Untangling a messy web of cables can be a frustrating and even hazardous experience. Whether in your home, office, or an industrial setting, disorganized wiring can lead to tripping hazards, equipment damage, and a generally unprofessional appearance. But what if there was a simple, effective solution?
Enter cable trunking. Often overlooked, this ingenious system is a cornerstone of efficient and safe cable management. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about cable trunking, from its fundamental purpose to its diverse applications and the many benefits it offers.
What is Cable Trunking?
Recommended Cable Trunking
Cable trunking is an enclosed system, typically rectangular, used to protect and organize electrical cables. It provides a neat and safe pathway for wiring in homes, offices, and industrial settings, preventing damage and improving overall aesthetics.
What is Cable Trunking Made of?
Cable trunking is manufactured from a variety of materials, primarily chosen based on the intended application, required durability, environmental conditions, and budget. The most common materials offer distinct advantages, from corrosion resistance to fire safety and ease of installation.
Common materials for cable trunking include:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): This is a very popular choice due to its lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. PVC trunking offers good electrical insulation, is resistant to corrosion, moisture, and most chemicals, and is often flame-retardant. It’s commonly used in residential and light commercial settings, and can be easily cut and adapted.
Metal (Galvanized Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel): Metal trunking provides superior strength, durability, and protection against physical damage and electromagnetic interference (EMI/RFI shielding).
- Galvanized Steel: Often hot-dip galvanized or pre-galvanized to provide excellent resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications, including industrial and harsh environments.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel but still offers good protection and is naturally corrosion-resistant. It’s often chosen where weight is a concern or a sleek, modern aesthetic is desired.
- Stainless Steel: Provides the highest level of corrosion resistance and is ideal for hygienic environments (e.g., food processing, medical facilities) or highly corrosive industrial settings.
Halogen-Free Materials (LSZH or LSF): These materials are crucial in environments where smoke and toxic fumes pose a significant safety hazard in the event of a fire, such as data centers, hospitals, and public transport systems. They produce low smoke and zero or low toxic fumes when burned.
Fiberglass (GRP – Glass Reinforced Plastic): GRP trunking is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and electrical non-conductivity. It’s often used in harsh, chemically aggressive, or outdoor environments where metal may corrode.
What is Cable Trunking Used for?
Cable trunking is an essential component of electrical installations, serving as an enclosed pathway to organize, protect, and route electrical cables and wires. It is widely used across residential, commercial, and industrial settings to ensure safety, improve aesthetics, and facilitate maintenance.
Key uses and benefits of the cable trunking include:
- Cable Protection: Shields cables from physical damage, dust, moisture, and environmental factors, extending their lifespan and reducing the risk of electrical faults or hazards like short circuits and fires.
- Organization and Aesthetics: Keeps cables neatly contained and out of sight, preventing tangling and clutter, which creates a cleaner, more professional, and visually appealing environment.
- Safety Enhancement: By enclosing cables, it minimizes tripping hazards and prevents accidental contact with live wires, thereby enhancing the safety of personnel and occupants.
- Ease of Maintenance and Accessibility: Many trunking systems feature removable or hinged covers, allowing for quick and easy access to cables for inspections, repairs, modifications, or upgrades, thus minimizing downtime.
- Versatility and Scalability: Available in various materials (PVC, metal), sizes, and configurations, cable trunking can accommodate different cable capacities and adapt to evolving wiring needs, making it suitable for diverse applications and future expansions.
Cable Trunking Benefits
Cable trunking offers a multitude of benefits for managing electrical installations, significantly improving safety, organization, and overall aesthetics. Its design provides a protected and systematic way to route cables, ensuring long-term reliability and simplifying future modifications.
Here are the key benefits of the cable trunking:
- Enhanced Safety: By enclosing cables, trunking prevents accidental contact with live wires, reduces tripping hazards from loose cables, and protects against physical damage, minimizing the risk of electrical faults or fires.
