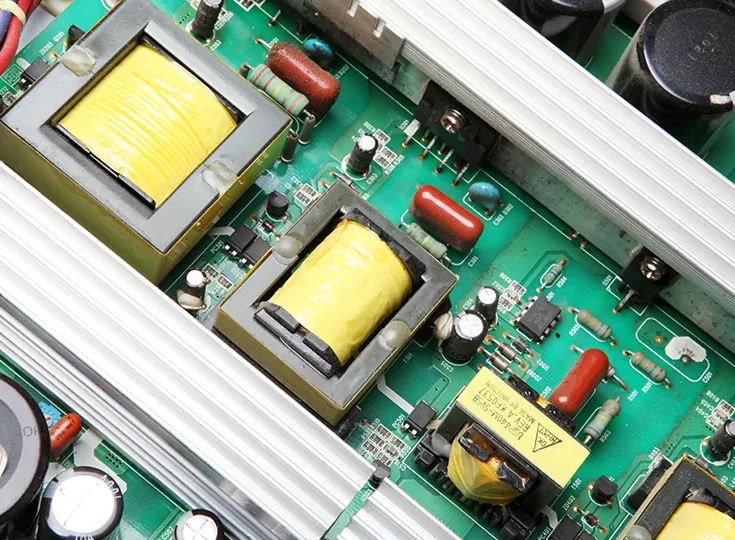
When you look at a control cabinet or panel, you might wonder what is inside a transformer. If you open it up, you’ll see several key parts that make the transformer work safely and efficiently. What is inside a transformer? You’ll find a sturdy core, copper windings, insulation, and secure terminals. What is inside a transformer also includes a mounting frame and a protective enclosure. Linkwell brings trusted control transformers and step down transformers for these applications. What is inside a transformer can vary, but in cabinets and panels, you’ll usually spot sizes like 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240. What is inside a transformer in a power station looks different, so let’s keep the focus on control transformers here.
Key Takeaways
- Transformers contain essential parts like a magnetic core, windings, insulation, terminals, and an enclosure that work together for safe and efficient operation.
- The core’s design and material significantly impact the transformer’s efficiency and voltage handling, making it crucial for performance.
- Windings convert voltage levels, with primary windings receiving energy and secondary windings delivering it at a different voltage, ensuring stable operation for control circuits.
- Good insulation protects against electrical faults and extends the transformer’s lifespan, making it vital for safety in industrial environments.
- Choosing the right control transformer involves matching its specifications to your cabinet’s voltage and power needs for optimal performance.
What Is Inside a Transformer: Key Internal Parts
When you open a control cabinet, you see a transformer that looks simple from the outside. Inside, though, you find several important components working together to keep your electrical system safe and efficient. Let’s break down the different parts of transformers you’ll find in Linkwell’s control transformers and industrial control transformers.
Core Structure and Materials
The core sits at the heart of every transformer. You’ll notice it’s made from magnetic materials like silicon steel, ferrite, or sometimes amorphous alloys. The magnetic core helps transfer electrical energy between windings. Silicon steel is common because it reduces energy loss and keeps your transformer running efficiently. Ferrite cores work well for high-frequency dry type transformers. Amorphous metals help lower no-load losses, which means better energy savings. The shape and lamination of the core also matter. Laminated sheets cut down on eddy current losses, so your transformer stays cool and reliable. Linkwell uses high-quality magnetic materials to make sure your transformer performs well in control panels and cabinets.
Tip: The core’s design and material choice directly affect how much voltage your transformer can handle and how efficiently it operates.
| Material | Impact on Efficiency and Performance |
|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | High magnetic permeability and low cost; reduces eddy current losses through lamination, improving overall efficiency. |
| Amorphous Steel | Reduces no-load losses significantly, enhancing energy efficiency for energy-saving applications. |
| Ferrite Cores | Low hysteresis loss, suitable for high-frequency applications, improving performance in electronic transformers. |
| Other Materials | Specialty soft magnetic materials offer higher saturation flux densities for specific industrial applications. |
Windings: Primary and Secondary
Windings are the coils of wire wrapped around the core. You’ll find two main types: the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding receives electrical energy from the power supply. It creates a magnetic field in the core. The secondary winding picks up this magnetic energy and turns it back into electrical energy at a different voltage. This is how the transformer steps voltage up or down for your control circuits.
