In today’s interconnected world, the performance and longevity of electronic equipment are paramount. Overheating, humidity, and dust can severely impact sensitive components housed within electrical cabinets, leading to costly downtime and failures. This is where cabinet air conditioners become indispensable.
This ultimate guide will delve into the world of cabinet air conditioners, explaining their vital role in thermal management. We’ll explore how these specialized cooling systems work, their various types, and the key features that ensure optimal protection and extended lifespan for your critical electronics.
What is a Cabinet Air Conditioner?
A cabinet air conditioner, also known as an enclosure or control cabinet air conditioner, is a specialized cooling system designed to regulate the temperature and humidity within enclosed electrical and electronic cabinets.
Unlike typical room air conditioners, these units operate on a closed-loop system, meaning they cool and recirculate the air inside the cabinet without introducing external air. This is crucial for protecting sensitive components from overheating, dust, moisture, and other contaminants that could lead to malfunctions, reduced lifespan, and costly downtime.
They are essential for maintaining optimal operating conditions for a wide range of critical equipment in various industrial, commercial, and telecommunications applications.
Types of Cabinet Air Conditioners
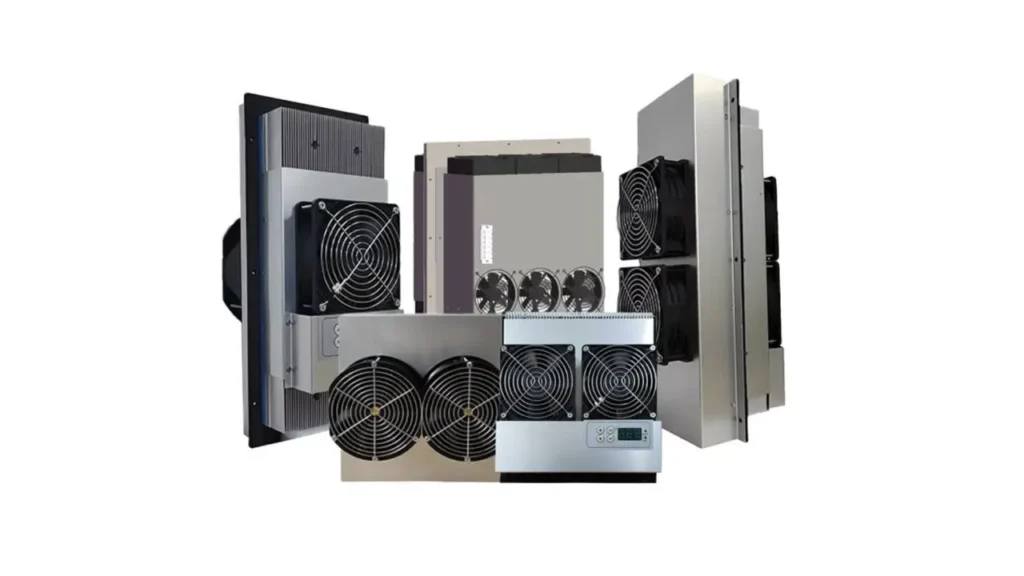

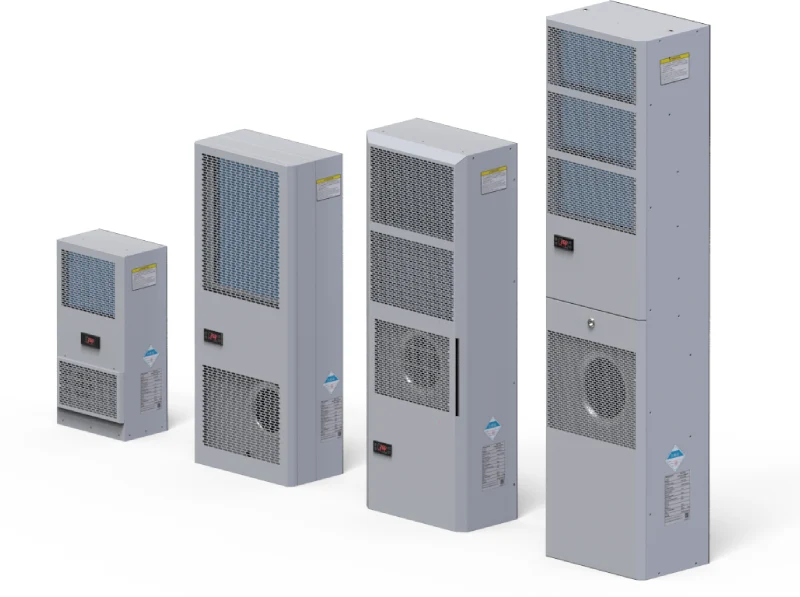
Understanding the various types of cabinet air conditioners is crucial for selecting the most appropriate thermal management solution for your specific needs. Each type offers distinct advantages depending on the application, space constraints, and cooling requirements.
