer is your go-to solution for converting high voltage to a usable level.
Step Down Transformer Definition Key Features
You might wonder what sets a step-down transformer apart from other types. Let’s break down the main features that make it unique:
| Feature | Step-Down Transformer Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Voltage Conversion | Converts higher primary voltage to lower secondary voltage |
| Winding Configuration | Primary winding has more turns than secondary winding |
| Current Characteristics | Secondary winding carries higher current than primary winding |
| Applications | Used in electrical distribution, control cabinets, telecom racks, and low-voltage panels |
| Contrast with Others | Unlike step-up transformers (which increase voltage) and isolation transformers (which maintain voltage for safety) |
- You get a transformer with a primary coil that has more turns than the secondary coil. This design gives you a lower voltage output, perfect for your equipment.
- The secondary winding delivers more current, which is ideal for powering devices in your electrical cabinet.
- Step-down transformers are built for low-voltage applications, not for boosting voltage like step-up transformers or just isolating circuits like isolation transformers.
- You’ll find them in places like control panels, telecom racks, and industrial machinery—never in substations.
If you need a reliable way to convert high voltage to a safe, usable level for your equipment, a step down transformer is the answer. It’s designed for efficiency, safety, and durability in low-voltage environments.
What Does a Step Down Transformer Do
A step down transformer reduces high input voltage to a lower, safer output voltage. It protects equipment, ensures stable performance, and is widely used in industrial, commercial, and electronic applications requiring safe, efficient power conversion.
Working Principle
Basic Principle
You might wonder how a step down transformer actually works inside your control cabinet or telecom rack. The basic principle behind transformer operation is electromagnetic induction. When you connect the primary winding to an alternating current (AC) source, the current flows through the coil and creates a changing magnetic field in the magnetic core. This magnetic field passes through the secondary winding, which sits right next to the primary. The changing magnetic flux induces a voltage in the secondary coil. This process is called mutual induction.
Let’s break down the basic principle in a way that’s easy to follow:
- The primary winding receives the primary voltage from your power source.
- The magnetic core channels the changing magnetic field between the windings.
- The secondary winding picks up the induced voltage, which is lower than the input.
Here’s a quick table to show you the scientific concepts at play:
| Principle/Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | AC in the primary coil creates a varying magnetic flux in the magnetic core. |
| Mutual Induction | The magnetic flux induces a voltage in the secondary coil proportional to the turns ratio of the coils. |
| Turns Ratio | Voltage ratio between primary and secondary coils is proportional to the ratio of their number of turns. |
| Step-Down Transformer Feature | Secondary coil has fewer turns than primary, resulting in lower voltage and higher current on the secondary. |
| Governing Equation | V1/V2 = N1/N2 = I2/I1, relating voltage (V), turns (N), and current (I) between primary and secondary coils. |
| AC Requirement | Transformer operation requires AC to produce changing magnetic flux necessary for induction. |
You’ll see this basic principle in action every time you power up your low-voltage electrical cabinet. The step down transformer working principle keeps your equipment safe by lowering the voltage to a usable level.
Note: Step down transformers like Linkwell’s are designed for low-voltage applications in control cabinets and telecom racks, not for use in substations.
