If you want to know how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures, you need a clear process. You start by figuring out the surface area. Use this formula: Surface Area = 2 x ((height x length) + (height x width) + (length x width)) / 144. Next, when you ask how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures, you look at the input power. Divide the heat in watts by the enclosure’s surface area. Many people also wonder how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures when it comes to temperature rise. For that, check a graph that matches your input power. You may ask how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures for safety. Accurate numbers help your equipment last longer. So, if you keep asking how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures, these steps will give you the answers.
Key Takeaways
- Gather all necessary data before starting calculations. This includes dimensions, temperatures, and power dissipation.
- Calculate the surface area accurately using the provided formula. This is crucial for determining heat dissipation capacity.
- Add up all heat sources, including solar gain, to find the total heat load. This helps ensure your enclosure can handle the heat.
- Use temperature rise charts to assess how much hotter the inside will get. This keeps your equipment within safe operating temperatures.
- Always include a safety margin in your calculations. This protects against unexpected heat spikes and equipment failure.
Heat Dissipation Basics in Electrical Enclosures
What Is Heat Dissipation?
When you place electrical components inside electrical enclosures, they generate heat during operation. Heat dissipation is the process of removing this unwanted heat from the enclosure. You want to keep the temperature inside safe for your equipment. If you ignore heat dissipation, the heat transfer load inside the enclosure can rise quickly. This means the heat has nowhere to go, and your devices can overheat. Good heat dissipation helps you control the heat transfer load and keeps your system running smoothly.
Why It Matters
You might wonder why you should care about heat dissipation in electrical enclosures. When heat builds up, you can see signs like charred or blackened parts, burn marks, or even bubbles on the board. Sometimes, you might notice a burning smell. These problems can lead to de-rated power performance, trip faults, or even system failures. You could face more downtime, higher costs, and unhappy customers. High temperatures can also shorten the lifespan of your panels and electronics. If you do not manage the heat transfer load, you risk losing money and wasting energy.
Tip: Always check for signs of overheating in your electrical enclosures. Early action can save you from expensive repairs.
Key Factors Affecting Heat Loss
Several things affect how well your enclosure handles heat dissipation and the heat transfer load. The main factors include:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct contact between materials, such as a heated surface and metal component. |
| Convection | Heat transfer through air barriers around pipes, heaters, or enclosures. |
| Radiation | Electromagnetic heat loss from uninsulated or exposed surfaces. |
The material of your enclosure also plays a big role. Materials like copper move heat away faster. If you use a copper heat pipe with a heat sink, you can boost heat dissipation by almost 96%. Without good materials, chips inside can reach very high temperatures. Adding a heat sink or thermal pads can improve heat transfer load and keep your electronics safe.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Calculate Heat Dissipation
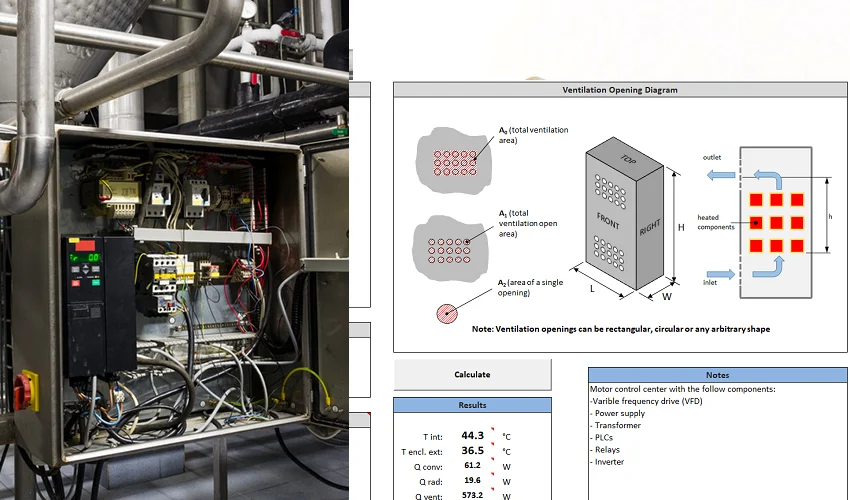
If you want to keep your electrical enclosure safe and your equipment running smoothly, you need a reliable way to handle heat. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of a heat dissipation calculation, so you can make sure your enclosure has enough cooling capacity and never overheats.
