Terminal blocks are fundamental to electrical systems, but their diverse types can be overwhelming. Understanding these variations is crucial for optimizing your project’s safety and efficiency. This guide will demystify the different terminal block types, helping you make informed decisions.
From basic screw-clamp designs to advanced specialized blocks, each type offers unique advantages. We’ll explore the common connection methods and their ideal applications, ensuring you select the perfect terminal block for your specific wiring needs.
What are Terminal Blocks?

Terminal blocks are modular, insulated electrical connectors designed to secure and organize the connection of two or more wires. They consist of an insulating body, typically made from plastic, which houses a conductive metal strip and a clamping mechanism (such as screws or springs) that holds the wires firmly in place.
These terminal blocks facilitate the safe and efficient management of complex electrical circuits by providing a centralized point for wire termination, thereby simplifying installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance across a wide range of applications.
How a Terminal Block Works

A terminal block operates by providing a secure and insulated junction for electrical conductors. At its core, it consists of an insulating body, typically made of plastic or ceramic, which safely houses a conductive metal component.
This metal part, often a copper alloy, acts as the electrical bridge between the wires. Wires are inserted into designated openings, and a clamping mechanism then applies pressure to firmly hold them against the conductive element, establishing a reliable electrical path while preventing accidental disconnections or short circuits.
The effectiveness of a terminal block lies in its ability to create both a robust mechanical connection and a low-resistance electrical connection. This is achieved through various clamping methods, each designed to optimize wire retention and conductivity for different applications. The insulating housing ensures that electrical current is safely contained and directed, preventing it from straying to adjacent connections or exposing live parts, thereby enhancing overall system safety and organization.
- Physical Connection: Wires are inserted into dedicated ports within the terminal block.
- Clamping Mechanism: A screw, spring, or other mechanism secures the bare wire against a conductive metal strip.
- Electrical Conductivity: The metal strip provides a continuous electrical path between the connected wires.
- Insulation: The non-conductive housing electrically isolates adjacent connections, preventing short circuits and ensuring safety.
- Modularity: Many terminal blocks are designed to be modular, allowing for easy expansion or reconfiguration of connections.
Terminal Block Types
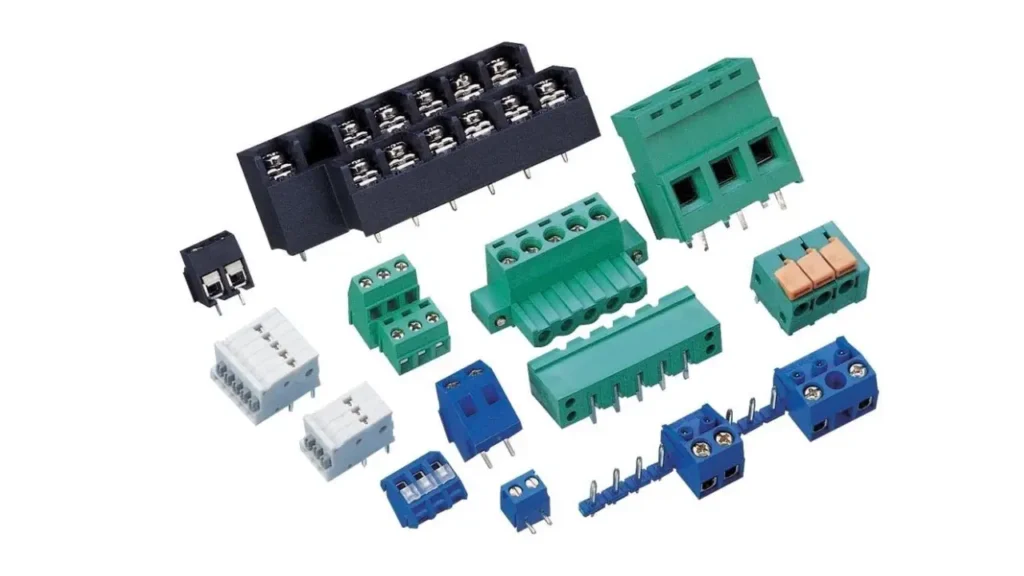
Understanding the various types of terminal blocks is essential for making informed decisions in any electrical design or installation. Each type is engineered with specific features to suit different wiring methods, environmental conditions, and application requirements. Knowing these distinctions ensures optimal performance, safety, and ease of use in your projects.
Screw Clamp Terminal Blocks
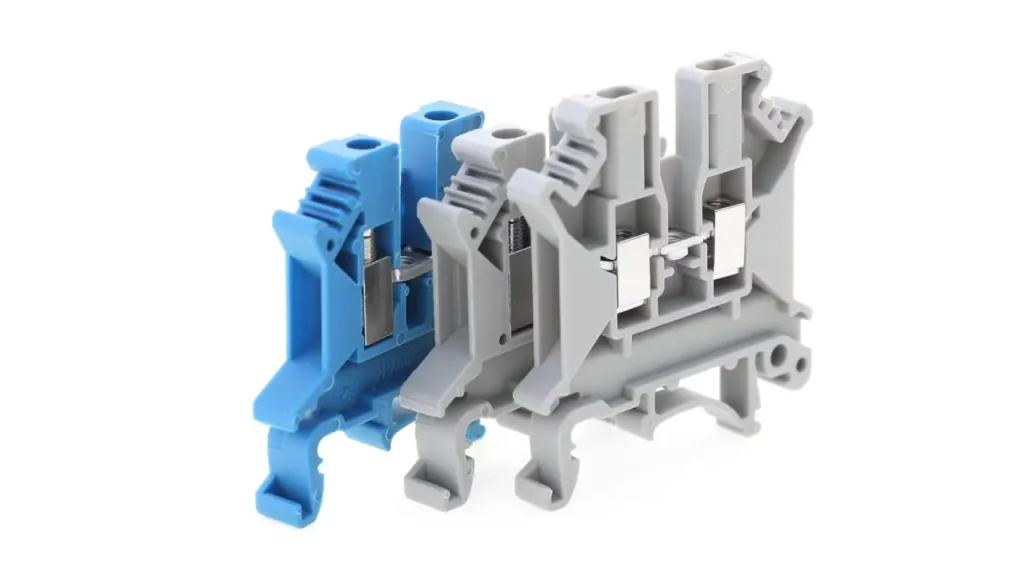

Screw clamp terminal blocks are perhaps the most common and widely recognized type, distinguished by their method of securing wires using a screw-tightened mechanism. The wire is inserted into a metal clamp or yoke, and a screw is tightened, pressing the wire firmly against the conductive current bar. This robust mechanical connection ensures excellent electrical contact and high pull-out force, making them suitable for demanding applications where vibration resistance is important. They are available in various sizes to accommodate a wide range of wire gauges.
Features of screw clamp terminal blocks include high clamping force, suitability for both solid and stranded wires, and a clear visual indication when the connection is tightened. Their robust design allows for reliable performance even in environments with moderate vibration.
Benefits encompass high reliability due to the strong mechanical connection, ease of visual inspection for proper tightening, and versatility in handling different wire types without requiring specialized tools beyond a screwdriver. They are also generally cost-effective.
Applications for screw clamp terminal blocks are incredibly diverse, spanning almost every sector of electrical engineering. They are widely used in industrial control panels, motor control centers, power distribution units, building automation systems, and HVAC controls. Their reliability makes them ideal for power circuits, where secure and long-lasting connections are paramount, as well as for general-purpose wiring in residential and commercial buildings.
