Choosing the right fan for your equipment makes a big difference. You need to understand how fan curve analysis works to get the best results. When you study how static pressure, airflow, and fan speed connect, you can match your fan to your system for better cooling.
- Fan curve analysis helps you pick the best fan for each job.
- Looking at fan curves lets you find the most efficient operating point.
- Knowing these details helps you control fans and meet your system’s needs.
Linkwell’s advanced fan products show how smart choices create reliable and energy-saving solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Learn about fan curves to pick the best fan for cooling. This helps get the right airflow and static pressure.
- Use fan curve analysis to find the best working point. This saves energy and makes your system work better.
- Match fan features, like airflow and static pressure, to what your equipment needs. This stops overheating and makes things more reliable.
- Think about things like temperature and humidity when picking a fan. This helps the fan work well in real life.
- Follow easy steps to choose a fan, like checking size, noise, and how much energy it uses. This helps you get better and smarter cooling.
Fan Curve Analysis Basics
What Is a Fan Curve?
A fan curve is a chart that shows how a fan works. It helps you see how much air the fan can move. It also shows how much pressure the fan can make. The main parts of a fan curve are static pressure, airflow, and power use. Static pressure means how hard the fan pushes air against things in the way. Airflow tells you how much air the fan moves in one minute. This is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Power use is how much energy the fan needs to run. When you look at a fan curve, you can find the best spot for your cooling needs. Where your system’s curve meets the fan’s static pressure curve is the best place for the fan to work.
Tip: The Air Movement and Control Association (AMCA) gives rules for reading fan curves. These rules help you pick the right fan for your job.
Key Fan Characteristics
You should know the main things to look for in fan curve analysis. Here is a table that shows the most important ones:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Static Pressure | The force the fan uses to push air through tight spots or filters. Higher numbers mean the fan works better in hard places. |
| Air Volume (CFM) | The total air the fan moves in one minute. A higher CFM means more air moves. |
| Brake Horsepower (BHP) | The power the fan needs to move air and make pressure. This changes how much energy the fan uses. |
Modern fans use new designs to help airflow and static pressure. Some fans, like Linkwell’s Computer Chassis Fan and Electrical Enclosure Fan, use smart controls and strong parts to work better and save energy.
Why Fan Curve Analysis Matters
Fan curve analysis helps you choose the best fan for your cooling system. You need to match the fan’s airflow and pressure to what your equipment needs. If you pick the wrong fan, your system could get too hot or waste energy. Engineers use fan curves to set limits for air speed and pressure drop. This helps you make good choices and keeps your equipment safe. You also follow the rules for airflow, pressure, and noise. Linkwell’s skill in cooling gives you products that meet these rules. When you use fan curve analysis, you get better cooling, less noise, and more efficiency.
- Knowing fan laws helps you see how fans work in your system.
- Finding the right spot on the fan curve makes sure your cooling needs are met.
- Knowing how airflow and pressure work together helps you get the best from your fan.
Reading Fan Performance Curves
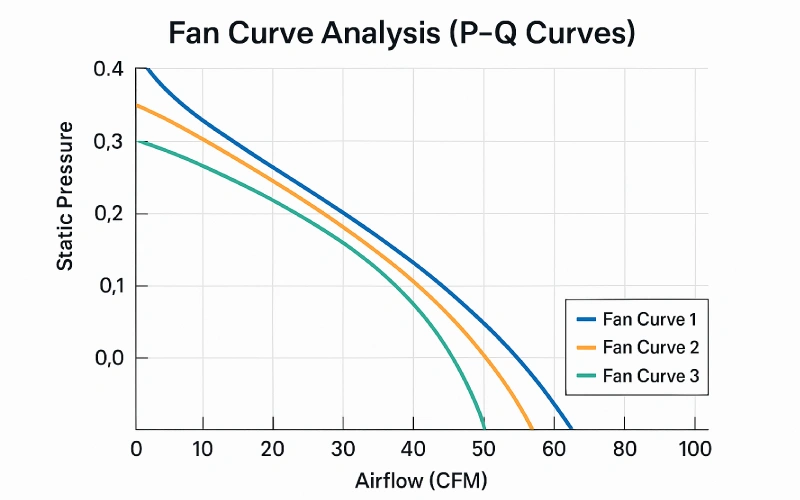
Static Pressure vs. Airflow
You can learn about fan performance curves by seeing how static pressure and airflow work together. When airflow goes up, static pressure goes down. If you block the space, static pressure gets higher and airflow gets lower. An open cabinet lets the fan move the most air with almost no pressure. A closed cabinet makes the fan push against the most pressure, but airflow drops to nothing.
Note: The fan gets its highest static pressure when airflow is zero. It gets the most airflow when static pressure is zero. Every spot between these two points is shown on the curve.