Self-Contained Cabinet Air Conditioners
Self-contained cabinet air conditioners, also known as monoblock units, are all-in-one solutions where the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and fan are integrated into a single, compact enclosure. Their primary advantage lies in their ease of installation, as they typically only require mounting to the cabinet and connecting to power.
This makes them ideal for individual cabinets, smaller enclosures, or situations where simplicity and rapid deployment are priorities. They are often used in light industrial settings, IT closets, or for standalone equipment where a dedicated cooling system is needed without complex installation.
Split System Cabinet Air Conditioners
Split system cabinet air conditioners function much like residential split AC units, separating the heat exchange process into two distinct units. The evaporator unit is installed inside the electrical cabinet, actively cooling the internal air, while the condenser unit, responsible for dissipating heat, is located externally.
This separation offers significant flexibility, particularly for larger enclosures or in environments where internal cabinet space is limited. It allows for the heavier and noisier condenser unit to be placed remotely, potentially in a less sensitive area, and can be more efficient for higher heat loads by allowing for a larger external heat rejection surface.
Thermoelectric Cabinet Air Conditioners
Thermoelectric cabinet air conditioners, often referred to as Peltier coolers, operate based on the Peltier effect, a phenomenon where a temperature difference is created across a junction of two dissimilar materials when an electric current flows through it.
These units are unique because they do not use refrigerants or compressors, resulting in a virtually maintenance-free operation with no moving parts (apart from fans). This makes them exceptionally reliable and suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control, operation in harsh environments, or in situations where vibration, noise, or the presence of refrigerants are concerns. They are particularly well-suited for smaller cabinets, telecommunications equipment, and medical devices.
Cabinet Air Conditioner Uses

Cabinet air conditioners are versatile thermal management solutions employed across various industries to protect sensitive electronics. Their closed-loop design makes them ideal for environments where maintaining a clean, controlled atmosphere is critical.
Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, cabinet air conditioners are crucial for protecting PLCs, VFDs, and other control components from heat and dust. This ensures continuous operation of machinery and prevents costly production downtime in factories and manufacturing plants.
Telecommunications
Telecommunication cabinets, often located outdoors, house critical networking equipment. Cabinet air conditioners maintain stable temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring uninterrupted network connectivity, vital for data transmission and communication services.
Data Centers
While data centers have overall cooling systems, individual server racks and network cabinets can develop hot spots. Cabinet air conditioners provide targeted cooling, supplementing the main system to protect high-density equipment and optimize performance.
Outdoor Applications
For outdoor enclosures exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, and contaminants, ruggedized cabinet air conditioners are essential. They safeguard traffic control systems, remote monitoring stations, and other outdoor electronic infrastructure from environmental damage.
How to Use Cabinet Air Conditioners
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are key to maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of your cabinet air conditioner, ensuring optimal protection for your valuable electronics. Following these steps will help you effectively utilize your cooling system.
Step 1: Proper Sizing and Selection
Before installation, accurately calculate the heat load generated by the components within your cabinet. An undersized unit won’t cool effectively, while an oversized one wastes energy. Consider the cabinet’s size, ambient temperature, and NEMA rating to select the appropriate air conditioner capacity and environmental protection.
Step 2: Strategic Mounting and Sealing
Mount the cabinet air conditioner in a location that ensures even air distribution within the enclosure and unimpeded external airflow. Crucially, ensure the cabinet is tightly sealed to prevent outside air, dust, and moisture from entering, maintaining the integrity of the closed-loop cooling system.
Step 3: Electrical Connection and Initial Startup
Connect the air conditioner to a dedicated, well-grounded power supply, ensuring the voltage and current match the unit’s specifications. After powering on, allow the unit to run for a short period (e.g., 5-10 minutes) to confirm the fans and compressor are operating without abnormal noise or vibration.
Step 4: Temperature Setting and Monitoring
Set the thermostat to the desired internal cabinet temperature, typically within the safe operating range for your electronics (e.g., 20°C to 45°C). Regularly monitor the temperature inside the cabinet, using a thermometer or integrated sensors, to ensure the air conditioner is maintaining optimal conditions.