Gather Data and Inputs
Before you start any calculations, you need to collect some important details about your enclosure and its environment. Here’s what you should have on hand:
- Dimensions (Length, Width, Height)
- Insulation Thickness
- Internal Temperature (the temperature you want to maintain inside)
- Ambient Temperature (the temperature outside the enclosure)
- Insulation Type (like foam insulation or glass wool)
- Active Power Dissipation (the amount of heat generated by your devices)
- Solar Heat Gain (if your enclosure sits in sunlight)
- Cabinet Exterior Finish (white, reflective metal, etc.)
Tip: Write down all these values before you begin. Missing even one can throw off your heat dissipation calculation and affect your cooling capacity.
Calculate Surface Area
The surface area of your enclosure plays a big role in how much heat it can lose to the environment. To measure it accurately, follow these steps:
- Use calipers to measure the length, width, and height of your enclosure. Make sure to include any parts that stick out, like connectors.
- Leave at least 5-10mm of extra space around your components for wiring and assembly.
- Keep 1-2mm of clearance between the edges of your components and the enclosure walls.
- For ports and mounting holes, add a clearance of 0.2-0.3mm around each opening.
- Place connectors near the edges to help with cable routing.
- Make sure there’s at least 3mm between mounting holes and nearby parts.
Once you have your measurements, use this formula to find the total surface area (in square feet):
Surface Area = 2 × ((Height × Length) + (Height × Width) + (Length × Width)) / 144
Getting this number right is key for an accurate heat dissipation calculation.
Find Total Heat Generated
Now, you need to figure out how much heat your components produce. This is called the total heat load. Here’s how you do it:
- Add up the power (in watts) used by all the devices inside your enclosure. This is your active power dissipation.
- If your enclosure sits in the sun, include the solar heat gain.
- To convert the heat generated from watts to Btu/hr (British thermal units per hour), use this formula:
Heat in Btu/hr = Heat in watts × 3.41
- The total heat load is the sum of all internal and external heat sources.
Note: The total heat load tells you how much cooling capacity you need to keep your internal temperature safe.
Calculate Temperature Rise
To keep your equipment safe, you need to calculate temperature rise inside the enclosure. This tells you how much hotter the inside will get compared to the outside. Here’s how you do it:
- Divide the heat dissipated (in watts) by the enclosure’s surface area (in square feet) to get watts per square foot.
- Use a temperature rise chart or graph. Find your watts per square foot on the horizontal axis. Draw a line up to the curve, then read across to see the temperature rise.
- Add this temperature rise to the ambient temperature. This gives you the internal temperature.
For example, if your ambient temperature is 30°C and your calculated temperature rise is 10°C, your internal temperature will be 40°C.
Remember: Ambient temperature has a big impact on your internal temperature. Always use the highest expected ambient temperature for your calculations.
Assess Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance tells you how well your enclosure materials slow down the flow of heat. Lower resistance means heat escapes more easily, which helps with heat dissipation. Here’s what you need to know:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures how well materials like rubber or plastic block heat flow. |
| Key Test Procedures | Includes preparing samples, setting up tests, measuring heat flow, and doing calculations. |
| Importance | Makes sure your enclosure meets safety and performance standards. |
You might also see terms like junction-to-board resistance (RΘJB) and junction-to-case resistance (RΘJC). These numbers help you understand how heat moves from your components to the enclosure walls.
Tip: If you want to improve heat dissipation, choose materials with lower thermal resistance and consider adding heat sinks or fans.
When you finish your heat dissipation calculation, always add a safety margin. Most experts recommend a 25% margin for cooling capacity. This helps your system handle unexpected heat spikes and keeps your equipment safe.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can make sure your enclosure has enough cooling capacity to handle the total heat load and keep your internal temperature in check. This will help your equipment last longer and work better, even in tough conditions.
Tips & Examples for Electrical Enclosures
Common Mistakes to Avoid
You want your electrical enclosures to work well, but some mistakes can cause big problems. Here are some common issues you should watch out for:
- Using the wrong starting data, like incorrect measurements or missing temperature and humidity records.
- Making your enclosure too big or too small for the heat load. Both can cause trouble when you add more equipment or face extreme weather.
- Picking thermal solutions that do not fit your cabinet. This often happens when you rush to meet deadlines.
- Choosing the wrong thermal management techniques. This can lead to higher costs and more repairs.
- Letting the inside get too hot. High enclosure temperature management mistakes can cause condensation, which may damage your equipment.
If you underestimate heat dissipation, you risk overheating. This can cause malfunctions, shorten component life, and even lead to plant shutdowns or safety hazards.