Spring Clamp Terminal Blocks

Spring clamp terminal blocks utilize a spring-loaded mechanism to secure wires, offering a faster and often tool-less connection compared to screw types. Wires are inserted into an opening, and a spring applies constant pressure to hold them against the current bar. These can be “push-in” types where rigid or ferruled wires are simply pushed in, or types that require a small tool (like a screwdriver or specific lever) to open the spring before wire insertion. The constant spring pressure ensures a vibration-proof and gas-tight connection, which is crucial in dynamic environments.
Key Features of spring clamp terminal blocks include quick wiring times, excellent vibration resistance due to the constant clamping force, and maintenance-free operation once installed. They are particularly beneficial in environments where vibrations might loosen screw connections over time.
Their Benefits include significantly reduced installation time, enhanced connection reliability in high-vibration settings, and reduced risk of human error in tightening. They also provide a gas-tight connection that prevents corrosion at the contact point.
Applications for spring clamp terminal blocks are increasingly popular in applications where speed and reliability are critical. They are extensively used in railway technology, wind power systems, machine building, and process automation. Their vibration resistance makes them ideal for mobile equipment and applications exposed to constant movement. They are also favored in data centers and telecommunication equipment due to the demand for quick, reliable, and consistent connections.
Distribution Terminal Blocks

Distribution terminal blocks are designed to provide a centralized and organized solution for distributing power or signals from one main input to multiple output circuits. While similar to busbar terminal blocks in function, distribution blocks often feature a more compact design with multiple individual connection points that are electrically commoned internally. They are ideal for efficiently splitting power to various loads or creating common potentials within a panel.
Features of distribution terminal blocks include multiple output terminals commoned to a single input, often a compact footprint, and various connection technologies (screw, spring, push-in) for the input and outputs. They prioritize efficient space utilization.
The Benefits include simplifying complex wiring layouts by consolidating multiple connections, saving significant wiring time and panel space, and improving overall system organization and troubleshooting by providing a clear distribution point.
Applications for distribution terminal blocks are widespread in control panels, lighting distribution, industrial machinery, and any application requiring efficient power or signal splitting. They are excellent for routing power from a single supply to several motors, solenoids, or control circuits, and for creating common voltage or ground rails, making them indispensable for neat and functional electrical enclosures.
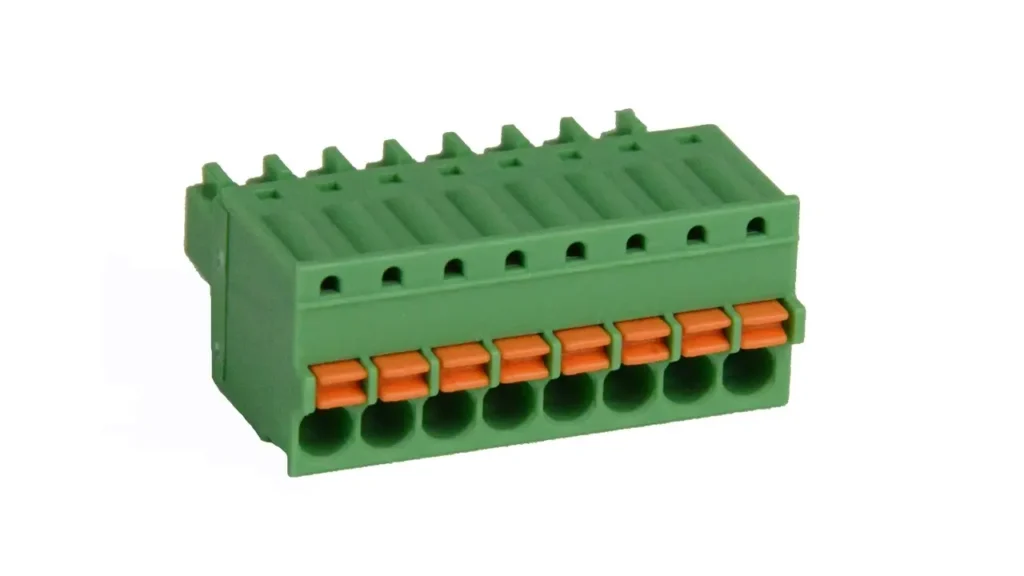
Push-in Terminal Blocks
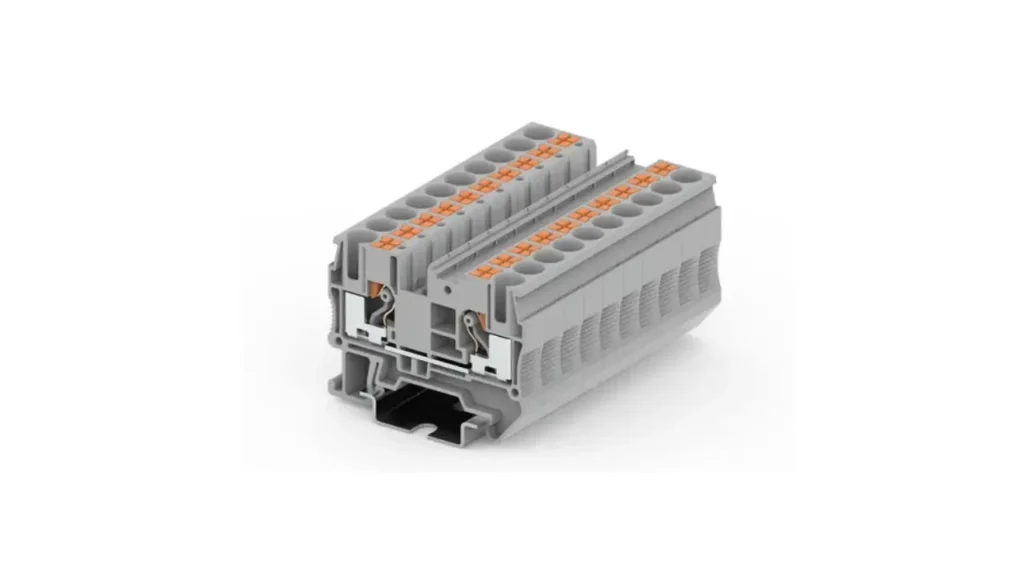
Push-in terminal blocks represent a specialized subset of spring clamp technology, optimized for extremely fast and tool-free wiring, particularly with solid wires or stranded wires equipped with ferrules. The design allows a prepared wire to be simply pushed into the connection point, where an internal spring mechanism automatically clamps it securely. For stranded wires without ferrules, a small tool may still be required to open the spring. This method significantly streamlines the wiring process, making it highly efficient.
Features of push-in terminal blocks are characterized by their rapid installation time, compact design, and vibration-resistant connection. The absence of a screw to tighten or loosen simplifies the wiring process dramatically.
Benefits include unparalleled wiring speed, which leads to significant labor cost savings, especially in large-scale projects. They offer a highly reliable and maintenance-free connection, as the spring continuously compensates for any wire settlement or temperature fluctuations. Their design also often allows for very high wiring densities.
Applications for push-in terminal blocks are prevalent where speed and efficiency are paramount, and where solid or ferruled wires are predominantly used. This includes serial production environments, control cabinet manufacturing, building installation (e.g., lighting, switches, outlets), and junction boxes. They are also increasingly adopted in sensor/actuator wiring and distributed I/O systems in automation, where many connections need to be made quickly and reliably.
