Unlock the secrets of junction box terminals! This comprehensive blog post dives deep into what junction box terminals are, their crucial role in electrical wiring, and the fundamental principles of how they function. Whether you’re a seasoned electrician or a curious homeowner, gain a clear understanding of these essential components that ensure safe and organized electrical connections in various applications.
Explore the different types of junction box terminals, learn about their installation processes, and discover best practices for ensuring reliable electrical circuits. We’ll break down the complexities into easy-to-understand explanations, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently navigate your electrical projects. Understand how these seemingly small parts contribute significantly to the safety and efficiency of your electrical systems.
What Is Junction Box Terminal
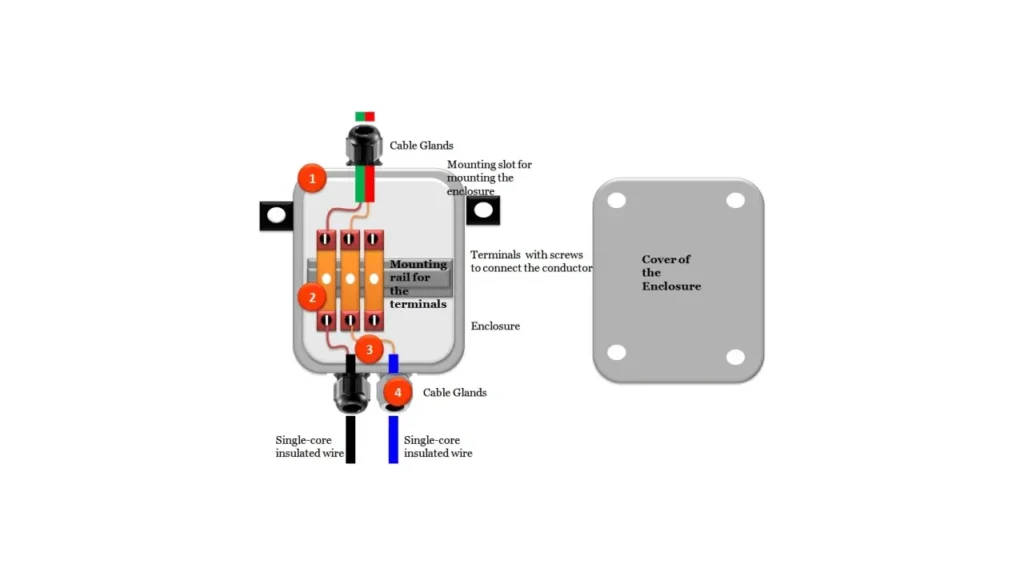
A junction box terminal refers to a specific type of electrical junction box that incorporates terminal blocks or strips inside. Unlike standard junction boxes where wires are typically joined together using wire nuts or other mechanical connectors, a junction box with terminals provides designated points for terminating and connecting wires. These terminals offer a more organized and often more secure method of making electrical connections, especially when dealing with multiple wires that need to be connected in a specific and repeatable manner.
The terminal blocks within these junction boxes usually consist of conductive strips with screw clamps or spring-loaded mechanisms. Each wire is inserted into a specific terminal and then tightened or secured, creating a reliable electrical connection.
This approach simplifies the process of joining wires, especially when dealing with different wire gauges or when connections need to be easily disconnected and reconnected for maintenance or troubleshooting. Junction boxes with terminals are commonly used in control systems, automation, and other applications where organized and secure wiring is essential.
Types of Junction Box Terminal

Junction boxes with terminals offer a structured and organized approach to electrical wiring, providing designated connection points for multiple wires. Instead of relying on wire nuts or direct splicing, these boxes incorporate terminal blocks, simplifying installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
The use of terminals ensures secure and reliable connections, especially in applications requiring frequent adjustments or complex wiring configurations. Different types of junction box terminals cater to various wiring needs and installation environments, offering flexibility and efficiency for a wide range of electrical projects.
Screw Terminals
Screw terminals are a common and versatile type found in junction boxes. They typically consist of a metal strip with a screw that, when tightened, clamps down on the inserted wire, creating a secure electrical connection. These terminals can accommodate a range of wire sizes and are relatively easy to use with standard screwdrivers.
Screw terminals offer a robust connection that can withstand vibration and are suitable for both solid and stranded wires. They are widely used in general-purpose wiring, control circuits, and power distribution applications where a reliable and easily maintainable connection is required.
