If you’ve ever wondered how your devices get the right voltage, you’re thinking about the job of a transformer. A step up and down transformer changes voltage levels—either increasing or decreasing them—using electromagnetic induction. Step up transformers boost voltage for things like power transmission, while step down transformers lower voltage to safe, usable levels for homes, offices, and especially industrial cabinets.
You’ll find step down transformers hard at work in electrical cabinets, telecom racks, and control panels, keeping equipment safe and efficient. Check out the table below to see how industrial systems use these transformers:
| Application Segment | Market Share (2023) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Utility Companies | 50% | Largest segment |
| Power Plants | 30% | Second largest segment |
| Industrial Plants | 15% | Third largest segment; fastest growing |
You can trust Linkwell for reliable step down transformers designed specifically for electrical cabinets.
Key Takeaways
- Step up transformers increase voltage to send electricity efficiently over long distances, while step down transformers lower voltage to safe levels for homes, factories, and electrical cabinets.
- Both transformers work using electromagnetic induction, where the number of wire turns in the coils controls whether voltage goes up or down.
- Step down transformers protect your equipment by providing stable, safe voltage and are commonly used in industrial control panels, telecom racks, and homes.
- Choosing the right transformer means matching voltage, current, and size to your needs, considering future growth, safety standards, and cooling methods.
- Linkwell offers reliable, customizable step down transformers with strong safety features and certifications, ensuring long-lasting performance in industrial electrical cabinets.
Step Up and Down Transformer Basics

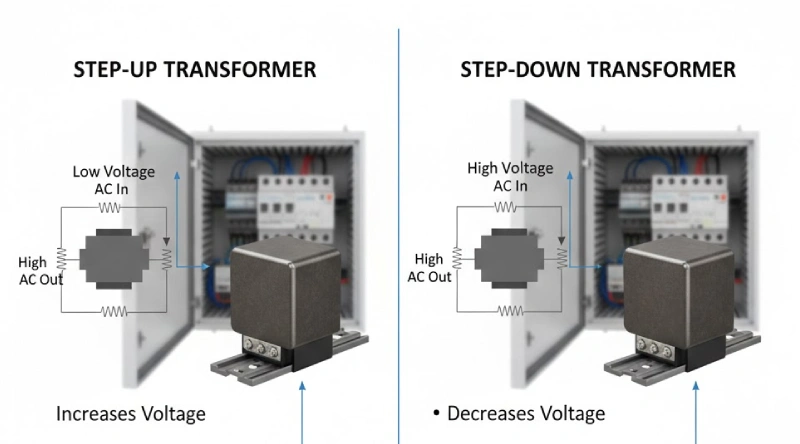
What Is a Step-Up Transformer
When you hear about a step-up transformer, think about a device that helps you increase voltage from one level to a much higher one. You’ll find step up transformers in power plants and substations, where they play a key role in sending electricity over long distances. The main job of a step-up transformer is to take the voltage from the primary coil and boost it in the secondary coil. This happens because the secondary coil has more turns of wire than the primary coil. The more turns you have in the secondary, the higher the voltage you get out.
A step-up transformer works by using electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field. This field passes through the iron core and reaches the secondary winding. Because the secondary has more turns, the voltage increases as it moves from the primary to the secondary. This process lets you send electricity across cities and even countries without losing too much energy along the way.
Here’s a quick look at typical voltage ranges for step up transformers in industrial settings:
| Application Type | Primary Voltage | Secondary Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Step-Up | 22 kV | 400 kV |
| Industrial Substation | 132 kV | 220 kV |
| Manufacturing Plant | 1 kV | 35 kV |
You’ll see step up transformers everywhere in the power grid. They make sure electricity travels efficiently by increasing voltage and reducing current, which cuts down on energy loss.
What Is a Step-Down Transformer
A step-down transformer does the opposite job. It takes high voltage from the primary coil and decreases it to a safer, lower voltage in the secondary coil. You’ll find step-down transformers in electrical cabinets, homes, and factories. The secondary coil in a step-down transformer has fewer turns than the primary coil. This design lets you decrease voltage to levels that your equipment and devices can safely use.
For example, when electricity arrives at your neighborhood, it’s still at a high voltage. A step-down transformer in a cabinet or on a utility pole lowers that voltage to 120V or 240V, which is safe for your lights and appliances. In industrial settings, step-down transformers inside electrical cabinets adjust voltage to match the needs of machines and control panels. You might see a step-down transformer converting 480V down to 277V or even 220V down to 110V.