Barrier Terminal Blocks
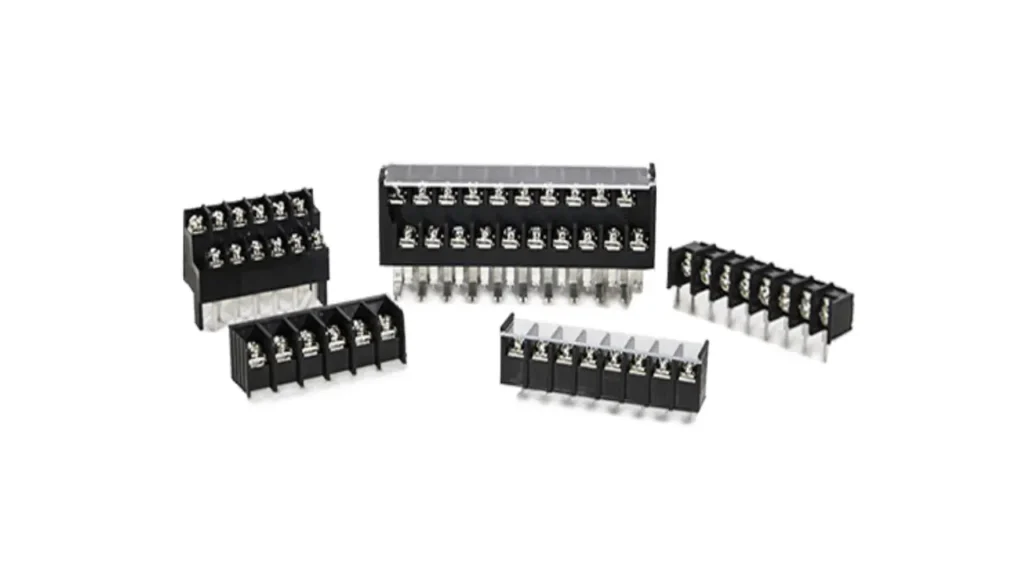

Barrier terminal blocks are characterized by their design, featuring individual insulated compartments that separate adjacent connection points, creating a physical “barrier” between them. This structure helps prevent accidental short circuits between terminals. Wires are typically secured using screws within each compartment. Their robust construction and clear separation make them highly reliable for multi-wire connections, especially in applications where space is less of a concern and clear isolation is crucial.
Features of barrier terminal blocks include excellent insulation between circuits, a sturdy and often larger footprint, and clear labeling areas for easy identification of connections. Their design inherently reduces the risk of arc-over.
The Benefits of using barrier terminal blocks include enhanced safety due to superior isolation, simplified wire management by providing clear, segregated channels, and robustness for demanding industrial environments. They also offer a clear visual layout for troubleshooting.
Applications for barrier terminal blocks are common in various sectors that require robust and clearly defined multi-wire connections. You’ll frequently find them in distribution panels, motor control boxes, power supply units, and HVAC systems. They are well-suited for high-power applications where accidental contact between terminals must be rigorously avoided, ensuring reliable and safe operation in industrial and commercial settings.
European-Style Terminal Blocks
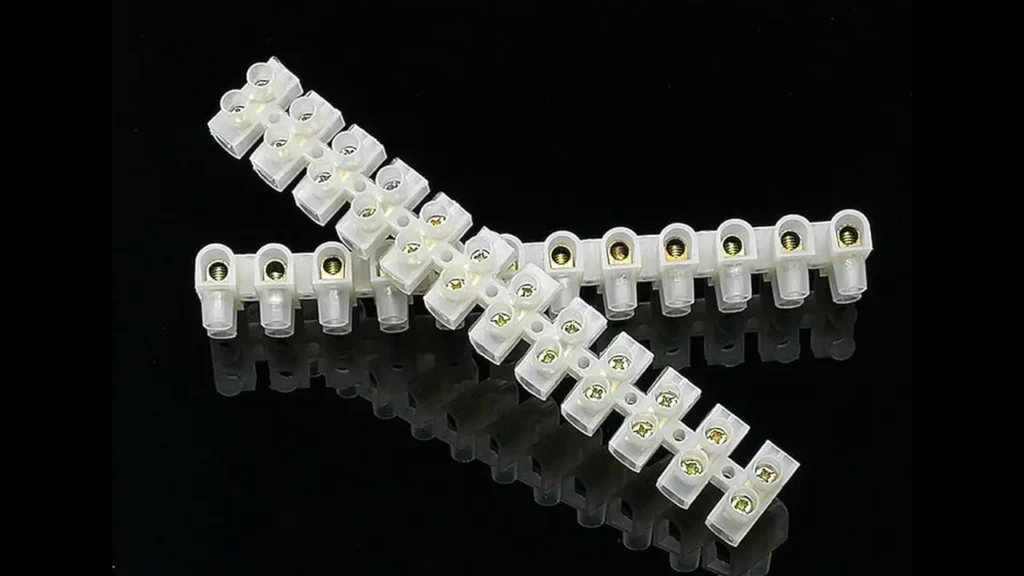

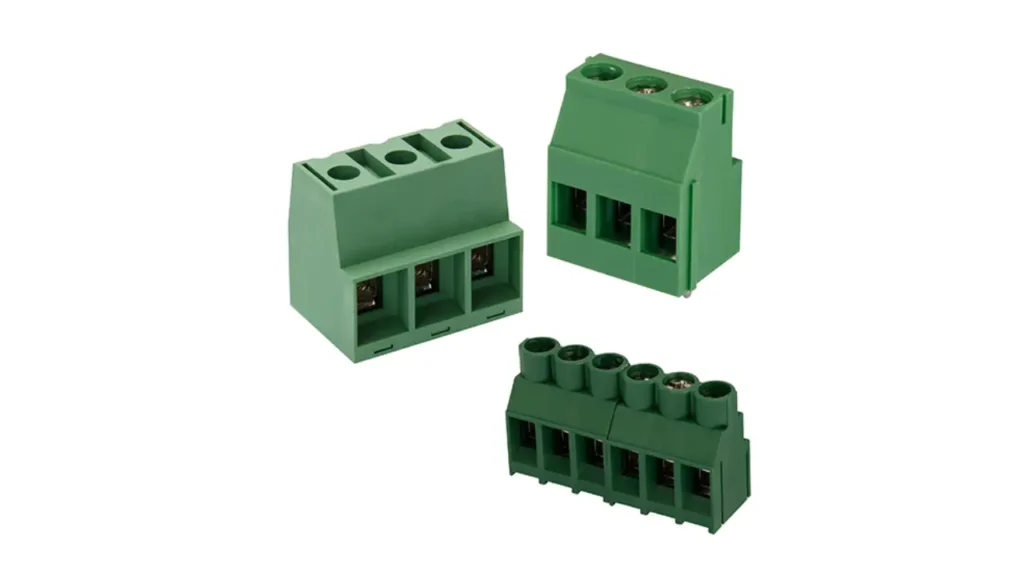
European-style terminal blocks, often referred to as “Euroblock” or “pluggable terminal blocks,” are distinct for their modular and often pluggable design. They typically feature screw-clamp connections within a compact, often green-colored housing that can be directly mounted to a PCB or form part of a larger interconnect system. Their key characteristic is the ability to easily plug and unplug entire sets of connections, simplifying installation, maintenance, and replacement of electronic components.
Key Features of European-style terminal blocks include their modularity, pluggable design (allowing for quick disconnection), and suitability for multi-strand wires. They often have internal metal contacts that ensure a reliable connection when plugged in.