Example Calculation
Let’s walk through a simple heat dissipation calculation for an industrial enclosure. Imagine you have:
- Q_gen (W): 120 watts of heat from your devices
- Ti (°C): 50°C (max safe internal temperature)
- To (°C): 35°C (ambient temperature)
- A (m²): 1.2 square meters (surface area)
You use the formula:
Q = U × A × ΔT
Suppose U (overall heat transfer coefficient) is 5 W/m²·K. The temperature difference (ΔT) is 15°C. So,
Q = 5 × 1.2 × 15 = 90 watts
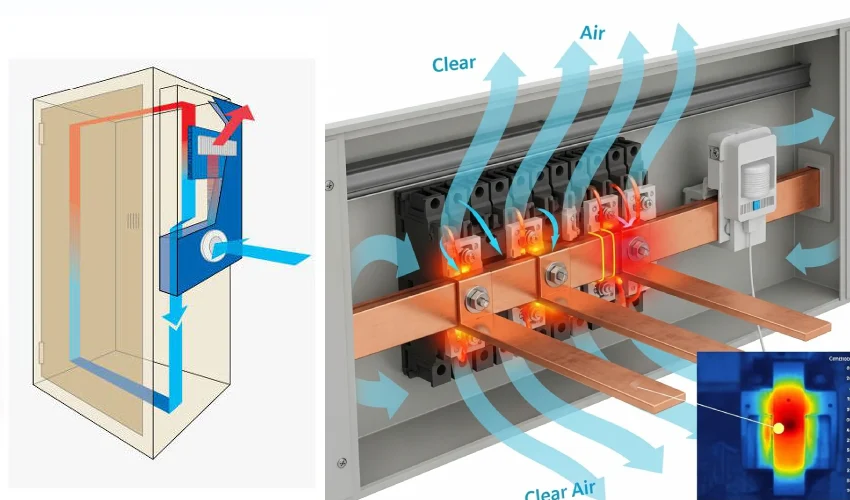
Since your devices generate 120 watts, natural cooling is not enough. You need extra heat dissipation measures, like forced air ventilation or a thermal management system.
Advice for Different Enclosure Types
Outdoor electrical enclosures need special care. First, list all equipment you plan to install, including future upgrades. Check each device’s specs, like size, airflow, and heat output. Place hotter devices near the top, where warm air rises. Always design for the highest expected heat load. Pick a thermal management system that matches both your inside and outside temperatures. Good enclosure temperature management keeps your equipment safe and running longer.
Tip: Regularly review your heat dissipation setup. As you add more devices, your heat load can change. Stay ahead with smart thermal management techniques.
Conclusion
You’ve now got a clear roadmap for calculating heat dissipation in electrical enclosures. This process might seem tricky at first, but you can handle it step by step. When you gather the right data, measure your enclosure, and use the formulas, you set yourself up for success. You don’t have to guess or hope for the best. You can make smart choices that protect your equipment.
Let’s recap the main steps:
- Gather all your measurements and details about your enclosure.
- Calculate the surface area so you know how much space you’re working with.
- Add up the total heat generated by your devices and any outside sources.
- Figure out the temperature rise using charts or formulas.
- Check the thermal resistance and pick materials that help heat escape.
Remember: Always add a safety margin to your calculations. This gives you extra protection if something unexpected happens.
You should always check your results against the safety limits for your electrical enclosures. If you notice your numbers are close to the maximum, consider adding fans, vents, or even a cooling unit. Don’t wait for a problem to show up. Take action early and keep your system running smoothly.
If you want to go further, create a checklist for your next project. Write down each step and check it off as you go. This habit helps you avoid mistakes and saves time. You can also look for advanced guides if you work with larger or more complex electrical enclosures.
You have the tools and knowledge now. With careful planning, you can keep your electrical enclosures safe, efficient, and reliable for years to come.
You now know how to calculate heat dissipation in electrical enclosures. Here’s a quick recap:
- Gather your data and measurements.
- Calculate the surface area.
- Add up all heat sources.
- Check the temperature rise.
- Review thermal resistance.
Tip: Always compare your results with safety limits for your equipment. Use a checklist for every project. If you want to go deeper, explore advanced guides and keep learning!
FAQ
How do I know if my enclosure needs extra cooling?
If your calculated internal temperature goes above your equipment’s safe limit, you need more cooling. You can add fans, vents, or air conditioners. Always check your numbers before you install new devices.
Can I use any material for my enclosure?
Not all materials work the same. Metal enclosures lose heat faster than plastic ones. If you want better heat dissipation, pick materials with low thermal resistance.
What happens if I ignore heat dissipation?
You risk overheating your equipment. This can cause shutdowns, damage, or even fires. Always check for signs like hot surfaces or strange smells.
Do I need to include solar heat gain?
Yes, if your enclosure sits in sunlight. Sunlight adds extra heat. You should always include it in your calculations for outdoor enclosures.