Spring Clamp Terminals
Spring clamp terminals utilize the force of a spring to secure the inserted wire. These terminals offer a tool-less connection, making wiring faster and potentially more consistent as the clamping force is pre-determined by the spring.
Spring clamp terminals are known for their vibration resistance and ability to maintain consistent contact pressure over time. They are particularly advantageous in applications where quick installation and reliable connections are crucial, such as in automation systems, control panels, and building technology.
Push-in Terminals
Push-in terminals provide an even quicker wiring method, allowing solid or ferruled stranded wires to be directly inserted into the terminal without the need for tools. An internal spring mechanism grips the wire securely. To release the wire, a lever or button is typically pressed.
Push-in terminals are ideal for applications where speed and ease of installation are paramount, such as in residential wiring and some industrial applications. They offer a clean and organized wiring appearance and can save significant time during large-scale installations.
Barrier Strip Terminals
Barrier strip terminals, also known as terminal blocks or terminal strips, consist of a series of individual screw-down terminals separated by insulating barriers. These strips often have multiple connection points and can accommodate multiple wires per terminal in some designs.
Barrier strips provide a robust and organized way to connect multiple circuits or components and are commonly used in control panels, power supplies, and industrial equipment where clear segregation and secure connections are essential. They offer flexibility in wiring configurations and easy access for testing and maintenance.
IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) Terminals
IDC terminals offer a unique method of connection that eliminates the need to strip wire insulation. The terminal has sharp metal contacts that pierce the insulation as the wire is pressed into the connector, establishing an electrical connection with the conductor.
IDC terminals are particularly well-suited for low-voltage and signal wiring, such as in telecommunications, data networks, and some control systems. They provide a fast and reliable connection, often used for terminating multi-conductor cables and creating permanent connections. The gas-tight seal formed by the connection helps prevent corrosion and ensures long-term signal integrity.
Fuse Terminals
Fuse terminals are specialized terminal blocks that incorporate a fuse holder directly into the connection point. This design allows for easy circuit protection at the terminal level. If an overcurrent occurs, the fuse within the terminal will blow, interrupting the circuit and protecting downstream components.
Fuse terminals are commonly used in control circuits, power distribution, and machinery where individual circuit protection is required and easy fuse replacement is essential. They help in quickly identifying and resolving overcurrent issues, minimizing downtime and enhancing system safety.
Grounding Terminals
Grounding terminals are specifically designed for creating secure and reliable earth ground connections within a junction box. They typically feature a robust clamping mechanism and are often connected directly to the metal body of the junction box to ensure a low-impedance path to ground.
Proper grounding is crucial for electrical safety, providing a path for fault currents to flow safely to the earth, preventing electric shock hazards and protecting equipment from damage. Grounding terminals are essential in all electrical installations and are often color-coded green or have a ground symbol for easy identification.
Thermocouple Terminals
Thermocouple terminals are specialized terminal blocks designed to minimize the creation of unwanted thermal electromotive force (EMF) when connecting thermocouple wires. Thermocouples are temperature sensors that generate a small voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two dissimilar metals.
To ensure accurate temperature readings, the terminals used for connecting thermocouple wires must be made of the same or compatible materials as the thermocouple alloys (e.g., Chromel, Alumel, Constantan). These terminals often have a specific color coding to match the thermocouple type and are crucial in industrial temperature measurement and control applications where precise readings are essential.
Barrier Terminals with Test Points
Some barrier strip terminals come equipped with integrated test points. These small receptacles or posts allow for easy connection of test probes and measurement instruments without having to disconnect the wiring. Test points are invaluable for troubleshooting, diagnostics, and routine maintenance of electrical circuits.
They provide a safe and convenient way to take voltage, current, or resistance readings at specific points in the circuit without interrupting its operation. Barrier terminals with test points are commonly found in control panels, power distribution systems, and industrial automation equipment where regular monitoring and testing are required.
Knife Disconnect Terminals
Knife disconnect terminals provide a means to quickly and visually interrupt an electrical circuit without having to completely remove a wire. They feature a hinged or removable “knife” or blade that can be opened to break the connection.
These terminals are useful for isolating circuits for maintenance, testing, or safety purposes. The open state of the knife provides a clear visual indication that the circuit is disconnected. Knife disconnect terminals are often used in control systems, instrumentation, and safety circuits where the ability to quickly isolate parts of the system is important.