The Benefits include simplified field wiring and component replacement, reduced downtime for maintenance or upgrades, and a clean, organized appearance on circuit boards or control panels. They offer high flexibility for system design and modification.
Applications for European-style terminal blocks are widespread in industrial control systems, automation equipment, and consumer electronics where ease of installation and maintenance is paramount. They are commonly used for connecting sensors, actuators, and power supplies to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in PLCs, motor drives, and other electronic modules. Their pluggable nature makes them ideal for devices that might need to be swapped out or serviced regularly.
PCB Terminal Blocks
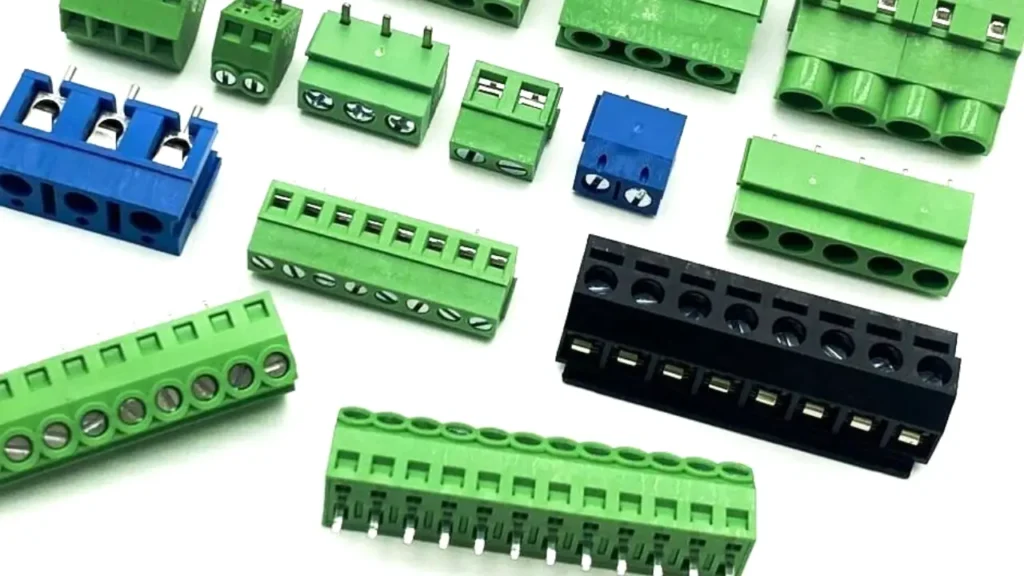

PCB (Printed Circuit Board) terminal blocks are specifically designed to be mounted directly onto a printed circuit board, serving as the interface between external wiring and the electronic circuits on the board. They provide a secure and reliable way to connect wires to the PCB, eliminating the need for separate wire-to-board connectors. These blocks are available in various orientations (horizontal, vertical, angled) to optimize space and wiring paths on the PCB.
The primary Features of PCB terminal blocks are their solder pins for direct mounting onto a PCB, compact design, and compatibility with various wire gauges and clamping mechanisms (screw or spring). They are engineered for stable electrical and mechanical connections directly to the board.
Benefits include saving valuable board space, reducing wiring complexity by integrating connections directly, and providing a robust physical connection point that simplifies assembly and troubleshooting of electronic devices.
Applications for PCB terminal blocks are pervasive in virtually all electronic devices that require external wiring. You’ll find them in industrial control systems, power supplies, test and measurement equipment, consumer electronics, and communication devices. They are crucial for connecting power inputs, sensor signals, control outputs, and communication lines to the internal circuitry of electronic products.
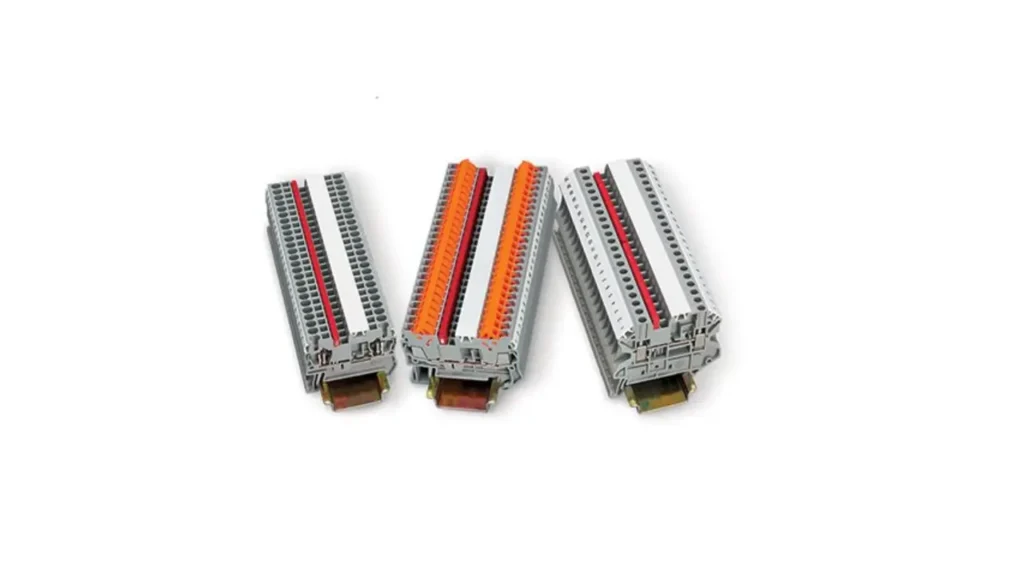
DIN Rail Terminal Blocks
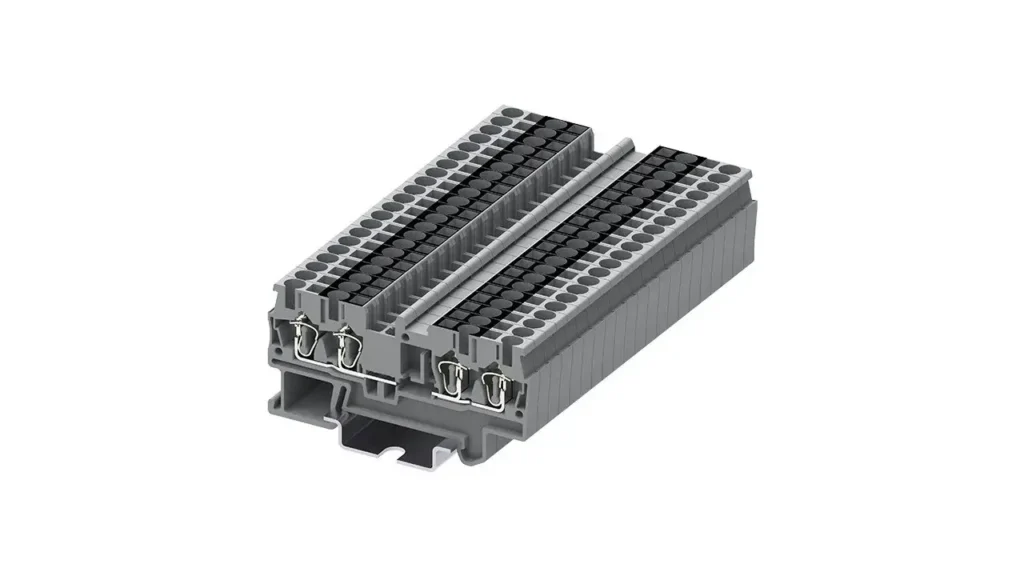

DIN rail terminal blocks are specifically engineered for mounting on standard DIN rails (e.g., TS 35, TS 32), which are widely used in industrial control cabinets and electrical enclosures. This mounting method allows for standardized, flexible, and scalable organization of wiring within a panel. They can be easily snapped onto or slid along the rail, enabling quick installation, rearrangement, and expansion of circuits without the need for individual fastening.