- Improved Organization and Aesthetics: Cable trunking keeps wires neatly bundled and out of sight, transforming cluttered spaces into clean, professional-looking environments. This organized approach simplifies cable identification and maintenance.
- Cable Protection and Longevity: The enclosed structure shields cables from dust, moisture, chemicals, and physical impact, extending their lifespan and reducing the need for premature replacement due to wear and tear.
- Ease of Maintenance and Accessibility: Many trunking systems feature removable covers, allowing quick and easy access to cables for inspections, repairs, modifications, or upgrades without significant disruption or complex dismantling.
- Versatility and Scalability: Available in various materials, sizes, and configurations, cable trunking can accommodate different cable capacities and adapt to evolving wiring needs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and future expansions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While there’s an initial investment, the long-term benefits of reduced cable damage, simpler maintenance, and quicker modifications often lead to overall cost savings over the lifespan of the electrical system.
Types of Cable Trunking
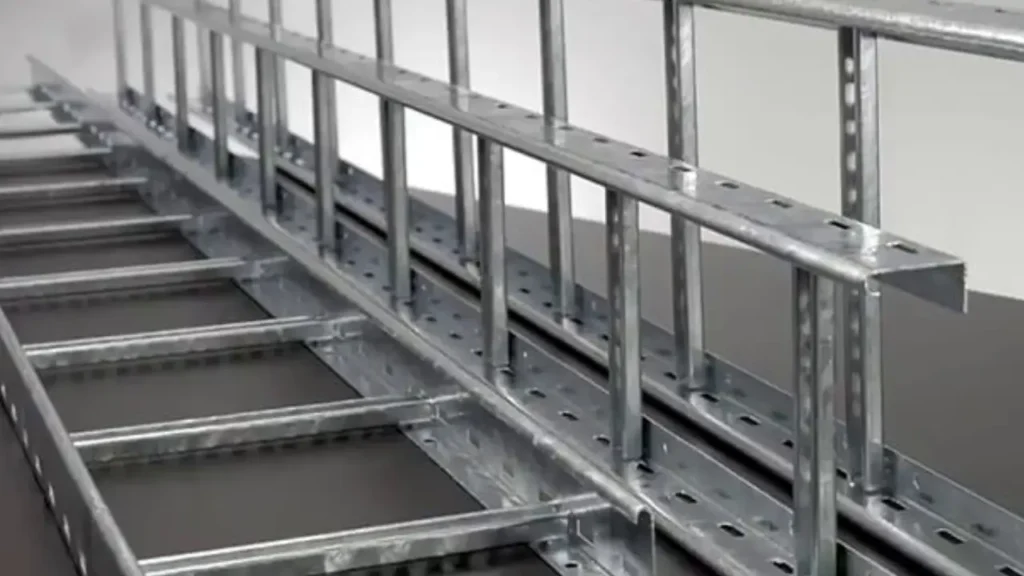

Cable trunking comes in various designs, each tailored for specific installation needs and environmental conditions.
UPVC Cable Trunking
UPVC (unplasticized polyvinyl chloride) cable trunking is a lightweight and cost-effective solution commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. It is highly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and general wear and tear, making it a durable choice for indoor applications. Its non-conductive properties provide excellent electrical insulation, enhancing safety, and its smooth finish allows for easy cleaning and a neat appearance.
Metal Cable Trunking
Metal cable trunking, typically made from galvanized steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, offers superior mechanical protection and durability, making it ideal for industrial environments or areas requiring robust cable management. It provides excellent shielding against electromagnetic interference and can withstand harsh conditions, including high temperatures and physical impact. Metal trunking systems often include various fittings like bends, tees, and reducers to facilitate complex cable routes.
Flexible Cable Trunking
Flexible cable trunking, often resembling corrugated conduits, is designed for applications where rigid trunking is impractical or impossible due to tight spaces, curves, or movement. It is commonly made from PVC, nylon, or sometimes metal, offering good protection while allowing for considerable bending and twisting. This type is particularly useful for connecting moving parts of machinery or in installations where future reconfigurations are anticipated.