Here’s how step-down transformers work in real-world electrical cabinets:
Step-down transformers in cabinets reduce high transmission voltages to safe, usable levels for equipment. For example, they can convert 480Vac input to 277Vac output, or 347Vac to 200Vac, making sure your devices run smoothly and safely.
How They Work
Both step up and down transformers rely on the same basic principle: electromagnetic induction. When you send alternating current through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field in the iron core. This changing field induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The number of turns in each coil decides if you increase voltage (step up) or decrease voltage (step down).
Here’s a simple table to show how the winding ratio affects transformer operation:
| Parameter | Step-Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Turns Ratio | Secondary > Primary | Secondary < Primary |
| Voltage Change | Increases (Vs > Vp) | Decreases (Vs < Vp) |
| Current Change | Decreases (Is < Ip) | Increases (Is > Ip) |
- The voltage ratio between the secondary and primary coils matches the ratio of their turns.
- The current ratio works the opposite way: as voltage goes up, current goes down, and vice versa.
- Power stays nearly the same from primary to secondary, except for a little loss as heat.
Transformers only work with alternating current (AC). Here’s why:
- AC creates a changing magnetic field in the core, which is needed for electromagnetic induction.
- Direct current (DC) does not change direction, so it creates a constant magnetic field. This means no voltage gets induced in the secondary coil.
- Using DC can even damage the transformer by causing the core to overheat.
So, whenever you use a step up and down transformer, remember that AC is essential for voltage transformation. The clever design of the primary and secondary windings lets you control whether you increase voltage or decrease voltage, making these devices vital for safe and efficient power distribution.
Difference Between Step Up and Down Transformer
Recommended products
Voltage and Current Changes
When you look at a step-up transformer, you see a device that takes the voltage from the primary side and increases it on the secondary side. The step-up transformer does this by having more turns on the secondary winding than on the primary winding. As the voltage goes up, the current on the secondary side goes down. This means you get higher voltage but lower current coming out of the secondary coil. You often find step-up transformers in power plants and transmission stations, where boosting voltage helps electricity travel long distances with less energy loss.
On the other hand, a step-down transformer works in the opposite way. It takes high voltage from the primary winding and reduces it to a safer, lower voltage on the secondary side. The secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary winding, so the voltage drops and the current increases. You see step down transformers in electrical cabinets, factories, and homes, where they make sure your equipment gets the right voltage and enough current to run safely.
Tip: The wire on the winding that carries higher current is usually thicker. In a step-down transformer, the secondary winding often uses thicker wire because it handles more current.
Both step up transformers and step down transformers keep the power nearly the same from primary to secondary, except for a little loss as heat. This balance helps protect your devices and keeps energy use efficient.
Winding Ratio Comparison
The winding ratio is the secret behind how a transformer changes voltage. In a step-up transformer, the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding. This ratio boosts the voltage on the secondary side. For example, if the primary has 100 turns and the secondary has 1,000 turns, the voltage increases by ten times.
In a step-down transformer, the primary winding has more turns than the secondary winding. This setup lowers the voltage on the secondary side. If the primary has 1,000 turns and the secondary has 100 turns, the voltage drops to one-tenth of the original value.
Here’s a quick table to help you compare:
| Transformer Type | Primary Turns | Secondary Turns | Voltage Change | Current Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step-Up Transformer | Fewer | More | Increases | Decreases |
| Step-Down Transformer | More | Fewer | Decreases | Increases |
The winding ratio must match the design needs of your system. If the ratio is off, you risk voltage mismatches, energy loss, or even damage to your equipment. Regular testing helps you catch problems early and keeps your transformer running safely.
- Winding ratios set the voltage transformation between primary and secondary windings.
- Accurate ratios mean efficient power transfer and safe operation.
- Incorrect ratios can cause overheating, voltage drops, or equipment failure.
- Turns Ratio Tests help you spot faults and keep your transformer reliable.
Typical Uses
You’ll find step-up transformers and step-down transformers in different places, each serving a unique role.
Step-up transformer uses:
- Power plants: Boost voltage for long-distance transmission.
- Renewable energy: Raise voltage from wind turbines or solar panels to match the grid.
- Industrial manufacturing: Supply high voltage to heavy machinery.
- Data centers: Ensure stable voltage for critical systems.
- Electric vehicle charging stations: Convert grid voltage for fast charging.
Step-down transformer uses:
- Electrical cabinets: Lower voltage for control panels and sensitive electronics.
- Factories: Provide safe voltage for motors, drives, and automation.
- Homes and offices: Make utility voltage safe for everyday devices.
- Machine control panels: Deliver stable power for servo drives and emergency feeds.