Key Features of DIN rail terminal blocks include their snap-on or slide-on mounting mechanism for DIN rails, modular design that allows for building custom blocks of any length, and compatibility with various accessories like end plates, end clamps, and jumpers.
Benefits encompass highly organized and professional cabinet layouts, significant time savings during installation and modifications, and improved troubleshooting due to standardized arrangement. Their modularity offers exceptional flexibility in system design and expansion.
Applications for DIN rail terminal blocks are dominant in industrial automation, control panel manufacturing, power distribution, and building management systems. They are the backbone of most electrical enclosures, organizing power circuits, control signals, and instrumentation wiring in PLCs, motor control centers, circuit breaker panels, and various machinery. Their standardized mounting ensures interchangeability and system consistency across different installations.
Waterproof Terminal Blocks
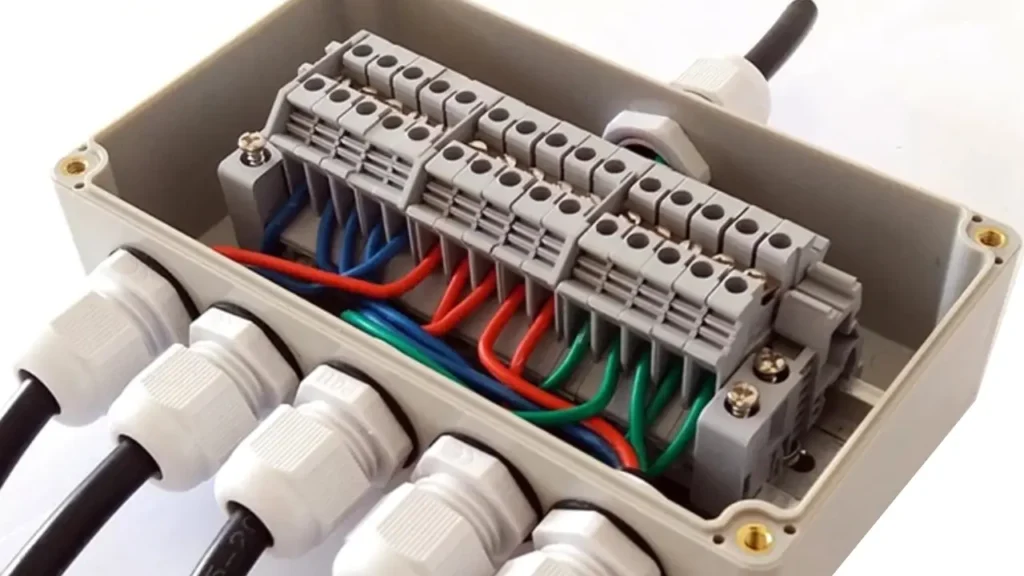
Waterproof terminal blocks are specifically designed to provide robust and reliable electrical connections in environments exposed to moisture, dust, and other contaminants. They feature enhanced sealing mechanisms, often incorporating gaskets, O-rings, or potting compounds, to prevent ingress of liquids and particulates. These blocks are typically constructed from durable, UV-resistant materials that can withstand harsh outdoor or industrial conditions, maintaining electrical integrity even when submerged or subjected to splashes.
The main Features of waterproof terminal blocks are their high IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, excellent sealing properties, and resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation. They often have robust housings and secure locking mechanisms to ensure a tight seal.
Their Benefits include preventing electrical failures caused by moisture, ensuring long-term reliability in challenging environments, and enhancing safety by isolating live components from external elements. They significantly extend the lifespan of connections in damp or dirty settings.
Applications for waterproof terminal blocks are critical in outdoor lighting, marine applications, irrigation systems, industrial machinery exposed to washdowns, tunnel wiring, and any electrical installation in humid or dusty conditions. They are indispensable for solar panel installations, outdoor signage, and other areas where exposure to the elements is unavoidable, ensuring continuous and safe operation regardless of environmental challenges.
High Voltage Terminal Blocks
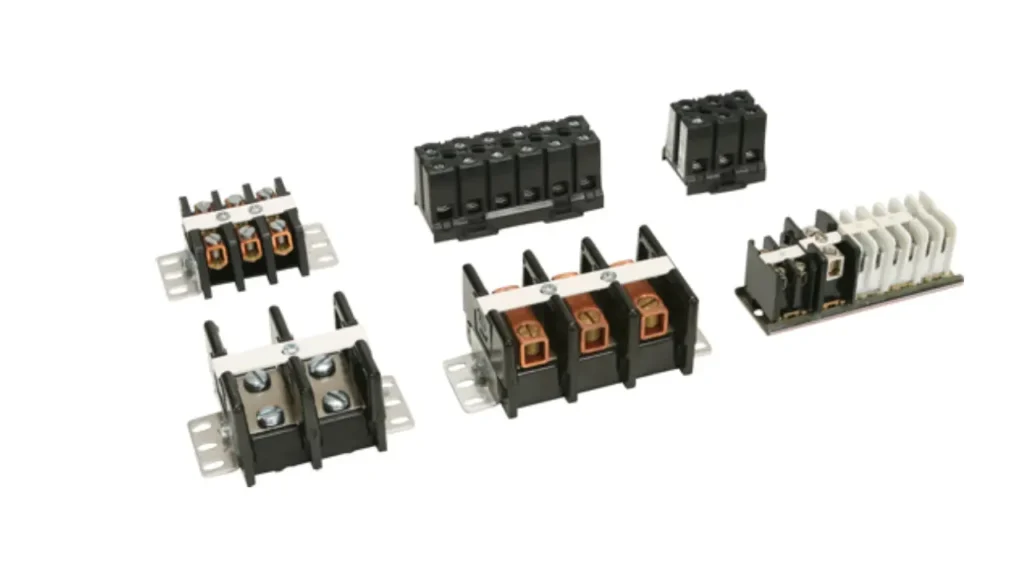

High voltage terminal blocks are specialized connectors engineered to safely handle and isolate circuits operating at elevated voltage levels. They are constructed with significantly increased creepage and clearance distances between conductive parts to prevent arcing and tracking, and they use materials with superior dielectric strength. Their design prioritizes insulation integrity, ensuring that high voltages are safely contained and prevented from causing breakdowns or hazards.
Features of high voltage terminal blocks include enlarged insulation bodies, greater spacing between terminals, and the use of high-dielectric-strength insulating materials like specialized ceramics or high-performance plastics. They often incorporate enhanced safety features to prevent accidental contact.
The Benefits are paramount for safety: they effectively prevent arcing, reduce the risk of insulation breakdown, and ensure reliable operation in high-potential environments. They are crucial for maintaining system integrity and operator safety.
Applications for high voltage terminal blocks are found in power generation and distribution, high-voltage test equipment, industrial motor control panels, renewable energy systems (e.g., wind turbines, solar arrays’ main power circuits), and specialized machinery that utilizes high-voltage components. They are essential wherever electrical potential poses a significant risk if not properly isolated and managed.
