You want to know what is cfm in fans and how to calculate cfm for your space, right? The basic formula is simple: measure the air velocity and the area where the fan moves air, then multiply them together. In 2025, picking the right fan matters more than ever.
Accurate cfm makes your home or workplace comfortable, safe, and energy-efficient. Different types of fans, like ceiling fans, exhaust fans, and Linkwell’s fan filter units, each have their own cfm needs. Fan choice affects energy use, noise, and air quality, so matching cfm to your environment keeps everything running smoothly.
Cfm in Fans Key Takeaways
- CFM measures how much air a fan moves each minute and helps you pick the right fan for your space.
- Use the formula CFM = (Room Volume × Air Changes per Hour) ÷ 60 to calculate airflow needs for rooms and cabinets.
- Different fans need different CFM calculations based on their use, like cooling electronics or ventilating rooms.
- Adjust your CFM needs for factors like heat load, filters, ductwork, and climate to keep air fresh and equipment safe.
- Using a fan or CFM calculator makes it easy to find the best fan that matches your space and airflow requirements.
What is CFM in Fans
Cubic Feet per Minute Explained
You might wonder, what is cfm in fans and why does it matter? CFM stands for cubic feet per minute. This number tells you how much air a fan can move in one minute. When you see a fan rated at 200 cfm, it means the fan pushes 200 cubic feet of air every minute. This measurement helps you compare different fans and pick the right one for your needs.
Think of cfm as the “horsepower” for airflow. The higher the cfm, the more air your fan moves.
Engineers and designers use cfm to make sure fans work well in homes, offices, and industrial spaces. Over the years, measuring cfm has become more accurate. Today, experts use special tools and follow strict rules from groups like ASHRAE to measure cfm. They check how much air the fan moves by testing it in real-world conditions. This way, you get reliable numbers when you shop for a fan.
- CFM is based on the volume of air a fan’s blades move during operation.
- Standard methods and calibration keep cfm measurements consistent.
- Fan design, blade shape, and motor power all affect cfm.
Why CFM Matters
You need to know what is cfm in fans before you buy or install one. CFM is the main way to judge how well a fan will cool, ventilate, or filter air in your space. If you pick a fan with too low a cfm, your room might stay stuffy or your equipment could overheat. If you choose a fan with the right cfm, you get better airflow, energy savings, and longer-lasting equipment.
- Fans are chosen based on cfm to match the airflow needs of each job.
- Higher cfm means better air movement, which is key for cooling and ventilation.
- Actual airflow can be less than the fan’s maximum cfm, so always check the specs.
- Environmental factors like temperature and altitude can change how much air your fan really moves.
Tip: Always look at cfm ratings when comparing fans. This helps you find the best fit for your space, whether you need a ceiling fan for your living room or a Linkwell fan filter unit for your control cabinet.
Understanding what is cfm in fans gives you the power to make smart choices. You get the right fan, save energy, and keep your space comfortable and safe.
Calculate CFM for Different Types of Fans
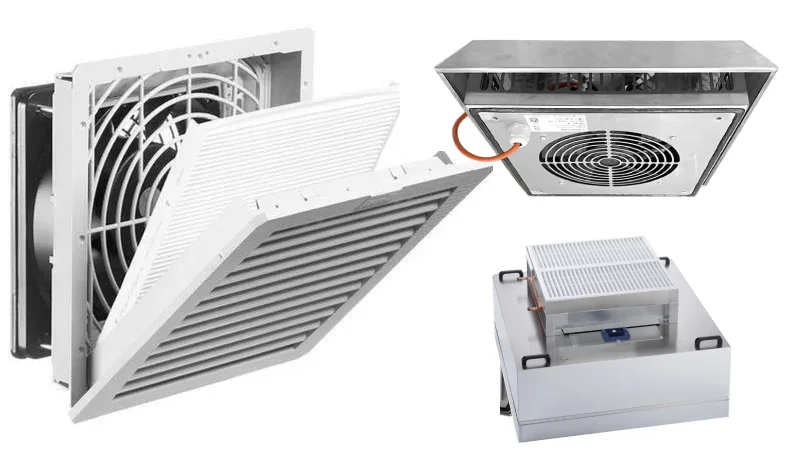

When you want to calculate cfm for your space, you need to know the right method for each fan type. Different types of fans have unique requirements, so using a cfm calculator or fan calculator helps you get the best results. Let’s break down the process for each fan style, so you can match cfm ratings to your needs.