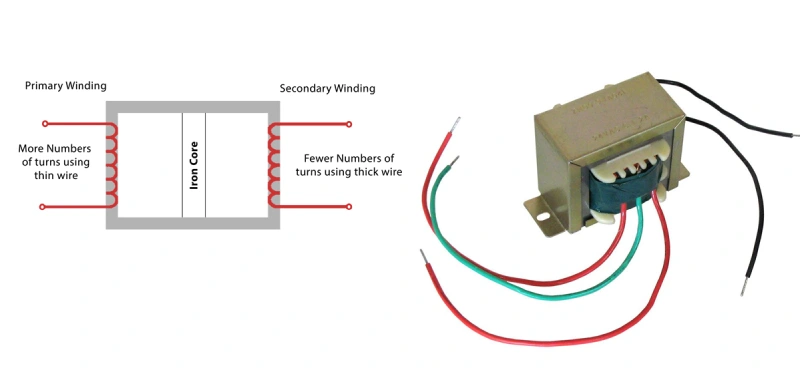
Step Down Transformer Diagram
Voltage and Current
Let’s talk about voltage transformation and output voltage calculation. The step-down transformer formula is simple but powerful. The voltage you get out of the secondary winding depends on the ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils. If you want to calculate the output voltage, just use this formula:
Vs / Vp = Ns / Np
Where:
- Vs = secondary voltage
- Vp = primary voltage
- Ns = number of turns in the secondary winding
- Np = number of turns in the primary winding
Here’s how it works:
- The primary winding gets the primary voltage from your AC supply.
- The secondary winding has fewer turns, so the secondary voltage is lower.
- The current in the secondary winding increases to balance the power.
You can see the relationship in action:
- If the primary winding has 480 turns and the secondary has 240, the secondary voltage will be half the primary voltage.
- The transformer operation keeps the power nearly constant (ignoring small losses), so when voltage drops, current rises.
Tip: If you need to step down from 480V to 240V in your control panel, just make sure the secondary winding has half as many turns as the primary.
Linkwell’s step down transformer uses heat-resistant copper windings and a high-quality magnetic core. These materials help reduce energy loss and keep your transformer working efficiently. Copper’s low resistance means less heat and better performance, while the magnetic core minimizes losses from eddy currents and hysteresis. You get a reliable transformer that stays cool and lasts longer, even in demanding industrial environments.
- Heat-resistant copper windings lower energy waste and extend service life.
- Laminated magnetic cores cut down on constant losses, boosting efficiency.
- Linkwell transformers are built for low-voltage electrical cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels—never for substations.
When you use a step down transformer in your electrical cabinet, you’re relying on a proven working principle that keeps your equipment safe and your energy bills low.
Step Down Transformer Main Components
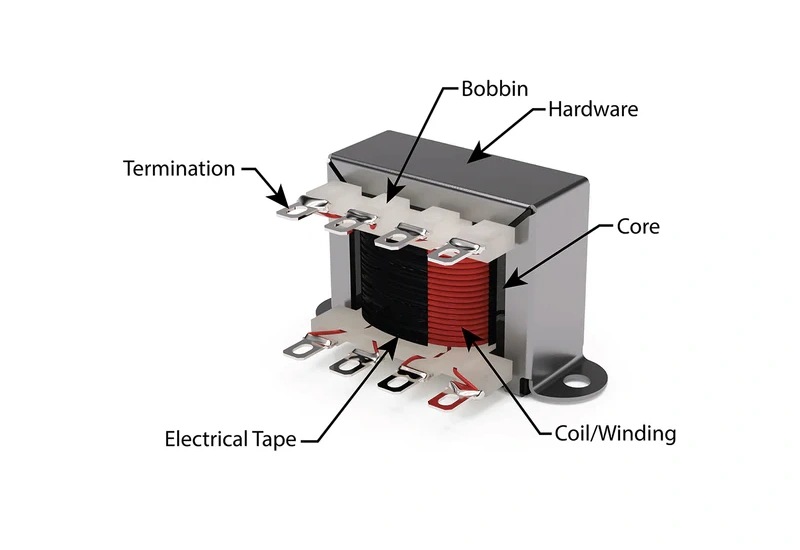
Windings and Core
When you look inside a step down transformer, you’ll find two main parts: the windings and the core. These parts work together to safely lower high voltage for your low-voltage electrical cabinets and control panels.