High Current Terminal Blocks

High current terminal blocks are robust connectors specifically designed to safely carry large electrical currents without excessive heat buildup or voltage drop. They feature larger conductive cross-sections, often made from highly conductive materials like copper, and larger clamping mechanisms to accommodate thicker gauge wires required for high current flow. Their design prioritizes efficient heat dissipation and low electrical resistance to prevent energy loss and ensure reliable operation.
Key Features of high current terminal blocks include larger physical dimensions, heavy-duty clamping mechanisms, and often multiple connection points per pole to accommodate large conductors. They are designed for superior heat dissipation.
The Benefits are critical for power applications: they ensure stable and efficient power transmission, prevent overheating and potential fire hazards, and minimize voltage drop across the connection, thereby maintaining system performance and reliability.
Applications for high current terminal blocks are widespread in power distribution boards, main circuit connections in industrial machinery, motor control centers, heavy-duty equipment, battery charging stations, and renewable energy installations where significant power needs to be transmitted. They are essential for any system handling substantial amperage, ensuring that high power loads are safely and efficiently managed.
Modular Terminal Blocks

Modular terminal blocks are highly versatile components that allow users to assemble custom terminal strip configurations by combining individual modules. These modules can have different functions, such as standard pass-through terminals, grounding terminals, fused terminals, disconnect terminals, or even components like diodes or LEDs. This “build-your-own” approach offers unparalleled flexibility in designing and adapting wiring solutions to precise application requirements, maximizing space and functionality.
The primary Features of modular terminal blocks are their interlocking design, which allows them to snap together to form a continuous strip, and the wide array of functional modules available. They often support various clamping technologies within the same series.
The Benefits are immense: they provide ultimate flexibility in circuit design, allow for easy customization and expansion of wiring solutions, optimize space utilization in control cabinets, and simplify inventory management as fewer distinct parts are needed.
Applications for modular terminal blocks are prevalent in complex control panels, industrial automation systems, machine building, and any application where specific functionalities need to be integrated into a single wiring solution. They are ideal for creating tailored power distribution blocks, integrated signal and power solutions, or specialized control circuits where standard, fixed terminal blocks would be inefficient or impractical.
Fuse Terminal Blocks

Fuse terminal blocks integrate a fuse holder directly into the terminal block design, providing both electrical connection points and overcurrent protection within a single compact unit. This design streamlines wiring by combining two essential functions, saving space in control panels and simplifying maintenance for fused circuits. They typically allow for easy replacement of the fuse without disturbing the wiring.
Features of fuse terminal blocks include an integrated fuse holder, often with visual indicators for blown fuses, and various fuse types (e.g., glass tube, blade fuse). They are designed for quick and safe fuse replacement.
The Benefits are significant: they save panel space, simplify circuit protection by combining it with termination, and facilitate rapid troubleshooting and fuse replacement, reducing downtime for fault isolation.
Applications for fuse terminal blocks are widespread in industrial control systems, machinery, power supplies, and any application where individual circuits require overcurrent protection. They are commonly used for protecting control circuits, sensor lines, and low-voltage power distribution, ensuring that faults in one part of the system do not cascade and affect other critical components.
Disconnect Terminal Blocks
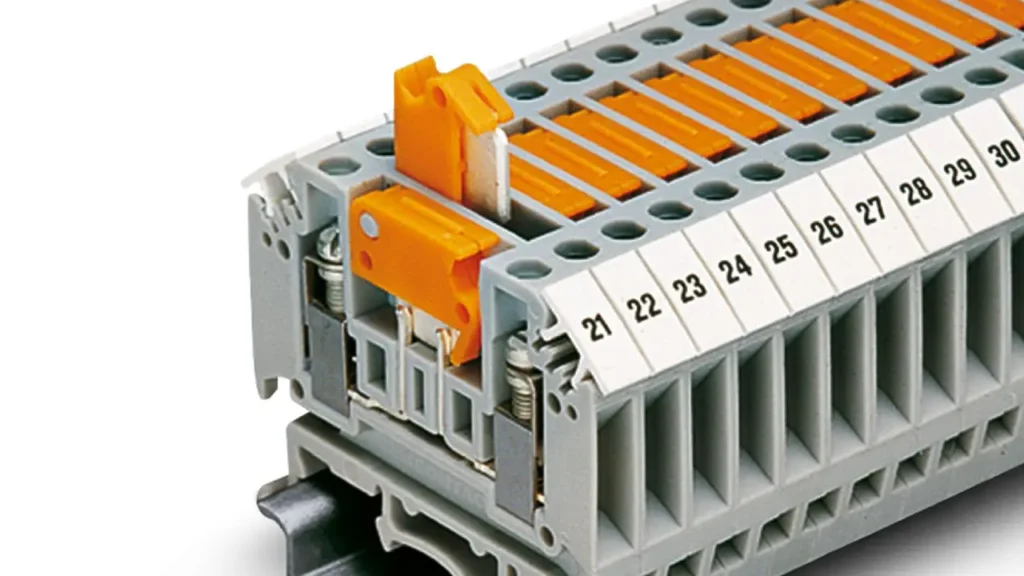
Disconnect terminal blocks, also known as knife disconnect or switch disconnect terminal blocks, provide a convenient and safe way to isolate a circuit without completely removing the wires. They feature a built-in mechanism, often a lever or a knife-edge contact, that allows the electrical connection to be opened or closed manually. This enables easy testing, troubleshooting, or maintenance of individual circuits without disrupting the entire system.
Features of disconnect terminal blocks include an integrated disconnect mechanism, often with a visible indication of the open/closed state, and the ability to accept test plugs. They typically maintain wire integrity even when disconnected.
The Benefits are invaluable for diagnostics and maintenance: they allow for quick and safe isolation of circuits for testing or repair, reduce downtime, and eliminate the need for complicated wiring modifications when temporary disconnections are required.
Applications for disconnect terminal blocks are essential in control panels, instrumentation circuits, and test equipment where frequent circuit isolation for measurement, calibration, or troubleshooting is necessary. They are commonly used in process automation, building management systems, and any scenario where individual circuits need to be easily isolated for maintenance or fault finding.