Fan and Filter
Recommended products
You often see fan and filter combinations in grow rooms, server cabinets, or industrial enclosures. To calculate cfm for these setups, follow these steps:
- Measure the room or enclosure volume. Multiply length × width × height. For example, an 8′ × 8′ × 8′ space equals 512 cubic feet.
- Decide how quickly you want to exchange the air. Divide the total volume by the number of minutes per air exchange. For example, 512 cubic feet ÷ 3 minutes = 171 cfm.
- Adjust for extra factors:
- Add 5% for each air-cooled HID light or 10–15% for non-air-cooled HID lights.
- Add 5% if you use CO2 enrichment.
- Add 20% if you use a carbon filter.
- Add 25–40% for hot or humid climates.
- Add up all adjustments to get your minimum required cfm.
- Use a fan calculator to pick a fan that matches or slightly exceeds your calculated cfm.
Tip: Place your fan on top of the filter and make sure you have an intake port on the opposite side for fresh air. This setup improves airflow and keeps your equipment cool.
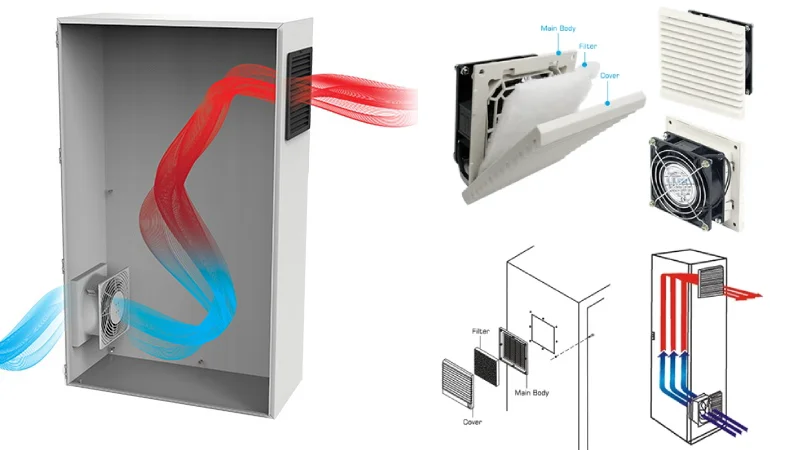
Enclosure Cooling Fan
If you need to cool electrical or electronic enclosures, you must calculate cfm based on heat load and temperature rise. Here’s a simple way to do it:
| Parameter | Description | Example Value / Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Watts (W) | Heat from electronics | 120 W |
| Conversion factor | Watts to BTU/hr | 1 W = 3.415 BTU/hr |
| BTU/hr (Q) | Heat load in BTU/hr | 120 × 3.415 = 410 BTU/hr |
| Temp difference (ΔT) | Max enclosure temp – ambient temp | 192°F – 70°F = 122°F |
| Specific heat of air (Cp) | Heat capacity of air | 0.240 Btu/lb-°F |
| Air density | Density at 70°F | 0.07634 lb/ft³ |
| CFM formula | Required airflow | CFM = (BTU/hr) / (Cp × Density × 60 × ΔT) |
| Example calculation | Using above values | CFM = 410 / (0.240 × 0.07634 × 60 × 122) ≈ 3.06 |
You can also use a shortcut:Q = 1.76 × W / Tc
Where Q is cfm, W is watts, and Tc is the allowed temperature rise in °C. For 300 watts and a 10°C rise:Q = 1.76 × 300 / 10 = 52.8 cfm
Double your calculated cfm for safety and check vent sizes to reduce static pressure.