Linkwell uses copper windings with enamel coatings for durability. You might see winding types like PEW, UEW, EIW, SEIW, and FEAI, each offering different temperature resistance grades. Insulating paper or tape separates the windings from each other and from the core. This keeps your transformer safe and prevents electrical shorts.
| Winding Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Primary Winding | Receives electrical energy from the supply |
| Produces magnetic flux in the core | |
| Determines input voltage characteristics | |
| Secondary Winding | Receives induced voltage from the magnetic field |
| Supplies power to the load | |
| Determines output voltage and current |
Insulation and Protection
Insulation is one of the most critical components inside a transformer. It keeps the electrical windings from touching each other or the core, which could cause dangerous short circuits. You’ll find solid insulation materials like cellulose, epoxy resin, and pressboard. Linkwell transformers use high-temperature resistant insulating paper, which offers flame retardant and moisture resistance. Sometimes, you see liquid insulation like mineral oil or ester-based fluids, but dry type transformers in cabinets usually rely on solid insulation.
Linkwell’s control transformers meet UL, CE, and ISO 9001 standards. This means you get reliable insulation and protection that matches global safety requirements. The insulation ensures your transformer can handle high voltage without risk, keeping your electrical system safe.
Note: Good insulation not only protects the transformer but also extends its lifespan, especially in demanding industrial environments.
Terminals and Connections
Terminals are the points where you connect your electrical wires to the transformer. You’ll see primary terminals marked as ‘Primary’ or ‘P’ for the incoming high-voltage supply. Secondary terminals, marked as ‘Secondary’ or ‘S’, connect to your control circuits and deliver the required output voltage. These components make installation easy and help you match the transformer to your system’s needs.
Linkwell designs terminals for secure connections, reducing the risk of loose wires or electrical faults. The layout is straightforward, so you can quickly identify where to connect each wire.
- Primary terminals: Connect to the high-voltage supply.
- Secondary terminals: Deliver the stepped-down voltage to your control panel.
Mounting Frame and Enclosure
The mounting frame and enclosure protect the transformer’s internal components. You’ll find sturdy metal frames that hold the transformer in place inside the cabinet. The enclosure shields the transformer from dust, moisture, and accidental contact. Linkwell uses weatherproof, tamper-resistant enclosures to keep your transformer safe in harsh industrial settings.
Sealed enclosures limit access to electrical parts, reducing the risk of accidents and fires. High-quality materials ensure your transformer lasts for years, even in environments with vibration, temperature changes, or corrosive agents. Typical dimensions for these transformers in cabinets are around 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240, making them easy to fit into standard control panels.
Safety Alert: Always make sure the enclosure is properly sealed before powering up your transformer. This keeps both your equipment and your team safe.
Parts of a Transformer: Quick Reference
Here’s a quick look at the different parts of transformers you’ll find in Linkwell’s control transformers:
- Magnetic core: Transfers energy between windings.
- Primary winding: Receives electrical energy and creates magnetic flux.
- Secondary winding: Delivers output voltage to the load.
- Insulation: Protects windings and core from electrical faults.
- Terminals: Connect your electrical supply and control circuits.
- Mounting frame and enclosure: Shields and secures all components.
You’ll see these components working together in every Linkwell control transformer, making sure your electrical system runs smoothly and safely. Dry type transformers in cabinets and panels rely on these features for reliable voltage conversion and electrical isolation. Power station transformers have different designs and sizes, so always focus on the control transformer when working with cabinets and panels.
Functions of Each Transformer Part

You might wonder how each part inside a control transformer works together to keep your cabinet or panel running smoothly. Let’s break down the functions of different parts and see how Linkwell’s electrical transformers deliver safe, efficient transfer of electrical energy for your industrial needs.
