You probably notice your electronics get warm during use. That heat can shorten a device’s life if you don’t manage it properly. Thermal management solutions keep your electronics safe by controlling temperature. These include both passive and active cooling methods. Passive cooling uses things like heat sinks or vented enclosures, while active cooling relies on fans or air conditioners. Over 55% of device failures come from temperature problems, so picking the right electronics thermal solution really matters. Linkwell stands out as a trusted partner for industrial cooling, helping you protect your equipment and keep everything running smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- Electronics generate heat during use, which can lead to damage and reduced lifespan. Proper thermal management is essential to keep devices running smoothly.
- Passive cooling solutions, like heat sinks, use natural processes to dissipate heat without extra energy. They are ideal for low-power devices and environments with good airflow.
- Active cooling methods, such as fans and air conditioners, are necessary for high-performance electronics that generate significant heat. They provide faster heat removal but require more maintenance.
- Choosing the right cooling solution depends on your device’s power level, the environment, and your budget. Assess these factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Linkwell offers customized cooling solutions tailored to specific industry needs, ensuring reliable thermal management for various applications.
Thermal Management Overview for Electronics
Why Electronics Need Cooling
You might wonder why your electronics need cooling in the first place. Every device you use, from your phone to industrial machines, creates heat as it works. If you ignore this heat, you risk damaging your devices. Overheating can cause all sorts of problems, like slower performance, shorter battery life, or even permanent damage to the parts inside.
Take a look at what can happen when electronics get too hot:
| Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Damage | Heat can melt solder joints or warp circuit boards, leading to costly repairs. |
| Reduced Lifespan | Components wear out faster, so your device fails sooner. |
| Performance Degradation | Devices may lag, freeze, or shut down unexpectedly. |
| Shortened Battery Life | Batteries lose capacity and die quicker. |
| Material Deformation | Parts can bend or break, causing more failures. |
Thermal management systems help you avoid these issues. They keep your electronics running smoothly, make them last longer, and improve reliability. You get better performance and fewer headaches.
Tip: Good cooling isn’t just for big machines. Even small gadgets benefit from proper heat control.
How Heat Is Generated in Devices
So, where does all this heat come from? Most of it starts with the main parts inside your electronics. Here are the usual suspects:
- Central Processing Units (CPUs): These chips work hard and get hot during calculations.
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): They heat up fast when handling graphics or video.
- Power Electronics: Parts like MOSFETs and IGBTs generate heat in high-power systems.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): These tiny chips can still produce a lot of heat.
- LEDs and Displays: Even your screen and lights add to the heat load.
As devices get smaller and more powerful, managing heat becomes even more important. That’s why you need a solid thermal management overview before choosing a cooling solution.
Passive Cooling Solutions Explained

Principles of Passive Cooling
You might wonder how passive cooling systems work without fans or moving parts. The answer lies in the basic laws of physics:
The laws of physics define three ways heat is moved: radiation, conduction, and convection. Radiation involves heat transfer as infrared electromagnetic waves, conduction is the flow of heat through solid materials, and convection is the transfer of heat by a fluid. These principles are essential in understanding how passive cooling operates in electronics.
Passive cooling solutions use these natural processes to move heat away from sensitive parts. You don’t need extra energy or complicated controls. Instead, you rely on smart design and materials to keep things cool.
Heat Sinks and Natural Convection
Heat sinks play a huge role in passive cooling. Here’s how they help your devices stay safe:
- Heat sink absorbs heat from the device through conduction.
- Heat is transferred to the surrounding air or liquid through convection.
- This process disperses heat over a larger area, significantly reducing the device’s temperature.
You often see heat sinks with fins or ridges. These shapes increase the surface area, which helps move more heat into the air. Natural convection then carries the warm air away. The bigger the surface area, the better the heat sinks work.
| Heat Transfer Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Heat moves from the device into the heat sinks. |
| Convection | Heat leaves the heat sinks and enters the surrounding air. |
You’ll find heat sinks in power supplies, inverters, and many other electronics. Their design makes a big difference in how well your device handles heat.
Applications in Low-Power Devices
Passive cooling solutions shine in low-power devices. You see them in:
- Embedded AI processors, like the AMD Kria K24 SOM, which runs on just 2.5 watts and uses a passive heat sink.