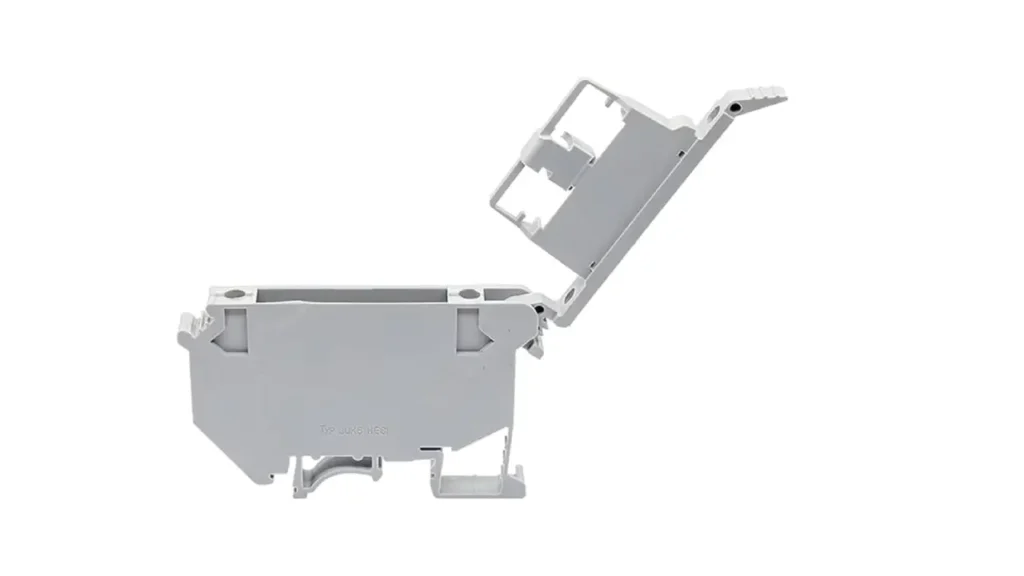
Grounding Terminal Blocks
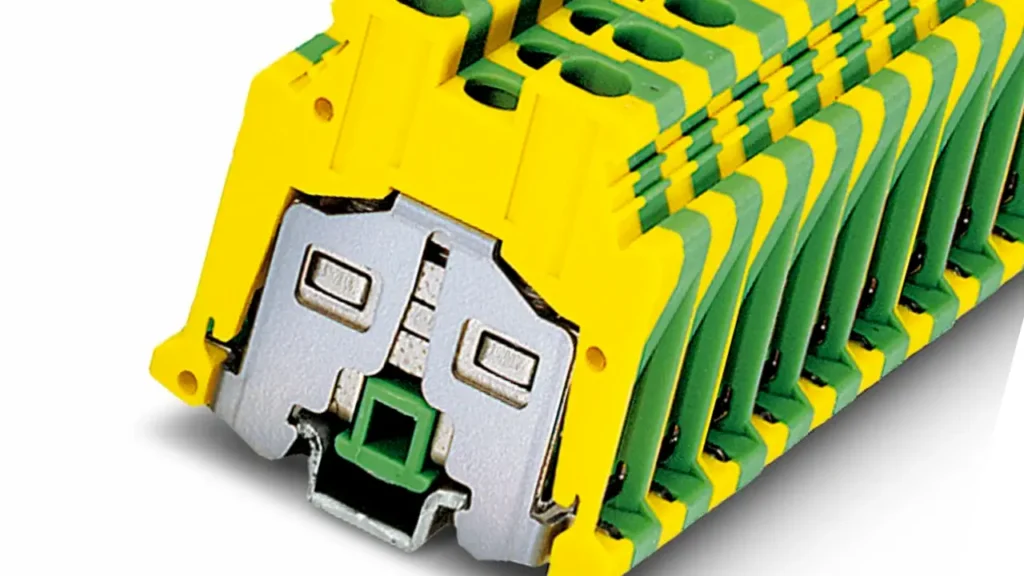
Grounding terminal blocks, also known as earth terminal blocks, are specifically designed to provide a secure and reliable connection to the protective earth (ground) conductor in an electrical system. They feature a direct, low-resistance electrical connection to the DIN rail or mounting surface, which in turn is connected to the system’s main ground bar. This ensures that fault currents are safely diverted to the earth, protecting equipment and personnel from electrical shock.
Features of grounding terminal blocks include a green-yellow color coding (standard for ground), a direct metal-to-metal connection to the mounting rail, and often multiple clamping points for connecting ground wires from different circuits. Their design prioritizes low resistance. The critical
Benefits are enhanced safety and regulatory compliance: they provide a secure and reliable path for fault currents to safely dissipate, reducing the risk of electric shock and ensuring that electrical installations meet safety standards.
Applications for grounding terminal blocks are mandatory in virtually all electrical installations, including industrial machinery, control cabinets, commercial buildings, and residential wiring. They are used to ground metal enclosures, equipment chassis, and the protective earth conductors of power cables, forming an essential part of the electrical safety system.
Thermocouple Terminal Blocks
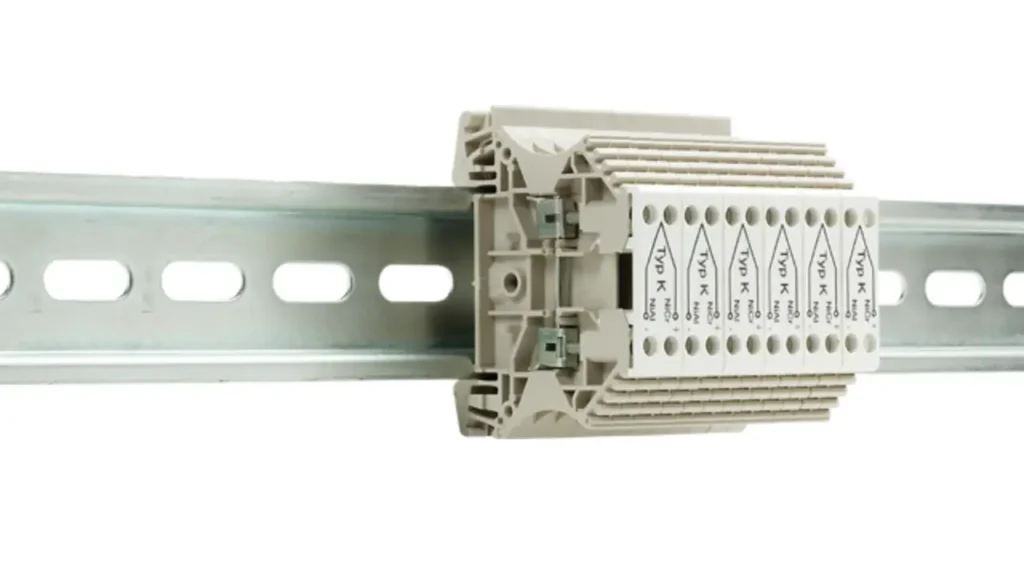
Thermocouple terminal blocks are specialized connectors designed to accurately terminate thermocouple wires without introducing errors due to dissimilar metals. Standard terminal blocks, made from copper, can create unwanted thermocouple junctions if used with thermocouple wires, leading to inaccurate temperature readings. These specialized blocks use the same material as the thermocouple alloy (or a compensating alloy) for the conductive path, ensuring the integrity of the thermocouple circuit.
Features of thermocouple terminal blocks include conductive components made from thermocouple-compatible alloys (e.g., J, K, T, E types), often color-coded according to thermocouple standards, and a design that minimizes thermal gradients across the connection. They maintain the cold junction compensation integrity.
The crucial Benefits are accurate temperature measurement and reliable sensor performance. By preventing spurious thermocouple junctions, they ensure that the signal from the thermocouple accurately reflects the measured temperature.
Applications for thermocouple terminal blocks are indispensable in process control, industrial furnaces, HVAC systems, laboratories, and any application where precise temperature measurement using thermocouples is critical. They are used to connect thermocouples to temperature controllers, data loggers, and other instrumentation, ensuring signal integrity from the sensor to the measurement device.