Core: Magnetic Path and Efficiency
The core sits at the center of every transformer. Its main function is to provide a magnetic pathway for transferring electrical energy between windings. When you power up your transformer, the core guides magnetic flux, which is essential for efficient transmission. A well-designed core minimizes energy losses and boosts overall efficiency. In Linkwell control transformers, you’ll find magnetic cores made from silicon steel or amorphous alloys. These materials help maximize performance by reducing eddy current losses and hysteresis. The core’s shape and lamination also play a big role in ensuring reliable and stable power transmission. You get a transformer that works hard to keep your control circuits safe and energy costs low.
Tip: The core’s design directly impacts how much voltage your transformer can handle and how efficiently it operates.
Windings: Voltage Conversion
Windings are the coils of wire wrapped around the core. Their main function is voltage conversion. The primary winding receives electrical energy from the supply and creates a magnetic field in the core. The secondary winding picks up this magnetic energy and converts it back into electrical energy at a different voltage. This process allows your transformer to step voltage up or down, depending on your control circuit’s needs.
Here’s a quick look at what affects winding performance:
| Factor | Effect on Transformer Performance | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Impacts magnetic flux transfer | Use low-loss silicon steel or amorphous metal |
| Winding Resistance | Higher resistance increases energy loss | Use high-conductivity copper windings |
| Leakage Flux | Uncoupled flux reduces efficiency | Optimize winding placement to minimize leakage |
| Hysteresis & Eddy Currents | Core losses reduce overall efficiency | Use laminated cores and low-loss materials |
You’ll see Linkwell control transformers handling typical voltage ranges like 440 volts input and 220 volts output. This voltage transformation is essential for the efficient and safe operation of industrial machinery. The windings work with the core to ensure a consistent output voltage, protecting your equipment from overloads and voltage spikes.
Insulation: Safety and Reliability
Insulation is the unsung hero inside every transformer. Its function is to keep electrical components separated, ensuring proper insulation and preventing dangerous short circuits. You’ll find high-temperature resistant insulating paper and flame-retardant materials in Linkwell transformers. These materials help dissipate heat and prevent dielectric breakdown, which keeps your transformer safe even under heavy loads.
- Electrical Isolation: Insulation separates windings and core, preventing short circuits.
- Thermal Management: Insulation helps manage heat, extending transformer lifespan.
- Preventing Dielectric Breakdown: Insulation withstands high voltages, stopping electrical arcs.
- Mechanical Protection: Insulation cushions components against vibration and shock.
- Electrical Efficiency and Safety: Proper insulation reduces power losses and protects you from electric shocks.
When you choose Linkwell, you get electrical transformers that meet UL, CE, and ISO 9001 standards. This means you can trust your transformer to deliver reliable and safe performance in any industrial environment.
Terminals: Input and Output
Terminals are where you connect your wires to the transformer. Their function is to provide secure input and output points for electrical transmission. Primary terminals take in the supply voltage, while secondary terminals deliver the stepped-down voltage to your control panel. Linkwell designs terminals for easy installation and strong connections, so you don’t have to worry about loose wires or electrical faults.
- Primary terminals: Connect to the incoming voltage supply.
- Secondary terminals: Output the converted voltage to your control circuits.
You get clear markings and sturdy construction, making it simple to wire up your transformer and keep your system running smoothly.
Cooling and Protection Features
Transformers generate heat during operation. Cooling and protection features work together to prevent overheating and electrical faults. In Linkwell control transformers, you’ll find natural air cooling and forced air cooling systems. Air circulates through and around the windings, carrying away heat and keeping the transformer at a safe temperature. Some larger transformers use fans to boost cooling, which increases power rating and reliability.
| Cooling Method | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Air Cooling (AN) | Uses natural convection to dissipate heat | Simple, low cost, quiet operation | Smaller transformers, control cabinets |
| Forced Air Cooling (AF) | Fans enhance heat dissipation | Handles higher loads, increases power rating | Industrial panels, enclosed spaces |
You’ll also find temperature relays and trip functions inside Linkwell transformers. These features monitor winding temperatures and disconnect the transformer if things get too hot. This protects your equipment and ensures efficient transfer of electrical energy, even in demanding environments.
