Industrial air conditioning refers to specialized HVAC systems designed for large buildings such as factories and warehouses. So, what is industrial air conditioning exactly? It involves controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality to protect equipment and maintain a healthy environment for people. Facility managers choose industrial air conditioning for several important reasons:
- Zoning allows precise control of temperature and air quality in different areas, providing greater flexibility and energy savings.
- Advanced control systems enable monitoring and management from a single location, further enhancing energy efficiency.
- Proper ventilation and filtration ensure clean air for occupants inside the facility.
- Energy recovery systems reduce overall energy consumption by capturing and reusing waste heat.
Industrial Air Conditioning Key Takeaways
- Industrial air conditioning cools and manages air in big buildings like factories and warehouses. It helps keep people and machines safe. These systems use smart controls, zoning, and strong filters. They keep the temperature, humidity, and air quality at the right levels. Industrial HVAC moves heat outside. It uses a refrigeration cycle with parts like compressors and condensers. Industrial air conditioning is larger and more complicated than home systems. It needs skilled workers to take care of it. Using industrial HVAC saves energy and makes buildings safer. It also helps buildings follow strict health and environmental rules.
What Is Industrial Air Conditioning

Definition
Industrial air conditioning means using advanced HVAC systems in big places. These places include factories, warehouses, and plants. These systems do more than just cool the air. They keep the temperature, humidity, and air quality just right. This helps protect machines and keeps workers safe. They also help with production. Industrial air conditioning uses special parts and controls. These can handle lots of heat and tough jobs.
Industrial air conditioning is not the same as home or commercial systems. It works in much bigger spaces and deals with more heat. These systems often connect to facility management platforms. Skilled technicians are needed to take care of them. Industrial HVAC systems have things like process cooling and advanced filtration. They also control humidity to meet strict rules.
| Feature | Residential Air Conditioning | Commercial Air Conditioning | Industrial Air Conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Comfort in small living spaces | Comfort and business needs in medium to large spaces | Process control, safety, and specialized environmental needs |
| Scale | Small scale | Medium scale | Large scale |
| System Complexity | Simple systems with basic controls | Moderate complexity with Building Management Systems | Complex, specialized systems integrated with process controls |
| Capacity | Low capacity (1.5 to 5 tons; up to ~60,000 BTUs) | Moderate to high capacity (10+ tons; 60,000+ BTUs) | Very high capacity (hundreds to thousands of tons; millions of BTUs) |
| Control | Simple thermostat control | Multiple thermostats, zone controls, BMS | Advanced integrated process control with redundancy and fail-safes |
| Maintenance | Basic maintenance by general technicians | Regular professional maintenance | Extensive, frequent maintenance by highly skilled technicians |
| Air Quality | Basic filtration | Advanced filtration and air quality standards | Specialized filtration and ventilation for hazardous materials and strict air quality requirements |
| Cost | Lowest initial and operating costs | Higher costs due to complexity and scale | Highest costs reflecting complexity, size, and specialized nature |
| Regulation | Basic energy efficiency and minimal regulations | Stricter energy and air quality regulations | Most stringent, industry-specific regulations for safety and environmental compliance |
Key Features
Industrial air conditioning is special because it can handle lots of heat. It keeps the environment controlled and follows strict rules. These systems use different HVAC types like central air conditioning, split systems, packaged rooftop units, VRF/VRV systems, and industrial chillers. Each type is good for different needs.
- Central air conditioning moves air with advanced ductwork. It keeps big buildings cool and clean. It can handle more than 50 tons of cooling.
- Split central air conditioning has outdoor compressors and indoor air handlers. This setup is good for saving energy and cooling certain areas.
- Packaged rooftop units send lots of cool air through ducts. They can cool many zones and save space.
- VRF/VRV systems use inverter compressors. They give precise and energy-saving control for many zones.
- Industrial chillers use chilled water or fluids for cooling. They are important for process cooling and heavy loads.