Linkwell’s Computer Chassis Fan works best in open cases. It gives lots of airflow for cooling. The Electrical Enclosure Fan is made for closed cabinets. It needs more static pressure to push air through filters and tight spots.
Steep and Flat Curves
Fan performance curves can be steep or flat. Steep curves mean the fan keeps moving air even when static pressure rises. These fans are good for places with lots of resistance, like dusty or tight spaces. Backward curved fans are efficient and handle high pressure well. They are great for factories and big machines. Flat curves show fans that move a lot of air but lose pressure fast. Forward curved fans are quieter and work well in offices or homes.
| Curve Type | Best Use Case | Example from Linkwell |
|---|---|---|
| Steep Curve | High pressure, dusty areas | Electrical Enclosure Fan |
| Flat Curve | High airflow, low noise | Computer Chassis Fan |
Fan Speed and Frequency
Fan speed changes the shape of the fan curve. When you make the fan go faster, the curve moves to the right. This means the fan can move more air and make more pressure. PQ curves show how airflow and static pressure change with speed. You can use these curves to pick the right fan and fix cooling problems.
Tip: Always look at the working points on the curve. Do not pick a point past the bend, or the fan may not work as you expect.
If you need more airflow, choose a fan with a curve that meets your needs at the right static pressure. Linkwell’s fans come in many speeds and curve shapes. This helps you match the fan to your system.
Fan Curve Analysis in Applications
Industrial and IT Cooling
Cooling in factories and IT rooms can be hard. Fan curve analysis helps you fix these problems. It keeps your machines working well.
- Fan performance curves help you pick the right fan for each job. This makes sure you get the airflow and pressure you need.
- Fan curves help you spot problems like blocked filters or closed dampers. These issues can make cooling less effective.
- When you know how to read fan curves, you can make fans work better. This means less downtime and better system performance.
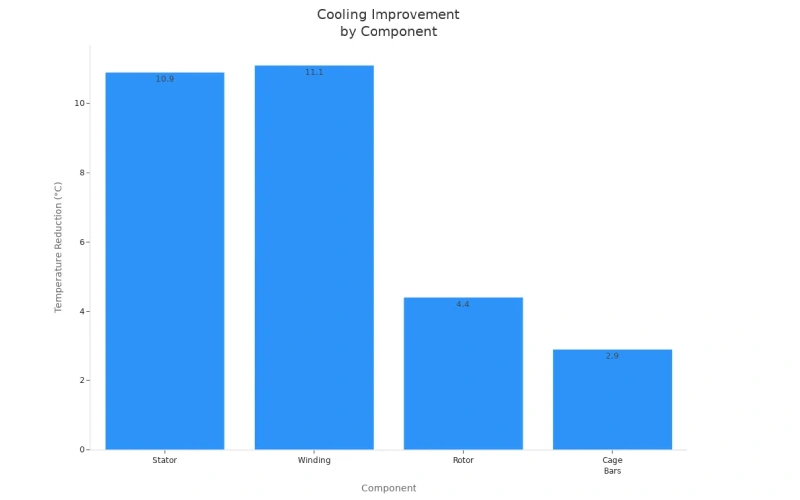
You can see how fan curve analysis helps by looking at numbers. The table below shows how the best fan model lowers the temperature of important machine parts:
| Component | Original Model Temperature (°C) | Optimal Model Temperature (°C) | Temperature Reduction (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator | 124.1 | 113.2 | 10.9 |
| Winding | 121.4 | 110.3 | 11.1 |
| Rotor | 87.2 | 82.8 | 4.4 |
| Cage Bars | 88.1 | 85.2 | 2.9 |
Fan curve analysis also helps you use less energy. The next table shows how picking the right fan saves energy in different places:
| Location | Month | Conventional Cooling Energy Consumption (kWh) | Developed Cooling Energy Consumption (kWh) | Utility Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incheon | 7 | 335.5056 | 321.3907 | 8090 |
| Daejeon | 7 | 419.4348 | 389.5906 | 32,020 |
| Busan | 7 | 417.7351 | 391.3584 | 32,540 |
You should think about the environment when choosing a fan. Temperature and humidity can change how your fan works. The table below shows how these things affect fan performance:
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Fan Performance |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Affects material selection and durability of fan blades |
| Humidity | Influences airflow dynamics and energy efficiency |
You also need to think about shock, vibration, and air cleanliness. These things can change how your fan works in real life.
Renewable Energy and Medical
Cooling needs are different in renewable energy and medical equipment. Medical devices get hot when used. You need good cooling to keep them safe and working right. Fans help keep medical equipment at safe temperatures and meet strict rules.
Renewable energy systems also need cooling, but the needs change with the technology and place. Fans cool electronic boxes in wind and solar power systems. The way each system is built changes what kind of fan you need.
- Medical equipment needs fans to keep devices safe and up to code.