Safety Alert: Always check that your transformer’s cooling system is working before powering up. This keeps your equipment safe and extends its lifespan.
When you look inside a Linkwell control transformer, you see how each part—core, windings, insulation, terminals, and cooling features—works together for efficient transmission and reliable performance. You get a transformer that’s built for industrial control cabinets and panels, with typical dimensions like 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240. These electrical transformers deliver the function of transformer you need for safe, stable, and efficient operation.
Comparing Control Transformers and Power Transformers
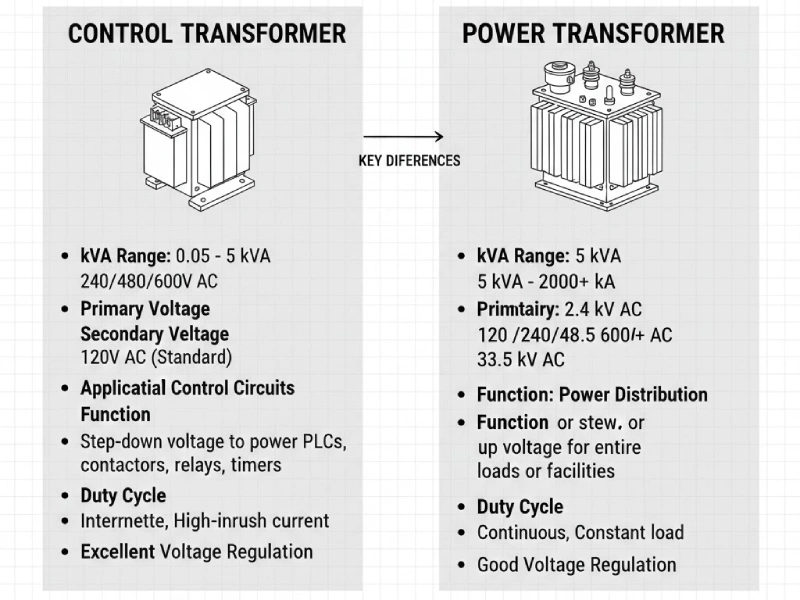
Internal Structure Differences
When you look inside a transformer, you’ll notice that control transformers and power transformers have different designs. Control transformers, like the ones you find in Linkwell’s lineup, focus on delivering stable voltage for control circuits in cabinets and panels. They usually come in compact sizes, such as 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240, and are often single-phase. Power transformers, on the other hand, handle much higher voltages and are built for large-scale energy transfer in substations or for distribution transformer roles.
Here’s a quick comparison to help you see the differences:
| Feature | Control Transformer (CPT) | Power Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Winding | Connects to main power circuit voltage (e.g., 480V) | Typically connects to high voltage |
| Secondary Winding | Provides control voltage (e.g., 120V/24V AC) | Steps down voltage for distribution |
| Core | Optimized for control applications | Designed for high efficiency and capacity |
| Wiring/Mounting | Typically single-phase, mounted on DIN rail | Can be three-phase, larger installations |
| Taps | May include taps for voltage adjustment | Often includes tap changers for load variations |
You’ll see that control transformers are designed for precision and safety in smaller spaces, while a power transformer is all about handling big loads and high efficiency.
Application in Cabinets and Panels
You use control transformers in places where you need reliable, low-voltage power for control circuits. These transformers fit perfectly inside industrial cabinets and panels. They power things like relays, PLCs, sensors, and contactors. You’ll find them in automation systems, motor control centers, and even HVAC panels.
Check out some common applications:
| Application Area | Example Use |
|---|---|
| Industrial automation | Powering PLC inputs and I/O modules |
| Motor control centers | Supplying contactor coils |
| Packaging machinery | Powering sensors and indicators |
| HVAC control panels | Supplying relays and thermostats |
| Renewable energy systems | Auxiliary control power |
A power transformer or distribution transformer usually sits outside, handling the main voltage step-down for entire buildings or grids. You won’t see these large units inside a control cabinet or panel.
Tip: If you’re working with control panels, always choose a control transformer that matches your voltage and space requirements.