Floor Cable Trunking
Floor cable trunking is specifically designed to safely route cables across floors in offices, retail spaces, or public areas, preventing tripping hazards. It typically features a low-profile, durable design, often made from heavy-duty PVC or rubber, that can withstand foot traffic and light vehicle loads. Some designs include multiple compartments to separate power, data, and communication cables, and they often come with anti-slip surfaces for added safety.
Lighting Cable Trunking
Lighting cable trunking, also known as dado trunking or skirting trunking, is integrated into the architectural design, often appearing as a decorative strip along walls at skirting board or dado rail height. It is primarily used for routing electrical cables for lighting, power outlets, and data networks in commercial and domestic settings. This type of trunking effectively conceals wiring while maintaining a clean aesthetic and allowing for easy access for maintenance or future modifications.
How to Install Cable Trunking?
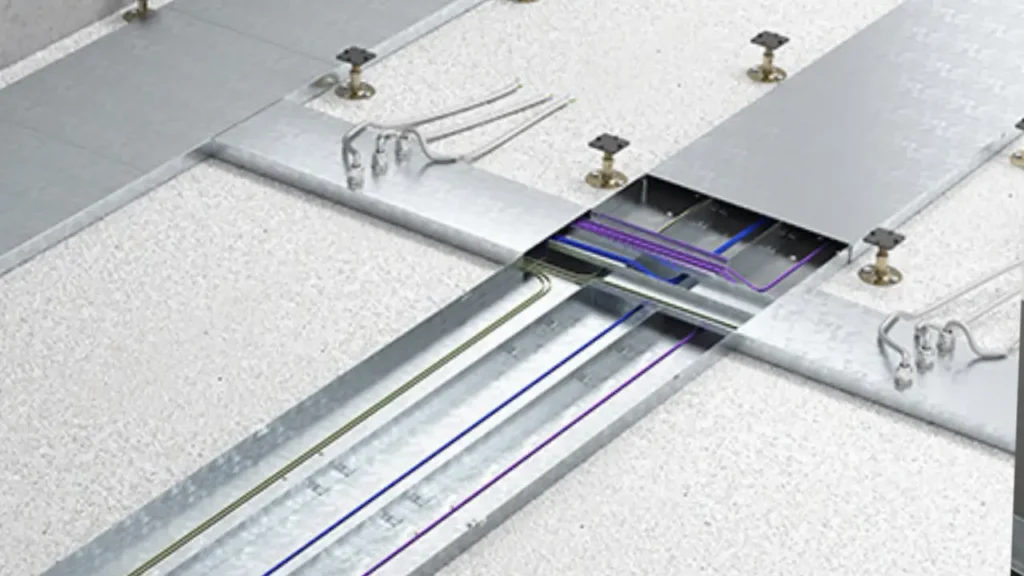
Installing cable trunking correctly is crucial for ensuring safety, organization, and the longevity of your electrical system. This process involves careful planning, precise measurements, and secure fitting of the trunking components to create a reliable cable management pathway.
Step 1: Plan and Measure
Begin by carefully planning the route of your cable trunking. Measure the total length required, noting any corners or obstacles that will necessitate bends or specialized fittings. Account for future expansion by selecting a trunking size that offers sufficient capacity for current and potential future cables.
Step 2: Cut and Prepare
Cut the trunking sections to the measured lengths using appropriate tools, such as a hacksaw or specialized trunking cutters. Ensure all cuts are clean and burr-free to prevent damage to cables. Drill any necessary mounting holes if the trunking does not come pre-drilled.
Step 3: Mount the Base
Securely mount the base of the trunking to the wall or surface using screws, clips, or adhesive, depending on the trunking type and surface material. Ensure the base is level and aligned to create a neat and professional appearance. Space fixings evenly for stability.