How to Terminate Wires in Junction Box
Terminating wires in a junction box correctly is crucial for safety and ensuring proper electrical function. This process involves securely connecting wires together based on their function (hot, neutral, ground) and the requirements of the circuit. Using the appropriate tools and techniques will result in reliable connections that are protected within the junction box. Always ensure the power to the circuit is turned off at the main breaker before beginning any wiring work.
Step 1: Prepare the Wires
Begin by carefully stripping the insulation from the ends of the wires that need to be connected within the junction box. The amount of insulation to remove typically ranges from 3/4 to 1 inch, but it’s best to refer to the instructions provided with your chosen wire connectors for the recommended stripping length. Take care not to nick or damage the copper conductors underneath the insulation, as this can weaken the wire and potentially lead to future failures. Separate the wires based on their color-coding: black or red for hot wires, white for neutral wires, and bare copper or green for ground wires.
Step 2: Connect the Ground Wires
The first connections to make are the ground wires. Gather all the bare copper or green wires within the junction box and twist them together firmly. Once they are securely twisted, use a green wire nut specifically designed for grounding to cap the connection. If the junction box is made of metal, you will also need to attach a grounding pigtail (a short piece of ground wire) to the metal box itself, usually using a grounding screw, and then connect this pigtail to the other ground wires with the green wire nut. A proper ground connection provides a safe path for electrical fault currents.
Step 3: Connect the Neutral Wires
Next, proceed to connect all the neutral wires, which are typically white. Twist the white wires together tightly to ensure good electrical contact. Then, screw on a wire nut that is appropriately sized for the number and gauge of wires you have joined. Make sure that no bare wire is exposed below the wire nut. The neutral wires provide a return path for the electrical current and should always be kept separate from the hot and ground wires within the junction box.
Step 4: Connect the Hot Wires
Now, connect the hot wires, which are usually black or red. The specific way you connect these will depend on the purpose of the junction box and the circuit’s wiring configuration. For example, you might be joining an incoming hot wire to several outgoing hot wires that feed different light fixtures or outlets. Twist the appropriate hot wires together securely and then cap the connection with a wire nut of the correct size. It is crucial to never connect hot wires from different circuits together.
Step 5: Secure the Connections
After making each wire connection, gently tug on the wires to ensure they are securely held by the wire nuts or other connectors you are using. This step helps to verify that the connection is mechanically sound and will not easily come apart. If a wire pulls out, re-do the connection, ensuring a tighter twist and a properly seated wire nut. Secure connections are essential for preventing loose wires, which can cause flickering lights, power outages, or even electrical fires.
Step 6: Neatly Arrange the Wires
Carefully fold and tuck the connected wires into the junction box. Arrange them so that they are not overly crowded or putting strain on the connections. The goal is to have the wires fit neatly within the box without being pinched or damaged when the cover is installed. Ensure that the wire nuts are not being forced or stressed by the positioning of the wires. A well-organized box makes future troubleshooting and modifications easier.
Step 7: Install the Junction Box Cover
Finally, securely attach the cover to the junction box. The cover provides physical protection for the wire connections inside, preventing accidental contact with live wires and shielding them from dust and debris. Use the appropriate screws or snap-fit mechanisms to ensure the cover is firmly in place. A properly installed cover is a crucial safety component of the electrical installation.
Conclusion
Junction boxes with terminals serve as essential components in electrical installations, providing a safe, organized, and accessible point for connecting and distributing multiple wires. The integrated terminal blocks within these boxes simplify the wiring process, allowing for secure and efficient connections without the need for twisting wires and using separate connectors. This not only streamlines installation but also facilitates easier troubleshooting and future modifications to the electrical system.
The versatility of junction boxes with terminals makes them suitable for a wide array of applications, from residential wiring to complex industrial control systems. By offering a protected enclosure for these crucial connections, they enhance safety by preventing accidental contact and shielding the wiring from environmental factors. Choosing the right junction box with appropriate terminal configurations is vital for ensuring a reliable and compliant electrical installation.
For businesses and projects seeking high-quality and cost-effective junction boxes with integrated terminals, Linkwell Electronics stands as a reputable wholesale manufacturer based in China. Their expertise in producing a diverse range of electrical connection solutions makes them a reliable partner for sourcing dependable junction boxes with terminals tailored to various specifications and requirements. Consider Linkwell Electronics for your wholesale needs to ensure efficient and secure electrical connectivity.