Panel Cooling Fan
Panel cooling fans keep industrial panels and control boxes from overheating. Here’s how you calculate cfm for these fans:
- Measure the panel’s length, width, and height to get the total volume.
- Decide how many air exchanges you need per hour.
- Use the formula:
CFM = Room Volume / Minutes Per Air Exchange - You can also use a fan calculator to multiply air velocity (feet per minute) by the cross-sectional area (square feet).
- For odd-shaped spaces, calculate each section’s volume and add them up.
- Use multiple measurement methods for accuracy.
- Choose a fan with a cfm rating that meets or slightly exceeds your needs.
Cabinet Ventilation Fan
Cabinet ventilation fans are common in assembly rooms, bakeries, classrooms, and warehouses. To calculate cfm, use this formula:
CFM = Room Volume / Minutes per Air Exchange
Room volume is length × width × height. The number of air exchanges per hour depends on the room type. Here’s a quick chart:
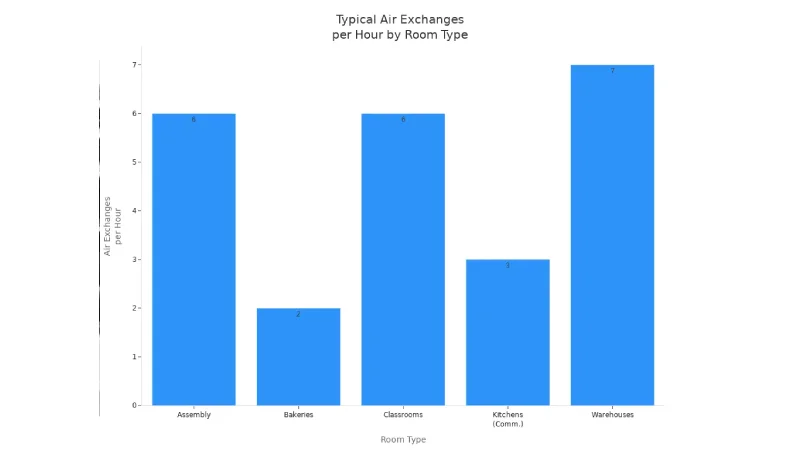
You should also add extra cfm for ductwork resistance. For example, each foot of duct pipe adds 1 cfm, each elbow adds 25 cfm, and a roof cap adds 40 cfm. Add these to your base cfm to get the total needed.
Note: Always consider noise, energy efficiency, and maintenance when picking a fan.
Control Cabinet Fan
Control cabinet fans keep sensitive electronics cool. To calculate cfm, measure the cabinet’s length, width, and height to get the volume. Then, divide by the minutes per air exchange. For example, a 10 ft × 12 ft × 8 ft cabinet has a volume of 960 cubic feet. If you want a full air exchange every 4 minutes,CFM = 960 / 4 = 240 cfm
You can also use a fan calculator to multiply air velocity by the cross-sectional area. The cabinet size directly affects the cfm you need. Bigger cabinets need more airflow.
Ceiling Fans
Ceiling fans help circulate air in homes and offices. To calculate cfm, first measure the room’s length, width, and height. Next, decide how many air changes per hour you want. Use the formula:CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) / 60
ACH stands for air changes per hour. For example, a bedroom might need 4 ACH, while a laundry room could need 8. You can also check cfm ratings for ceiling fans based on room size. For a medium bedroom (144–225 sq ft), look for fans with 1,600–4,500 cfm.
A fan calculator makes it easy to match fan size and cfm to your room.
Exhaust Fans
Exhaust fans remove stale air from bathrooms, kitchens, and industrial spaces. To calculate cfm, measure the room volume and pick an air change rate that fits the space. Use this formula:CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) / 60
Bathrooms need fewer air changes (4–10 per hour), while kitchens and industrial areas need more (up to 12). Always check cfm ratings and use a cfm calculator to make sure your fan can handle the job.