Industrial HVAC systems use smart controls. These include building automation and direct digital controls. They watch and change conditions right away. This keeps the inside climate steady, protects equipment, and meets rules.
Industrial air conditioning also cares about indoor air quality. It uses strong filters, controls humidity, and checks air quality all the time. These things help meet standards from groups like ASHRAE and OSHA.
Key features of industrial air conditioning are:
- High cooling power for big spaces and hot equipment
- Advanced zoning for exact temperature and humidity in each area
- Special filtration and ventilation to remove dangerous stuff and keep air clean
- Connection to facility management systems for easy control and monitoring
- Frequent maintenance to keep the system working well and safe
Industrial HVAC systems also try to help the environment. They use energy-saving equipment and eco-friendly refrigerants. Some use renewable energy to lower their impact. Regular care and upgrades help them last longer, usually 15 to 20 years.
Industrial air conditioning is very important. It helps production, protects equipment, and keeps people safe and healthy in big buildings.
How Industrial HVAC Systems Work
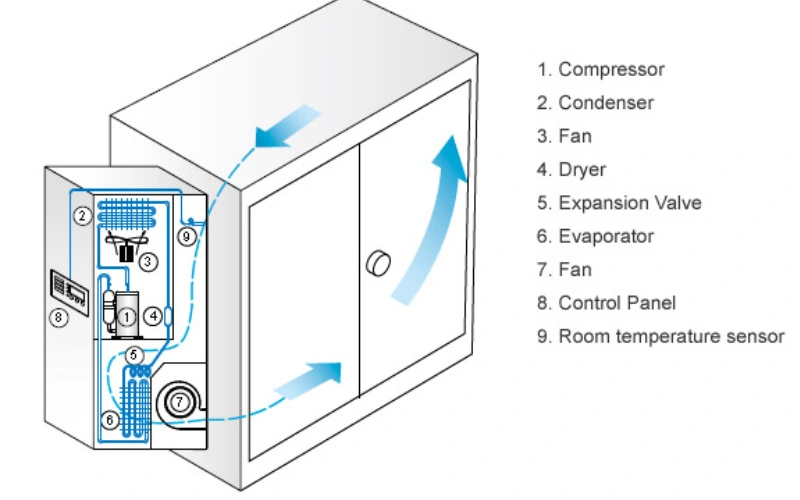
Main Components
Industrial HVAC systems have many special parts. These parts help keep big spaces safe and comfortable. Each part does something different. The table below lists the main parts and what they do:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Air Conditioning Unit | Pulls in warm air, cools it, and sends out cool air to keep the space comfortable. |
| Heat Exchanger | Moves heat between areas to warm or cool the space. |
| Thermostat | Tells the system when to heat or cool by checking the temperature. |
| Blower Motor | Pushes warm or cool air through the system to spread it around. |
| Air Ducts and Vents | Carry treated air from the HVAC units to different rooms. |
| Furnace or Boiler | Heats air or water by burning fuel and spreads heat in the building. |
| Evaporator Coil | Takes heat from warm air to cool it before sending it out. |
| Condenser | Gets rid of heat from the building; it is the hot part of the air conditioning unit. |
| Chiller | Takes heat out of liquid; can be water-cooled or air-cooled. |
| Control Systems | Watch and manage how the HVAC works; change things like temperature and airflow automatically. |
| Air Filters | Catch dust, allergens, and dirt before air moves around. |
| Humidifiers/Dehumidifiers | Change how much moisture is in the air for comfort and safety. |
| Industrial Ventilation | Makes sure air moves well, gets cleaned, and goes all over the building. |
Industrial HVAC equipment is made from strong materials. Steel, stainless steel, and copper alloys help stop rust and keep the system strong. Good insulation and special coatings save energy and stop water problems. Many systems use safe materials and refrigerants to help the environment.
Note: Industrial HVAC systems often have extra things like better filters, sensors, and smart controls. These help meet strict air quality and safety rules.
Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle is the main process in industrial air conditioning. It takes heat from inside and moves it outside. There are four main parts: compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.
- Compressor: The compressor squeezes the refrigerant gas. This makes it hot and high-pressure. Big industrial air conditioners often use many compressors in a separate room. This helps cool large spaces.
- Condenser: The hot gas goes to the condenser. Here, it cools down and turns into a liquid. Industrial HVAC systems often use water-cooled condensers or cooling towers. These work better than air-cooled units.
- Expansion Valve: The liquid refrigerant goes through the expansion valve. This valve lowers the pressure and makes the refrigerant cold.
- Evaporator: The cold refrigerant goes into the evaporator coil. Warm air from the building blows over the coil. The refrigerant takes in heat and turns back into a gas. The cooled air then moves through the ducts into the building.
This cycle keeps repeating to keep the space cool. Some industrial HVAC systems use electronic expansion valves for better control. Some use chilled water or brine loops instead of direct refrigerant. This helps cool very big spaces or equipment.
| Aspect | Industrial Air Conditioning Systems | Residential Air Conditioning Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigeration Cycle Type | May use absorption or compression cycles | Mostly single-stage vapor compression cycles |
| Compressors | Many compressors, bigger and more complex | Usually one compressor in a small unit |
| Heat Rejection Medium | Uses water-based cooling like cooling towers | Uses air-cooled condensers to send heat outside |
| Cooling Method | Often uses chilled water or brine loops to save water | Uses direct expansion with refrigerant and simple airflow |
| Refrigerants Used | Ammonia, halocarbons, sometimes water | Mostly halocarbon refrigerants |
| System Scale and Complexity | High capacity, works with process cooling | Made for comfort cooling in small temperature ranges |
| Heat Rejection Approach | Heat mostly goes to water, often with evaporative cooling | Heat goes to outdoor air |
Industrial HVAC systems also control humidity very well. In wet places, they use special dehumidifiers or humidifiers. Desiccant units can remove more moisture than regular coils. Good ventilation and insulation stop water drops and keep air clean.
Smart controls and building automation help run all these parts. Sensors check temperature, humidity, and air quality. Controllers and software change the system to keep things steady and save energy. This lets facility managers watch and control everything from one place.
Tip: Regular maintenance, changing filters, and checking the system help industrial HVAC work well and safely.
Industrial Air Conditioning vs. Residential
Key Differences
Industrial air conditioning and residential systems are made for different jobs. Industrial HVAC systems cool or heat big places like factories. Residential systems work in homes. The table below shows how these systems are not the same in size, setup, placement, zoning, ventilation, drainage, and maintenance:
| Operational Aspect | Industrial Air Conditioning Systems | Residential Air Conditioning Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Larger and more powerful | Smaller, for homes |
| Setup | Packaged units | Split setup |
| Placement | Rooftop or outdoors | Yard or side of the house |
| Zoning | Multiple zones, many thermostats | Usually one thermostat |
| Ventilation | Complex, less window access | Simpler, uses windows |
| Drainage Systems | Large, complex | Small, simple |
| Maintenance | More complex and challenging | Easier to maintain |
Industrial HVAC systems need special care more often. They use modular designs, so all the parts stay together. This makes upgrades easier. These systems have bigger drainage to handle more water. Residential systems only need simple yearly checkups and have small drainage.
Tip: Industrial HVAC systems cost more to take care of because they are bigger and harder to fix. Only skilled technicians should work on them.
Scale and Design
Industrial air conditioning systems must handle much bigger spaces than home systems. They use custom ductwork to move air to many zones. Each zone can have a different temperature at the same time. For example, a warehouse might need cooling in one spot and heating in another. Industrial HVAC systems use advanced airflow tools, like balancing and noise control.
Duct size is very important. If ducts are too small, less air moves and the system works harder. If ducts are too big, air moves too slowly. Industrial systems use round ducts to help air move better and avoid sharp turns. They use strong materials like metal to keep air moving smoothly.