- Heat pump water heaters, which cool as a byproduct without extra energy.
These devices don’t need fans or active cooling. Instead, they rely on heat sinks, ventilation grills, and filtered vents to stay cool.
Linkwell Electrical Enclosure Ventilation
If you need reliable passive cooling for your electrical enclosures, Linkwell has you covered. Their electrical enclosure ventilation products use smart airflow designs to keep your components safe. Here’s what makes them stand out:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-efficiency fans and filters | Reduces heat buildup and keeps components dry, preventing electrical failures and boosting system performance. |
| Ventilation mechanisms | Allows cooler outside air to enter and warmer inside air to escape, maintaining safe operating temperatures. |
| Removal of unwanted elements | Eliminates moisture, dust, fumes, and vapors that can damage components and interfere with performance. |
| Various ventilation types | Includes small openings, louvered windows, ventilation panels, and fan systems for effective airflow control. |
| Advanced systems | May include thermostats, filters, or heat exchangers for better control and cleaner airflow. |
You can trust Linkwell’s passive cooling systems to protect your electronics, lower maintenance needs, and extend the life of your equipment.
Active Cooling Solutions for Electronics
Principles of Active Cooling
When you need to cool electronics that generate a lot of heat, passive methods might not be enough. That’s where active cooling steps in. You use devices like fans or air conditioners to move heat away from sensitive parts. These systems rely on conduction and convection. Heat moves from hot components to cooler areas, and fans or coolants help carry it away faster. The Second Law of Thermodynamics tells us that heat always flows from hot to cold. Active cooling solutions use this principle to keep your electronics safe and efficient.
| Feature | Passive Cooling | Active Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Zero parasitic power loss. | Consumes a small amount of energy (typically 5-15W), slightly reducing net system efficiency. |
Fans, Air Conditioners, and Thermoelectric Coolers
You have several options for active cooling. Fans are the most common. They push air across hot surfaces, speeding up heat removal. Air conditioners use refrigerants and compressors to cool the air inside enclosures. Thermoelectric coolers work differently. They use electricity to create a temperature difference at a junction of two materials. This setup can cool or heat, depending on the direction of the current. Thermoelectric coolers are great for small spaces and run quietly, making them perfect for noise-sensitive areas.
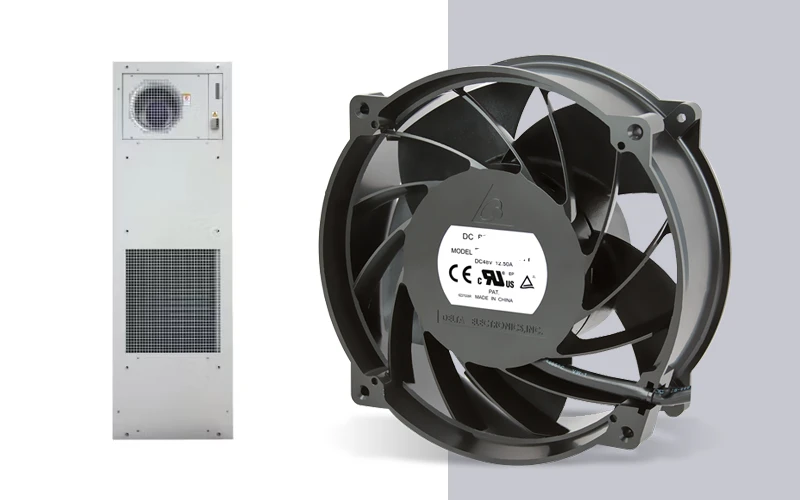
Linkwell Cabinet Air Conditioner and Axial Fan
If you want reliable cooling, Linkwell offers top-notch products. The Cabinet Air Conditioner keeps your control cabinets and sensitive electronics at the right temperature, even in tough environments. It features energy-efficient compressors, digital controls, and rugged construction. Linkwell’s Axial Fan, like the FL17238HA2B model, delivers strong airflow (300–378 m³/h), runs at 230 V AC, and lasts up to 50,000 hours. The Computer Chassis Fan is another great choice for stable, quiet cooling in IT and industrial setups.