Step 5: Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance is vital for efficiency. Periodically inspect the unit for wear, clean or replace air filters to prevent clogging and maintain airflow, and check condensate drainage. Consistent upkeep extends the unit’s lifespan and prevents unexpected failures.
Cabinet Air Conditioner Maintenance
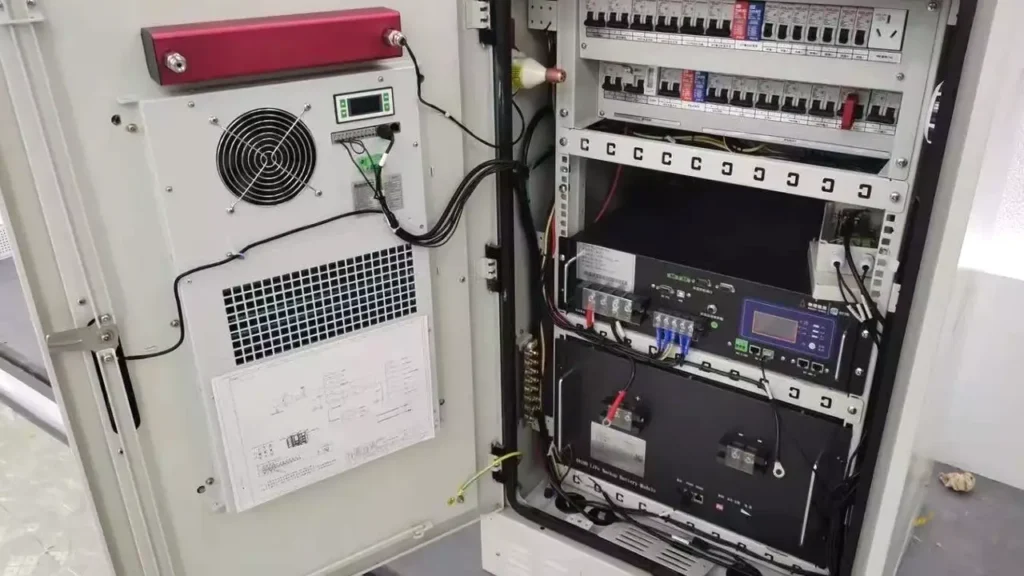

Proper maintenance is paramount for ensuring the longevity and efficient operation of your cabinet air conditioner. Neglecting routine care can lead to reduced cooling performance, increased energy consumption, and premature equipment failure, ultimately jeopardizing the sensitive electronics it protects. A proactive approach to maintenance will save time and money in the long run.
Regularly scheduled maintenance helps to prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. By consistently performing these checks and cleanings, you ensure the air conditioner continues to provide optimal thermal management, safeguarding your critical equipment from the detrimental effects of excessive heat and contaminants.
- Filter Cleaning/Replacement:Regularly inspect and clean or replace the air filters. Clogged filters restrict airflow, reducing cooling efficiency and increasing energy consumption. This simple step is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing overheating of the internal components.
- Condensate Drain Inspection:Check the condensate drain line for blockages and ensure proper drainage. A blocked drain can lead to water accumulation inside the cabinet, potentially damaging electronic components and fostering mold growth, which can harm both equipment and air quality.
- Fan Inspection and Cleaning:Examine the evaporator and condenser fans for any obstructions, dust buildup, or signs of wear. Clean the fan blades to ensure unrestricted airflow and check for smooth operation to prevent motor strain and maintain efficient heat exchange.
- Heat Exchanger Coil Cleaning:Periodically clean the evaporator and condenser coils. Dust and debris on the coils act as insulators, hindering heat transfer. Keeping them clean ensures maximum cooling capacity and energy efficiency, vital for the air conditioner’s performance.
- Electrical Connection Check:Inspect all electrical connections for tightness, signs of corrosion, or wear. Loose or corroded connections can lead to intermittent operation, electrical faults, or even fire hazards, ensuring the unit’s safe and reliable power supply.
Conclusion
Effectively managing the internal environment of electrical cabinets is not just about convenience; it’s critical for the performance, reliability, and lifespan of valuable electronic components. Cabinet air conditioners offer a robust solution, mitigating the risks posed by heat, humidity, and airborne contaminants.
By understanding the different types, proper sizing, and maintenance requirements, you can ensure your critical equipment operates within optimal conditions, preventing costly malfunctions and maximizing uptime. Investing in the right thermal management strategy pays dividends in the long run.
For reliable, high-quality cabinet air conditioners, consider exploring the wholesale options available from Linkwell Electrics. They offer a range of solutions to meet diverse industrial and commercial needs.