- Renewable energy systems use fans to cool electronic boxes.
You must match the fan curve to your job. Medical equipment often needs quiet fans with steady airflow. Renewable energy may need fans that can handle heat and changing weather.
Linkwell Product Solutions
You can use Linkwell’s Computer Chassis Fan and Electrical Enclosure Fan for many jobs. These fans help you solve cooling problems in factories, IT, renewable energy, and medical fields.
- The Computer Chassis Fan gives high airflow and low noise. It works for fast CPU cooling or in data centers where quiet is important.
- The Electrical Enclosure Fan is good for machines and renewable energy. It handles high static pressure and keeps things cool, even in tough places.
Pick the right fan by thinking about what matters most:
- High airflow: Needed for quick cooling in CPUs and machines.
- Low noise: Important for offices, medical gear, and IT rooms.
- Energy efficiency: Saves money in renewable energy and big factories.
- Durability: Needed for outdoor or rough places, like renewable energy and factories.
Tip: Always check the fan curve and match it to your job. This helps you get the best results and longest life from your cooling system.
Linkwell’s fans meet these needs. The Computer Chassis Fan uses smart PWM control for speed. The Electrical Enclosure Fan has weatherproof housing and saves energy. Both fans help you get good cooling and save energy in your jobs.
Comparing and Selecting Fans
Matching Curves to Requirements
You need to match the right fan curve to your cooling job. Start by looking at the air performance graph for each fan. This graph shows how airflow and static pressure change as the fan works. Use the following table to see which fan type fits your needs:
| Fan Type | Pressure Increase | Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Axial | Low | High |
| Radial | High | Low |
| Mixed-Flow | Medium | Medium |
You should:
- Understand fan efficiency for your system.
- Check airflow and pressure needs.
- Think about noise levels.
- Identify what your application needs most.
For example, axial fans work well in cooling systems that need high airflow but low pressure. Radial fans fit jobs with high pressure and low airflow. Mixed-flow fans balance both. Always use the air performance graph to compare options.
Comparing Models and Brands
When you compare fans, look at more than just the numbers. You want to see how each fan, blower, or cooling unit performs in real life. Some brands, like SANYO DENKI, offer high airflow and low noise. Others, such as SPAL, handle high temperatures. Linkwell fans give you strong performance, energy efficiency, and reliable speed control. You can use fan laws to check how changes in speed control affect airflow and pressure.
Tip: Use real-world benchmarks and reviews to see how fans perform in different cooling systems.
You should also compare the energy use, noise, and durability of each blower. Look for fans that meet your guidelines for efficiency and performance.
Practical Tips for Selection
You can follow these steps for smart fan selection:
- Check the size of the fan and blower. Larger fans often run quieter and move more air at lower speeds.
- Make sure the fan fits your case or cabinet. Compatibility matters for easy installation.
- Review the air performance graph for each model. This helps you match airflow and pressure to your cooling needs.
- Compare noise levels. Quieter fans help in offices and medical rooms.
- Use speed control features to adjust performance as needed.
- Look for energy efficiency ratings. Efficient fans save money and last longer.
- Read manufacturer data and customer reviews. These give you real feedback on fan performance.
Note: Always follow the guidelines from the manufacturer and use fan laws to predict how changes in speed control will affect your system.
When you use these steps, you make better choices for your cooling systems. Linkwell offers fans and blowers with advanced speed control, high efficiency, and strong performance for many jobs.
You can learn how to use fan curve analysis to pick the best fan. When you know how fan performance curves work, your system stays cooler and quieter. It also uses less energy.
- Engineers look at fan curves to find the best spot for the fan to work. This helps the fan run quietly and last longer.
- A good fan keeps important equipment safe and working for more time.
| Feature | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|
| Certified components | UL, cUL |
| International safety standards | UL, CE, ISO |
| Enclosure protection ratings | UL, cUL |
Linkwell sells fans with important safety certifications. You can trust these fans for your cooling jobs.
FAQ
What is a fan curve and why should you care?
A fan curve shows how much air a fan moves at different pressures. You use it to pick the best fan for your cooling needs. It helps you avoid overheating and wasted energy.
How do you read a fan curve chart?
Start at the left for high pressure and low airflow. Move right for low pressure and high airflow. Find the point where your system’s needs match the fan’s curve.
Tip: Always check your system’s airflow and pressure before choosing a fan.
Why does fan speed matter in cooling?
Fan speed changes airflow and pressure. Higher speed means more air and pressure. You adjust speed to get the best cooling for your equipment.
| Speed Setting | Airflow | Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Less | Lower |
| High | More | Higher |
Which Linkwell fan fits your application?
You choose the Computer Chassis Fan for high airflow and quiet operation. You pick the Electrical Enclosure Fan for strong pressure and tough environments. Both offer energy savings and easy installation.