Here’s a quick overview:
| Component | Description and Function |
|---|---|
| Core | Made of ferromagnetic material (iron) to provide a low-loss path for magnetic flux. It minimizes eddy currents and improves transformer efficiency by allowing smooth magnetic flux flow. |
| Windings | Consist of copper wire coils. The primary winding is connected to the AC power source, has thicker wire and more turns, while the secondary winding is connected to the load, has thinner wire and fewer turns to produce a lower voltage. The windings enable the transformer to step down voltage through mutual induction. |
The core in a step-down transformer uses laminated silicon steel sheets. These thin layers, coated with insulation, help cut down on energy loss from eddy currents. Sometimes, manufacturers use grain-oriented electrical steel to make the core even more efficient. For the windings, copper is the top choice because it carries electricity well and keeps the transformer compact. You might see aluminum windings in some cases, especially if weight or cost matters more.
Tip: Copper windings and a laminated steel core help your step down transformer run cooler and last longer in busy industrial cabinets.
Construction
The way a step-down transformer is built makes a big difference in how well it works and how long it lasts. You want a transformer that matches your power needs—usually rated two to three times higher than your actual load. This helps prevent overload and keeps your equipment safe.
Manufacturers stack thin sheets of iron or silicon steel to form the core. This design reduces wasted energy and boosts efficiency. The windings wrap tightly around the core, with the primary winding taking in high voltage and the secondary winding sending out a lower voltage. The number of turns in each winding sets the voltage ratio, so you always get the right output for your devices.
If you use a step down transformer in your control cabinet or telecom rack, you get stable voltage and reliable protection for your sensitive equipment. The transformer also acts as a filter, smoothing out voltage spikes and helping your system run smoothly. Choosing the right materials and making sure the transformer is properly rated means you’ll enjoy a longer service life and fewer headaches with your electrical setup.
- Laminated silicon steel core = less energy loss
- Copper windings = better conductivity and durability
- Proper rating = stable operation and longer lifespan
You won’t find these step-down transformers in substations. They’re made for low-voltage environments like electrical cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels—right where you need safe, efficient power.
Types and Applications
Step-Down Transformer Types
You’ll find several types of step down transformer in the field, each designed for specific needs. Some handle single-phase power, while others work with three-phase systems. You might use a dry-type step-down transformer in your control cabinet because it’s safe and easy to maintain. Oil-filled models suit outdoor or heavy-duty environments. If you need to fit a transformer into a tight space, compact designs are available.
Linkwell offers step down transformer options that match your voltage, frequency, and power requirements. You can request custom units for special applications, like telecom racks or industrial panels. Every transformer comes with ISO 9001 and CE certifications, so you know you’re getting reliable quality and safety. You can choose from models that convert 480V to 240V, 220V to 110V, or even 277V to 120V. This flexibility helps you power your equipment without worrying about compatibility.
Ac Step Down Transformer
We manufacture AC step down transformers designed to convert higher input voltage to a lower, safe output voltage suitable for various industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Our transformers ensure stable, reliable power supply, protecting sensitive equipment from voltage fluctuations and overloads. Built with high-quality materials, they offer long-lasting durability and excellent thermal performance. Easy to integrate with control panels, machinery, and lighting systems, these transformers deliver efficient energy conversion, enhanced safety, and consistent operational reliability in demanding environments.
Tip: If you need a step-down transformer for a unique project, Linkwell can customize the design to fit your cabinet or rack perfectly.
Industrial Uses
Step down transformer plays a huge role in low voltage environments. You’ll see them in control cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels. These transformers help you run machinery, lighting, and sensitive electronics safely. They also support power transmission by lowering voltage for final delivery to your equipment.
Here are some common applications:
- Electrical distribution: Reduces high voltage from power lines for commercial, industrial, and residential use.
- Industrial machinery: Matches voltage to your machines for safe operation.
- Electronics manufacturing: Powers devices by minimizing voltage.
- Power supplies: Delivers stable voltage for telecom, medical, and automotive electronics.
- Lighting systems: Lowers voltage for LED and fluorescent fixtures.
- HVAC systems: Powers control circuits and motors.