Industrial Fans and Linkwell Fan Filter (Telecom Cabinet Fan)
Industrial fans and Linkwell fan filter units are essential for telecom cabinets and control panels. Here’s how you calculate cfm for these applications:
- Find the heat load of your cabinet. For example, a mid-size telecom cabinet might dissipate 150 watts.
- Use a fan calculator to match the heat rejection requirement. For a 150-watt load, you might need a 100 cfm fan to keep the temperature rise under 10°C.
- Use CFD simulations to check airflow and avoid hot spots.
- Follow industry guidelines for fan sizing.
- Place intake fans low and exhaust fans high for best airflow.
- Add thermostats to control fan operation automatically.
- Choose the right fan type (centrifugal or axial) with cfm ratings between 50–250, depending on your needs.
- Consider thermally activated fans that adjust speed to reduce noise and extend life.
Example: If you use a Linkwell fan filter unit in a telecom cabinet with a 150-watt heat load, select a model rated for at least 100 cfm. This ensures your equipment stays cool and runs reliably.
A cfm calculator or fan calculator helps you compare different types of fans and pick the best one for your project. Matching cfm to your application keeps your equipment safe, saves energy, and extends the life of your system.
Factors Affecting CFM
When you want to get the right fan for your space, you need to know what affects the cfm you need. Let’s break down the main factors so you can make sure your airflow is optimized for your application.
Control Cabinet Size and Volume
The size and volume of your control cabinet play a big role in how much cfm you need. Bigger cabinets hold more components, which means more heat builds up inside. You have to calculate cfm for a room or enclosure by looking at the total heat load and the temperature difference you want to maintain. If your cabinet is large, you’ll need a fan that can move more air to keep everything cool and safe.
- Figure out the heat load from all the electronics inside.
- Decide the maximum temperature difference you’ll allow between inside and outside.
- Use the formula: CFM = (3.16 × Heat Load in Watts) / Temperature Difference (°F).
- Remember, cabinet material and where you place it (like in the sun or shade) also change how much cfm you need.
Room Size and Volume
Room size is just as important. The bigger the room, the more air you need to move for good air circulation. To calculate cfm for a room, multiply the length, width, and height to get the volume. Larger rooms or homes always need higher cfm to meet ventilation requirements and keep the air fresh.
| Floor Area (sq ft) | Continuous Ventilation Rate (CFM) |
|---|---|
| 1,000 | 50 |
| 2,000 | 100 |
| 3,000 | 150 |
Air Changes per Hour (ACH)
ACH tells you how many times the air in your space gets replaced every hour. This is key for keeping air clean and temperatures steady. Use this formula to find the right cfm:
CFM = (ACH × Room Volume) / 60
For example, if you have a 16 ft × 16 ft × 8 ft room (2,048 cubic feet) and want 6 air changes per hour, you’ll need about 205 cfm.
Fan Specifications
Not all fans are created equal. The cfm you get depends on the fan’s blade size, pitch, speed, and design. Larger blades and higher speeds move more air, but can also make more noise. You should also check the static pressure, especially if you have ductwork or filters, since resistance can lower the effective cfm.
- Rotations per minute (RPM) and motor power boost airflow.
- Blade shape and pitch help move air efficiently.
- Static pressure from filters or ducts can reduce cfm output.
Application Needs
Every space has unique airflow requirements. Maybe you need to control temperature in a server room or keep dust out of a workshop. The cfm you need changes based on these goals. For example, a garage with high ceilings and lots of equipment needs more cfm than a small bathroom. Environmental factors like altitude and humidity also affect how much air your fan must move.
Tip: Linkwell’s customizable fan filter units let you match airflow to your exact needs. You can pick the right motor, filter, and size for your project. Advanced features like variable speed drives and filter alarms help you keep airflow steady and maintenance easy. This makes it simple to meet even the toughest airflow requirements in industrial or commercial settings.