Step 4: Lay Cables
Once the base is firmly in place, carefully lay the cables inside the trunking. Ensure cables are neatly arranged and not excessively bent or strained. Avoid overfilling the trunking, as this can impede heat dissipation and make future access difficult.
Step 5: Attach the Lid
Finally, attach the lid or cover to the trunking base. Many trunking systems feature a snap-on or clip-on lid for easy installation. Ensure the lid is securely fastened along the entire length to fully enclose and protect the cables within the trunking.
Difference Between Cable Tray and Cable Trunking
While both cable trays and cable trunking manage electrical cables, they serve distinct purposes and are suited for different applications. Their primary differences lie in their design, level of cable protection, and installation environments.
Design and Structure
Cable trunking is an enclosed system, typically a solid box-like structure with a removable lid, providing complete encapsulation of cables. This design offers a high degree of protection from dust, moisture, and physical damage. In contrast, a cable tray is an open, U-shaped or ladder-like structure with perforated or mesh bottoms, allowing for ventilation and easier access to cables.
Cable Protection
Cable trunking provides superior protection against external elements, including dust, water, and physical impact, due to its enclosed nature. This makes it ideal for environments where cables need maximum safeguarding. Cable trays, being open, offer less physical protection but allow for heat dissipation, which is crucial for large bundles of power cables that generate significant heat.
Ventilation and Heat Dissipation
Cable trays excel in ventilation and heat dissipation due to their open design. This is a significant advantage for power cables that can overheat, as the open structure allows air to circulate freely around the cables. Cable trunking, being enclosed, can trap heat, making it less suitable for large numbers of high-power cables unless adequate ventilation measures are incorporated.
Installation Environment
Cable trunking is often preferred in indoor, less harsh environments, such as offices, residential buildings, and light commercial spaces, where aesthetics and high protection from dust and accidental contact are priorities. Cable trays are more commonly found in industrial settings, data centers, manufacturing plants, and outdoor applications where large volumes of cables need to be supported and heat management is critical.
Accessibility and Future Expansion
Cable trays offer easier accessibility for adding, removing, or modifying cables due to their open design. This flexibility is beneficial in environments where cabling infrastructure frequently changes or expands. While cable trunking also allows for access via removable lids, it generally requires more effort for modifications, as cables are more confined.
Cost and Installation Complexity
Generally, cable trunking can be more labor-intensive to install due to the need for precise cutting and fitting of solid sections and covers. Its cost can also be higher per meter for larger capacities. Cable trays, especially mesh or ladder types, can be quicker to install over long runs, and their open design can sometimes simplify cable laying, potentially leading to lower overall installation costs for high-volume applications.
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the differences between cable tray and cable trunking:
| Aspect | Cable Tray | Cable Trunking |
| Design and Structure | Open, U-shaped, ladder-like, perforated | Enclosed, box-like with removable lid |
| Cable Protection | Moderate; good for physical support, less for dust/moisture | High; excellent against dust, moisture, impact |
| Ventilation | Excellent; allows good heat dissipation | Limited; can trap heat |
| Installation Environment | Industrial, data centers, outdoor, heavy-duty | Residential, commercial, light industrial, indoor |
| Accessibility | Easy for additions/modifications | Moderate; requires lid removal |
| Cost & Installation | Potentially lower for large volumes, simpler installation | Higher for larger capacities, more involved installation |
Conclusion
Cable trunking is more than just a cover; it’s a fundamental component for modern electrical systems, ensuring safety, neatness, and longevity. By protecting wires from damage and keeping them organized, it prevents hazards and streamlines maintenance.
Embracing cable trunking means investing in a safer, more efficient, and aesthetically pleasing environment for all your wiring needs. From simple home setups to complex industrial installations, its benefits are undeniable.
For reliable and high-quality solutions, get wholesale cable trunking from our Inkwell Electrics. We provide a wide range of options to meet every requirement.