- Renewable energy: Converts high voltage from solar or wind plants for grid connection.
| Industrial Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Centers | Reduces high-voltage utility power for servers and infrastructure. |
| Water Treatment Plants | Powers pumps, motors, and control systems. |
| Oil and Gas Industry | Supplies voltage for pumps and compressors in refineries and pipelines. |
| Railway Systems | Controls voltage from overhead lines for trains and signals. |
You can rely on Linkwell’s step down transformer to keep your equipment safe and efficient. Every unit meets strict quality standards, so you get peace of mind with every installation.
Advantages
Equipment Protection
When you use a step down transformer in your electrical cabinet, you give your equipment the protection it needs. High voltage can damage sensitive devices and create safety risks. The step-down transformer lowers the voltage to a safe level, so your machines and control panels run smoothly. You avoid electrical stress, which means less wear and tear and fewer repairs.
Here’s how a step down transformer helps protect your equipment:
- It keeps voltage stable, preventing sudden spikes that could harm your devices.
- It limits fault currents, isolating problems before they reach your equipment.
- It reduces electrical noise, which is important for telecom racks and control cabinets.
- It supports safe maintenance and troubleshooting by complying with safety standards.
You get a longer lifespan for your machinery. Most step down transformers last 20 to 30 years in industrial use, especially when you follow good maintenance practices. Regular inspections, cleaning, and load management help your transformer work reliably in harsh environments. You spend less on repairs and replacements, and your operations stay safe.
Tip: Using a step down transformer in low-voltage electrical cabinets means you protect your investment and keep your workplace safer.
Energy Efficiency
A step down transformer does more than just protect your equipment. It also helps you save energy and lower costs. When you reduce voltage for your control panels or telecom racks, you cut down on energy loss during transmission. Electricity travels at high voltage to minimize loss, but you need lower voltage at the point of use. The step-down transformer makes this possible.
Check out these energy efficiency benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Energy Loss | Lower voltage at the destination means less wasted energy in your system. |
| Cost Savings | Efficient operation leads to lower electricity bills and operating costs. |
| High Efficiency | Modern step down transformers have minimal losses, so most input power reaches your equipment. |
| Less Heat Generation | Lower voltage means less heat, reducing cooling needs and improving safety. |
You get reliable power for your low-voltage electrical cabinets without wasting energy. The transformer’s compact design fits easily into tight spaces, making it perfect for industrial panels and telecom racks. You enjoy stable voltage, high-quality output, and long-term savings.
Note: Step down transformers are built for low-voltage environments, not for substations. You get the best results when you use them in control cabinets and similar settings.
Step Down vs Step Up Transformer
Key Differences
You might wonder how a step down transformer compares to a step-up transformer. Both devices change voltage, but they do it in opposite ways. If you work with low-voltage electrical cabinets or control panels, you’ll usually use a step-down transformer. Step-up transformers are more common in power plants or for long-distance transmission, not in your daily industrial or commercial setups.
Here’s a quick table to help you spot the differences:
| Aspect | Step-Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Output | Increases voltage from primary to secondary coil | Decreases voltage from primary to secondary coil |
| Coil Turns | Secondary coil has more turns than primary coil | Secondary coil has fewer turns than primary coil |
| Application | Used for long-distance power transmission | Used to reduce high voltage for safe, low-voltage use |
| Design Consideration | Primary coil fewer turns; secondary coil more turns | Primary coil more turns; secondary coil fewer turns |
| Current-Voltage Relation | Voltage increases, current decreases | Voltage decreases, current increases |
| Advantages | Reduces energy loss over distance | Safer voltage for equipment; simple design |
You’ll see that a step-down transformer is perfect for lowering voltage to safe levels in control cabinets, telecom racks, and industrial panels. You won’t find these in substations or for boosting voltage across cities.
Tip: Always choose the right transformer for your application. For low-voltage electrical cabinets, a step down transformer is the best fit.