CFM Quick Reference
Common Scenarios
You probably want to know how much airflow you need for your space. Different rooms and applications have different cfm needs. For example, a small bedroom might need less airflow than a busy workshop or a server room. Here’s a quick table to help you see typical cfm requirements for common spaces:
| Occupancy Category | Typical CFM Needed | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Small Bedroom | 1500–2500 | Good for air circulation |
| Garage (over 2000 sq ft) | 4000+ | Handles heat and fumes |
| Workshop | 4000–6000 | Removes dust and keeps air fresh |
| Server Room | High CFM | Keeps equipment cool, often 2000+ |
| Auto Repair Room | 1.5 cfm/ft² | Connect exhaust fans directly to engines |
| Woodwork Shop | 0.5 cfm/ft² | Controls dust |
Tip: Always check your room size and purpose before you pick a fan. Using a cfm calculator makes this step easy.
CFM Charts and Guidelines
You can use charts and guidelines to match the right fan to your space. Most experts use the formula:CFM = (Room Volume in cubic feet) × (Air Changes per Hour) ÷ 60
This formula helps you quickly estimate the airflow you need. Here’s a handy chart for air exchanges per minute in different rooms:
| Room Type | Air Exchanges per Minute |
|---|---|
| Assembly | 6 |
| Classrooms | 6 |
| Warehouses | 7 |
| Kitchens | 3 |
| Restaurants | 6 |
| Garages | 7 |
You can also look at this chart for recommended cfm by room area:
| Room Area (Sq. Ft.) | Recommended CFM (at 2 ACH) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 27 |
| 500 | 133 |
| 1000 | 267 |
Sample Calculations
Let’s walk through a few real-world examples. Suppose you have a warehouse that measures 100 ft × 50 ft × 20 ft. The volume is 100,000 cubic feet. If you want 7 air changes per hour, use the formula:
CFM = (100,000 × 7) ÷ 60 = 11,667 cfm
For a control cabinet with a volume of 20 cubic feet and 12 air changes per hour:
CFM = (20 × 12) ÷ 60 = 4 cfm
If you use a Linkwell fan filter unit in a telecom cabinet, you can use a cfm calculator to match the heat load and airflow. For example, a 150-watt heat load may need a fan with at least 100 cfm to keep equipment safe.
Using a fan calculator or cfm calculator helps you compare options and pick the best fan for your needs.
To get the best results from your fan, follow these steps:
- Measure your space to find the volume.
- Pick the right air changes per hour for your room type.
- Use the formula: CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) / 60.
Accurate cfm keeps your equipment safe and your air fresh. Need help? Linkwell offers expert advice, custom fan filter unit solutions, and easy-to-follow cfm resources. Reach out for support with any project!
FAQ
How do I know if my fan’s CFM is enough for my space?
You can measure your room’s volume and use the CFM formula:CFM = (Room Volume × Air Changes per Hour) / 60.
If your fan matches or slightly exceeds this number, you’re good to go!
Can I use a Linkwell fan filter unit outdoors?
Yes, you can! Just make sure you choose a model with the right IP rating, like IP54 or IP65. These ratings protect your fan from dust and water, so it works safely outside.
How often should I replace the filter in my fan filter unit?
Check your filter every 3–6 months. If your area is dusty or outdoors, you might need to change it more often. Clean filters keep airflow strong and protect your equipment.
What’s the difference between CFM and airflow?
CFM measures airflow in cubic feet per minute. Airflow is the movement of air, while CFM tells you how much air moves in a set time. Higher CFM means more air moves through your fan.
Where can I get help choosing the right Linkwell fan filter unit?
You can contact Linkwell’s support team anytime. They offer expert advice and help you pick the perfect fan filter unit for your project. Visit Linkwell’s website or reach out by phone or email for fast answers.
Conclusion
Understanding What is CFM in Fans is key to choosing the right control cabinet fan. The correct CFM ensures your electronics stay cool, safe, and efficient, preventing costly downtime. By calculating airflow needs accurately and factoring in heat load, enclosure size, and environment, you can select a fan that delivers optimal performance.
Linkwell offers custom fan filter units designed to match your exact CFM requirements for any control cabinet application.