Applications in High-Power Systems
You’ll find active cooling solutions in places where electronics work hard. Inverters in photovoltaic systems need fans or air conditioners to stay cool under high temperatures. Power electronics in factories rely on these systems to avoid overheating. You also see them in telecom cabinets, data centers, and anywhere reliable performance matters. Active cooling keeps your equipment running longer and safer, even in extreme conditions.
Comparing Passive and Active Electronics Thermal Solutions
When you look at cooling options for your devices, you’ll see two main paths: passive and active. Each electronics thermal solution has its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s break down what you need to know so you can make the best choice for your setup.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
You want your electronics thermal solution to be reliable, cost-effective, and easy to maintain. Here’s a quick comparison to help you see the differences:
| Cooling Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Passive Cooling | – Quiet operation – Reliable (no moving parts) – Energy-efficient – Lower initial and maintenance costs | – Less effective under high thermal loads – Efficiency depends on airflow and materials |
| Active Cooling | – Higher cooling capacity – Suitable for high-performance electronics – More effective for high thermal loads | – Increased cost – Noisy due to moving parts – Requires maintenance – Shorter lifespan due to mechanical wear |
Passive cooling works well when you want silent operation and low maintenance. You don’t have to worry about fans breaking down or dust clogging moving parts. You also save on energy bills because these systems don’t use extra power.
Active cooling steps up when your electronics thermal solution needs to handle more heat. Fans, air conditioners, and thermoelectric coolers push heat out quickly. You get better performance in high-power setups, but you might deal with more noise and higher costs. You also need to clean and check these systems regularly to keep them running smoothly.
Tip: If you want a solution that lasts longer and needs less attention, passive cooling is a solid choice. If your equipment runs hot or works in tough conditions, active cooling is the way to go.
Ideal Use Cases for Passive vs. Active Cooling
You might wonder which electronics thermal solution fits your needs. Here’s how you can decide:
- Passive Cooling
- Great for low-power devices like sensors, small controllers, and embedded systems.
- Works best in quiet environments, such as offices or classrooms.
- Fits budget-friendly projects where you want to keep costs down.
- Perfect for places with good airflow and moderate temperatures.
- You don’t need to worry about regular maintenance.
- Active Cooling
- Essential for high-performance computers, gaming rigs, and servers.
- Used in data centers, where keeping temperatures low is critical for reliability.
- Needed in industrial settings, like metalworking or plastics manufacturing, where machines generate lots of heat.
- Important for automotive electronics, especially in electric vehicles and engine control units.
- Works well in areas with poor airflow or high ambient temperatures.
| Scenario | Passive Cooling | Active Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Requirements | Low-power devices | High-power applications |
| Environmental Factors | Good airflow, moderate temperatures | Poor airflow, high ambient temperatures |
| Space Constraints | Larger enclosures | Compact form, limited space |
| Budget Considerations | Cost-effective | Higher initial investment |
| Noise Sensitivity | Silent operation | May produce noticeable noise |
You should also think about common failure modes. Passive systems sometimes struggle with high-performance devices because they can’t move enough heat. Active systems can break down due to worn-out fans or dust buildup. You need to clean active cooling systems and replace parts when they wear out.
When you choose an electronics thermal solution, look at your device’s power level, the environment, and your budget. Passive cooling is simple and quiet, while active cooling gives you more power and control. The right choice keeps your electronics safe and running for years.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Management Solution
Assessing Device Type and Environment
Choosing the right cooling method starts with knowing your device and where it operates. You need to think about the materials inside your electronics, how much heat they spread, and if the space allows for good airflow. High ambient temperatures or poor ventilation can make cooling harder. You also want to keep user safety in mind, especially if your device is portable or used in public spaces. Here are some things you should check before picking a solution:
- Material properties
- Ambient temperature
- User safety
- Device portability
- Heat-spreading restrictions
- Convection limitations
- Affordability
- Maintenance needs
If your device faces heat-spreading restrictions or convection limitations, you may need a more advanced cooling system. High ambient temperatures call for solutions that can handle extra stress. Always look at the environment—temperature, humidity, and airflow all affect how well your cooling works.
Tip: Devices in hot, humid places need stronger cooling than those in cool, dry rooms.