Why Choose Linkwell Control Transformers
You want your electrical panels to run safely and efficiently. Linkwell control transformers give you that peace of mind. They deliver stable voltage, protect your equipment, and fit easily into standard cabinet sizes. You get features like high inrush current handling, custom voltage combinations, and built-in protection options.
Here’s why Linkwell stands out:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliability | Proven performance in industrial control applications |
| High Inrush Current Handling | Handles surges from contactors and solenoids for stable voltage |
| Custom Voltage Combinations | Flexible options for different primary and secondary voltages |
| VA Ratings | Wide range to match your control circuit needs |
| Built-in Protection | Customizable with fuse blocks for overcurrent safety |
| Custom Mounting Options | Easy integration into your specific cabinet layout |
You also get premium build quality, full compliance with ISO 9001 and UL standards, and extensive customization options. Linkwell’s reputation for reliability and support makes it a smart choice for your next transformer project.
Conclusion
You’ve explored what’s inside a control transformer and how each part works together. When you open a control cabinet or panel, you see a compact transformer built for reliable performance. The magnetic core, copper windings, insulation, terminals, and sturdy enclosure all play a role in keeping your system safe and efficient. You get a transformer that fits standard cabinet sizes like 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240, making installation easy.
Let’s recap the essentials:
- The core transfers energy and boosts performance.
- Windings convert voltage for your control circuits, supporting stable performance.
- Insulation protects against electrical faults and improves performance in tough environments.
- Terminals make wiring simple and secure, helping maintain consistent performance.
- The enclosure shields everything, so you get long-lasting performance even in harsh industrial settings.
Remember: Control transformers in the 60Va~100Kva range are designed for control cabinets and panels. You won’t find these features in power or substation transformers, which serve different roles.
If you want safe, reliable, and efficient performance for your industrial cabinets, Linkwell control transformers are a smart choice. You can customize them to match your voltage and space needs. You also get support from a team that understands industrial requirements. Linkwell’s transformers meet strict standards and deliver the performance you expect.
Ready to upgrade your cabinet or panel? Visit Linkwell Electric’s official website to explore control transformers and step down transformers. You’ll find solutions that improve performance and keep your operations running smoothly.
You’ve seen how every part inside a control transformer matters. The core, windings, insulation, terminals, and enclosure all work together to keep your cabinet safe and efficient. Linkwell control transformers stand out because they deliver steady voltage, handle heavy loads, and stay cool—even in tough industrial settings.
- You get reliable power for your machines.
- You avoid energy loss and overheating.
- You enjoy stable operation, even with big equipment.
| Customization Option | Benefits for Industrial Users |
|---|---|
| Input/Output Voltage | Matches your exact needs and boosts efficiency. |
| Power Rating | Fits your workload for better performance. |
| Mounting Style | Installs easily in any cabinet or panel. |
| Enclosure Type | Protects against dust and moisture for long life. |
| Safety Standards | Keeps your team and equipment safe. |
If you want a transformer that fits your space and meets your specs, Linkwell gives you quality and flexibility. Choose Linkwell for safe, reliable, and efficient control transformers in your next project.
FAQ
What is the main job of a control transformer in a cabinet?
A control transformer gives you stable voltage for control circuits. You use it to power relays, sensors, and timers inside cabinets or panels. It keeps your equipment safe and running smoothly.
How do I pick the right size for my control transformer?
Check your cabinet’s voltage and power needs. Most control transformers for panels fit sizes like 380mm600mm600mm or 320300240. Match the VA rating to your load for best results.
Can I use a power transformer instead of a control transformer?
No, you shouldn’t. Power transformers work for high-voltage energy transfer in substations. Control transformers are built for cabinets and panels, handling lower voltages and smaller loads.
Why does insulation matter inside a transformer?
Insulation keeps wires and the core from touching. You avoid short circuits and electrical shocks. Good insulation helps your transformer last longer, especially in tough industrial settings.
Does Linkwell offer custom control transformers for my panel?
Yes! You can get custom input/output voltages, power ratings, and mounting styles. Linkwell helps you find the perfect fit for your cabinet or control panel.