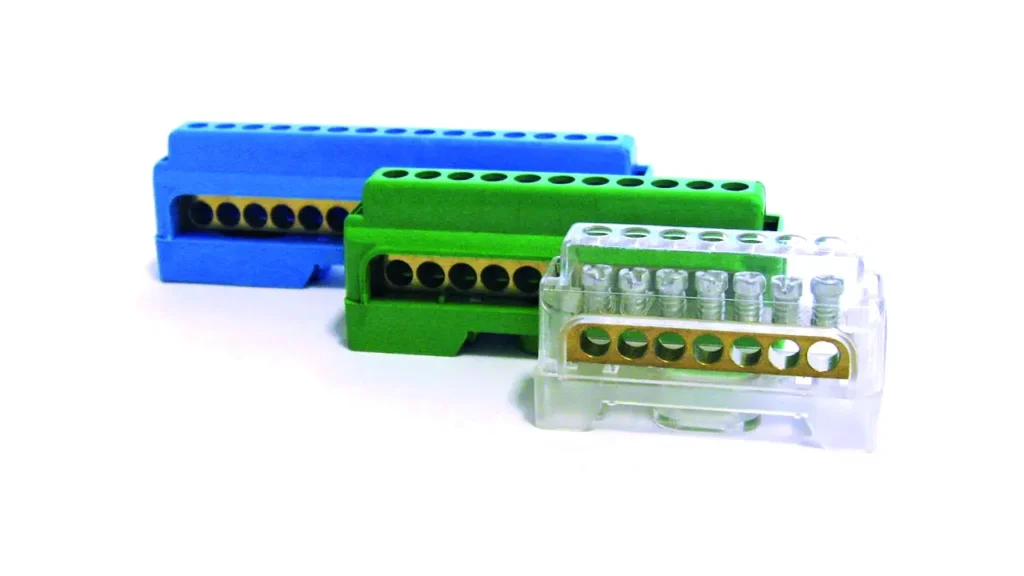
Busbar Terminal Blocks (Power Distribution Blocks)
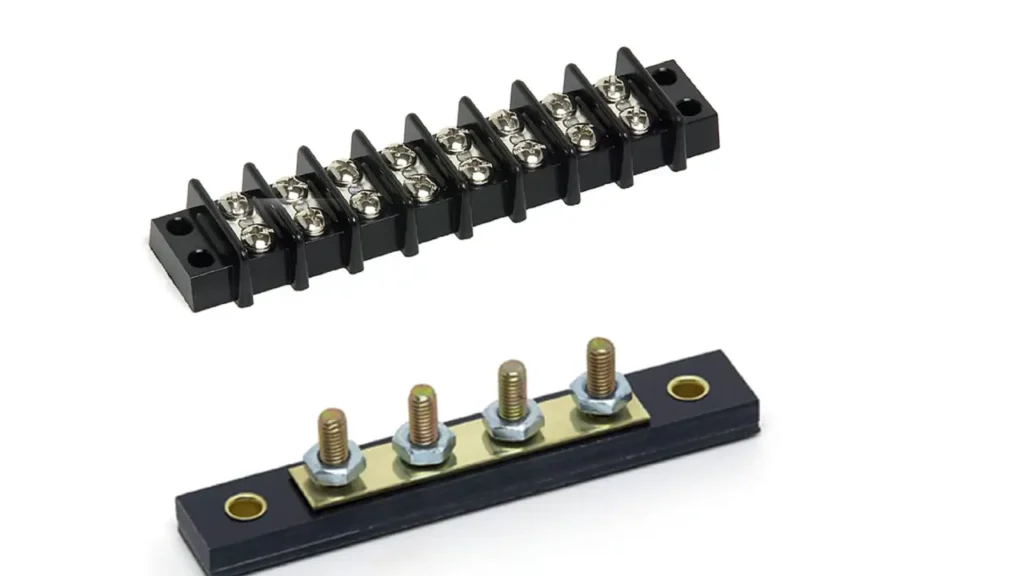

Busbar terminal blocks, often referred to as power distribution blocks, are designed for the efficient and compact distribution of high current or voltage from a single input to multiple outputs. They typically feature a large, robust conductive busbar internally, with numerous tap-off points for individual circuits. This consolidates multiple connections into a single, organized unit, eliminating the need for multiple individual terminal blocks for power distribution.
Features of busbar terminal blocks include a large internal conductive busbar, multiple output terminals, and often options for various input connection methods (e.g., large cable lugs). They are designed for high current capacity and efficient power splitting.
The Benefits are significant: they simplify and streamline power distribution wiring, save considerable panel space, reduce the number of components required, and provide a neat, centralized point for managing power feeds to multiple circuits.
Applications for busbar terminal blocks are common in industrial control panels, motor control centers, power distribution units, machinery power feeds, and large-scale electrical installations where significant power needs to be transmitted. They are essential for any system handling substantial amperage, ensuring that high power loads are safely and efficiently managed.
How to Choose Suitable Terminal Blocks
Choosing the right terminal block is paramount for ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of your electrical system. It’s not a one-size-fits-all decision, as various factors influence the optimal choice for a specific application. Careful consideration of these elements will prevent issues such as overheating, poor connections, and compliance failures.
The selection process involves evaluating both the electrical and mechanical requirements of your project, alongside environmental conditions and industry standards. Matching the terminal block’s specifications to your system’s demands will guarantee optimal performance and longevity.
Here are key factors to consider when choosing suitable terminal blocks:
- Current and Voltage Ratings: Always select a terminal block with current and voltage ratings that meet or ideally exceed the maximum expected values in your circuit. Over-rating by at least 150% is a common best practice to account for surges and ensure safety.
- Wire Size and Type Compatibility: Ensure the terminal block can accommodate the specific wire gauge (AWG or mm²) and type (solid or stranded) you plan to use. Different clamping mechanisms are better suited for different wire types.
- Connection Method: Choose between screw clamp, spring clamp, push-in, or insulation displacement (IDC) based on installation speed, vibration resistance, and ease of maintenance. Screw clamps are versatile, spring clamps offer quick connections, and push-in types are fast for solid or ferruled wires.
- Mounting Option: Consider how the terminal block will be installed. Common options include DIN rail mount (for industrial panels), PCB mount (for electronic circuits), and panel mount (for direct attachment to a surface).
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the operating environment. Factors like temperature range, humidity, dust, and vibration levels will influence the choice of material and construction (e.g., higher IP ratings for wet or dusty environments).
- Number of Poles/Circuits: Determine how many individual connections are needed. Terminal blocks come in various pole counts, and modular designs allow you to build custom lengths.
- Specialized Functions: If your application requires more than just basic wire-to-wire connections, consider specialized terminal blocks such as:
- Grounding Terminal Blocks: For creating secure earth connections.
- Fuse Terminal Blocks: To integrate circuit protection directly into the wiring.
- Disconnect Terminal Blocks: For easy circuit isolation during maintenance or testing.
- Thermocouple Terminal Blocks: For accurate temperature sensor connections.
- High Current/Voltage Terminal Blocks: For power distribution applications.
- Modular Terminal Blocks: For flexible, customizable setups.
- Space Constraints and Orientation: Consider the available space in your enclosure or panel. Terminal blocks come in various profiles (single, dual, or triple level) and wire entry orientations (horizontal, vertical, 45°) to optimize space utilization and accessibility.
- Regulatory Compliance and Certifications: Verify that the chosen terminal blocks comply with relevant safety standards and certifications (e.g., UL, IEC) required for your application and region.
- Quality and Manufacturer Reputation: Opt for terminal blocks from reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality, reliable components. This ensures consistency, performance, and adherence to specifications.
Conclusion
Understanding the diverse types of terminal blocks is crucial for optimizing any electrical project. Each type offers unique advantages in connection method, mounting, and specialized functions, directly impacting system efficiency and reliability. Choosing correctly ensures safe, robust, and adaptable wiring solutions tailored to specific needs.
Ultimately, the right terminal block enhances wiring organization, simplifies maintenance, and boosts overall system performance. A well-informed choice leads to safer installations and cost-effective operations.
For a reliable supply of various terminal block types at competitive prices, get wholesale terminal blocks from us.