Residential HVAC systems use simple duct layouts. They focus on comfort and quiet. Most homes have one or two zones, so they do not need advanced controls. Home ducts are often flexible and easy to put in.
Industrial HVAC systems often use special tools like airflow simulations before they are installed. These tools help find problems and make the system work better. Regular cleaning, repairs, and checkups keep airflow strong and save energy.
Applications of Industrial HVAC
Typical Facilities
Many big buildings need industrial HVAC systems. These systems help keep places safe and working well. Different buildings have different needs:
- Factories and warehouses use HVAC to keep air clean and cool for people and machines.
- Data centers and server rooms need exact cooling to protect equipment and save energy.
- Laboratories must control temperature and keep out bad stuff. They use special vents to get rid of fumes.
- Health care places use HVAC to meet health rules and keep patients safe.
- Aircraft hangars and repair shops use HVAC for spot cooling and to keep things working right.
- Fire and rescue stations need strong airflow to clear out exhaust and keep workers safe.
- Fitness centers, laundries, and dining areas use HVAC for comfort, clean air, and to follow safety rules.
These buildings use chillers, heat pumps, compressors, air separators, and smart controls. They also need good ventilation to get rid of dust, fumes, and other bad things. Many must follow strict rules from groups like OSHA, NFPA, and DOE-FEMP.
Why Use Industrial HVAC
Industrial HVAC systems give many big benefits to large buildings:
- Better air quality: Good airflow and filters take out bad particles and fumes. This keeps workers healthy.
- Energy savings: Smart controls and sensors help use less energy and save money.
- Equipment safety: Keeping the right temperature and humidity stops machines from breaking and helps them last longer.
- Product safety: Exact climate control keeps products safe and good, which is very important in food and medicine.
- Following rules: HVAC systems help buildings meet safety and environment rules. This helps avoid fines and shutdowns.
- Helping the planet: Many systems use less energy and green power to lower harm to the environment.
- Early repairs: Modern HVAC uses data to find problems early. This means less downtime and lower repair costs.
Industrial HVAC systems are very important for big buildings. They keep people, equipment, and products safe. They also help companies follow rules and save money.
Industrial air conditioning systems help big buildings stay safe and comfortable. These systems use smart controls and strong materials. They control temperature, humidity, and air quality. Facility managers should think about a few things when picking a system. They need to look at how much cooling is needed and the size of the space. They should choose the best unit type for the building. They must check how much energy the system uses. It is important to plan for easy repairs and future changes. Managers should also work with skilled experts.
Professionals follow strict rules like ASHRAE and local codes. This makes sure the system is safe and works well. Good planning and expert help give the best results.
FAQ
What makes industrial air conditioning different from commercial systems?
Industrial air conditioning systems cool bigger spaces and handle more heat. They use advanced controls and are built with stronger materials. These systems often link to facility management platforms. Only skilled technicians should take care of them.
How often should industrial HVAC systems get maintenance?
Facility managers need to plan maintenance every three months or sooner. If the system is used a lot, it may need checks each month. Regular inspections help stop breakdowns and keep things working well.
Can industrial air conditioning improve indoor air quality?
Yes. Industrial HVAC systems have strong filters and advanced ventilation. These features take out dust, fumes, and harmful particles. Clean air keeps workers and equipment safe.
What is the typical lifespan of an industrial air conditioning system?
Most industrial air conditioning systems last 15 to 20 years. Regular care and upgrades can help them last longer. Tough environments might make them wear out faster.
Do industrial HVAC systems help save energy?
Many industrial HVAC systems use smart controls and energy recovery. These tools help lower energy use and save money. Facility managers can watch how the system works and make changes for better efficiency.
Conclusion
what is industrial air conditioning helps facility managers make informed decisions. It’s more than just cooling—it ensures consistent temperature, humidity control, and equipment protection in high-demand environments. From factories to data centers, industrial AC systems are crucial for uptime, comfort, and safety. Choosing the right system can improve operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs significantly.