Performance, Cost, and Maintenance Factors
You want your electronics to run smoothly without breaking the bank. Passive cooling works well in moderate temperatures and open spaces. It costs less up front and needs almost no maintenance. Active cooling gives you better performance in tough conditions, but it costs more and needs regular cleaning. Here’s a quick table to help you compare:
| Feature | Passive Cooling | Active Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Great in moderate temperatures, good airflow | Best in high temperatures, enclosed spaces |
| Reliability & Maintenance | Very reliable, almost no maintenance | Needs cleaning, moving parts can wear out |
| Cost | Low initial and zero operational cost | Higher initial, some operational cost |
Regular inspections and cleaning help keep your cooling system working well. If you use fluids, check their quality often. Set up a schedule for maintenance and keep an eye on key parameters to catch problems early.
Linkwell’s Custom Solutions for Industry Needs
You might need a cooling system that fits your unique setup. Linkwell offers custom options for many industries. You can choose smart thermostats, special filters, protective grills, and even custom colors to match your cabinets. If you need a certain mounting style or airflow pattern, Linkwell can adjust the design for you. They also provide tailored control software for better management. You can pick from AC, DC, or EC axial fans, and even centrifugal fans for special projects.
| Customization Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Smart start/stop for energy savings |
| Filter | Blocks dust and contaminants |
| Protective Grill | Keeps out foreign objects |
| Custom color matching | Matches your cabinet style |
| Special mounting configurations | Fits your installation needs |
| Modified air flow patterns | Meets your cooling requirements |
| Tailored control software | Advanced control features |
With Linkwell, you get thermal management solutions that fit your device, environment, and industry. You can trust their expertise to keep your electronics safe and efficient.
Conclusion
You’ve learned a lot about keeping your electronics cool. Picking the right cooling method makes a big difference in how long your devices last and how well they work. Let’s look at the main differences between passive and active cooling. This table sums it up:
| Aspect | Active Cooling | Passive Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Power Use | Needs external power | No extra power needed |
| Maintenance | More frequent upkeep | Minimal upkeep |
| Noise | Can be loud (fans, pumps) | Silent |
| Cooling Potential | High capacity possible | Limited by design |
You can see that passive cooling works best when you want silence and low maintenance. Active cooling steps in when you need more power and control. Both have their place, and your choice depends on your device and environment.
If you ignore heat, you risk damaging your electronics. Too much heat can cause parts to wear out, slow down, or even fail early. Engineers face challenges like temperature rise, hotspots, and thermal cycling. As devices get smaller and more powerful, good thermal management becomes even more important for performance and reliability.
You want your electronics to last. Heat speeds up chemical reactions and can cause corrosion or aging in materials. That’s why you need to keep things cool, especially in tough conditions.
Linkwell’s products have proven their value in real-world situations. For example:
| Case Study Description | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Wall-mounted enclosure at a coastal depot | Zero water leaks after 6 years |
| Thermally bonded panels in racks | Internal temps dropped by 15°C, longer life |
| EV toll-road operator | No shutdowns during 47°C heatwaves |
| Maintenance teams in cold climates | Zero faults at –40°C; fans never iced over |
When you choose Linkwell, you get reliable cooling that stands up to harsh environments. You protect your investment and keep your systems running strong. Don’t let heat cut your electronics’ life short—pick the right solution and trust Linkwell to help you stay cool.
You now know the key differences between passive and active cooling. Passive cooling works quietly and needs little upkeep. Active cooling handles more heat but asks for regular checks. Good thermal management keeps your electronics safe and helps them last longer. When you pick a solution, think about heat levels, space, and safety standards. If you want reliable cooling, Linkwell offers EC fans for new setups and certified products for tough environments. You get peace of mind and strong performance.
FAQ
What’s the difference between passive and active cooling?
Passive cooling uses heat sinks or vents. You don’t need extra power. Active cooling uses fans or air conditioners. These need electricity and move heat faster. You pick based on your device’s heat level.
How do I know which cooling solution fits my device?
Check your device’s power and where you use it. Low-power gadgets work well with passive cooling. High-power systems or hot environments need active cooling. You can ask Linkwell for advice.
How often should I maintain my cooling system?
You should inspect fans and filters every few months. Clean dust and replace filters as needed. Passive systems need less attention. Active systems work best with regular checks.
Can Linkwell customize cooling solutions for my project?
Yes! Linkwell offers custom fans, filters, and mounting options. You can request special colors or control features. Their team helps you match the solution to your needs.