Reverse Use
You might ask if you can use a step down transformer in reverse, turning it into a step-up transformer. Technically, you can. Transformers work both ways. If you supply AC power to the secondary winding and take output from the primary, you’ll increase the voltage instead of lowering it.
But before you try this, keep these important points in mind:
- The voltage and current ratings must match the original design. Using the wrong voltage can cause overheating or insulation failure.
- The transformer’s frequency should stay the same (like 50 Hz or 60 Hz).
- The power rating (kVA) does not change, but efficiency may drop a little when used in reverse.
- You lose voltage tap adjustments, which can make voltage control harder.
- Inrush current can spike up to 16 times higher, possibly tripping breakers.
- Some wiring setups, like delta-wye, may lose their neutral connection, causing grounding issues.
- Most manufacturers recommend reverse use only for smaller transformers (75 kVA or less).
Note: For most low-voltage electrical cabinet applications, it’s safer and easier to use a purpose-built step-up transformer if you need to increase voltage. Reverse use can work, but only if you follow all safety guidelines and understand the risks.
If you stick to the right transformer for your job, you’ll keep your equipment safe and your system running smoothly.
You can see how important a step down transformer is for safe, efficient power in low-voltage electrical cabinets and control panels. The global market reached $18.5 billion in 2023, showing strong demand across many industries. Linkwell stands out as a trusted supplier, earning top ratings for quality and on-time delivery. When you choose Linkwell, you get reliable support, advanced technology, and products built for your needs—now and in the future.
FAQ
What is a step down transformer used for in electrical cabinets?
You use a step down transformer to lower the primary voltage to a safer, low voltage output. This helps protect sensitive equipment in control cabinets and ensures reliable transformer operation in industrial and commercial settings, not in substations.
How does the step down transformer working principle keep my devices safe?
The basic principle relies on electromagnetic induction. The transformer operation reduces high primary voltage to a lower secondary voltage. This voltage transformation prevents overloads and keeps your equipment running smoothly in low-voltage environments.
Can I calculate the output voltage of my step-down transformer?
Yes! Use the step down transformer formula:
secondary voltage / primary voltage = number of secondary turns / number of primary turns
This output voltage calculation helps you match the transformer to your equipment’s needs.
Where should I install a step down transformer?
Install your step down transformer inside low-voltage electrical cabinets, telecom racks, or industrial panels. Avoid using it in substations. These transformers work best for power transmission and voltage transformation close to your equipment.
What types of applications need a step-down transformer?
You’ll find step-down transformers in control cabinets, telecom racks, lighting systems, and industrial panels. They support power transmission by providing the right low voltage output for your devices, making them essential for safe and efficient working in many industries.
Price of Step Down Transformer
The price of a Step Down Transformer depends on several factors such as power rating, voltage capacity, customization needs, and certification standards. Smaller models for basic control cabinets may cost less, while industrial-grade transformers for telecom signal cabinets or base stations are higher priced. As a direct manufacturer, we at Linkwellelectrics provide competitive pricing, bulk discounts, and custom design options.
For accurate pricing, we recommend contacting us with your exact voltage requirements, load capacity, and application details. This ensures you receive the right transformer at the best value for your business.
Industrial Control Transformer and Step Down Transformer
An Industrial Control Transformer supplies stable low voltage for control circuits, while a Step Down Transformer reduces high voltage for safe equipment use. Both ensure reliable power distribution in control cabinets, telecom shelters, and industrial systems, supporting efficiency, safety, and smooth operation in demanding electrical environments.
Conclusion
What is a Step Down Transformer is essential for anyone dealing with electrical systems. It ensures safe voltage conversion, equipment protection, and energy efficiency. At Linkwellelectrics, we manufacture reliable, customizable solutions tailored for industrial buyers, wholesalers, and large projects.
Choosing the right transformer supports long-term performance, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures compliance with safety standards. Partner with us to receive expert guidance, quality products, and on-time delivery, making your business more competitive in today’s demanding electrical market.