- Telecom racks: Protect equipment by isolating circuits and balancing loads.
Here’s a table showing where you might see each type:
| Location/Use Case | Step-Up Transformer | Step-Down Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Power Generation Plant | Yes | No |
| Transmission Network | Yes | No |
| Industrial Cabinet | No | Yes |
| Residential Distribution | No | Yes |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Yes | No |
| Machine Control Panel | No | Yes |
Step-up transformers focus on boosting voltage for efficient transmission. Step-down transformers make sure you get safe, usable voltage for your equipment. Both types are highly efficient, but their design and maintenance needs differ. Step-up transformers need strong insulation for high voltage, while step-down transformers require good cooling for higher current loads.
Note: Both step up transformers and step down transformers play a key role in keeping your electrical system safe, reliable, and energy-efficient. You just need to choose the right type for your application.
Step Down Transformer in Electrical Cabinets by Linkwell
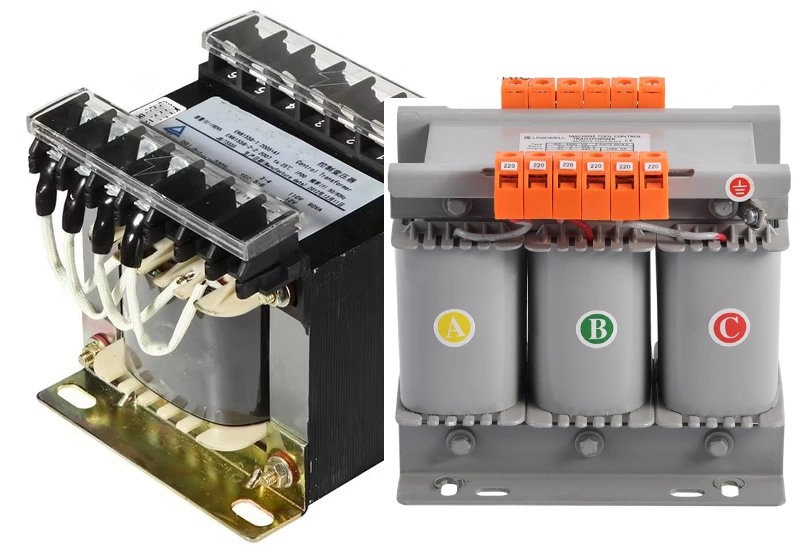

Product Features
When you choose a step down transformer from Linkwell for your electrical cabinet, you get more than just a voltage converter. You get a transformer built for reliability and safety. These step down transformers feature robust construction, excellent voltage regulation, and compact designs that fit easily inside control panels. You’ll notice protective metal enclosures and integrated safety features that keep your equipment secure. Linkwell step down transformers hold certifications like UL5085, CE, RoHS, CCC, and ISO9001. These certifications show that your transformer meets international safety and performance standards. You also benefit from high electrical isolation, which protects sensitive electronics from noise and voltage spikes.
| Transformer Type | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Control Voltage Transformers | Excellent voltage regulation, compact design, robust construction | Reliable voltage step-down, protection against voltage fluctuations, improved device performance |
| Enclosed Control Transformers | Protective metal enclosures, various NEMA ratings, integrated safety features | Enhanced safety, environmental protection, reduced maintenance |
| Industrial Control Transformers | Heavy-duty construction, high insulation, handles demanding loads | Long service life, reliable power in harsh environments, minimized downtime |
Tip: Linkwell step down transformers undergo strict quality inspections and third-party audits, so you can trust their performance in your cabinet.
Industrial Applications
You’ll find Linkwell step down transformers working hard in many industries. In manufacturing, these transformers automate machines and help control motors for efficient production. Telecommunications companies use step down transformers in base station cabinets to manage backup power and cooling. Water treatment plants rely on these transformers to automate pumps and sensors, keeping operations smooth. You can use a step down transformer to reduce voltage from 415 volts to 110 volts, making sure your control circuits run safely. These transformers power relays, contactors, timers, and PLCs inside industrial cabinets. You get stable, isolated power that protects your equipment and keeps your system reliable.
- Manufacturing: Automates machines and controls motors.
- Telecommunications: Manages backup power and cooling in base stations.
- Water Treatment: Automates pumps and sensors for smooth operation.
Customization and Value
Linkwell knows that every project is different. You can customize your step down transformer with your own logo, packaging, or graphics if you order at least 500 pieces. This helps you match your brand and meet specific installation needs. You get a transformer that fits your cabinet perfectly, whether you need a special voltage, frequency, or mounting style. Linkwell step down transformers improve operational efficiency by providing stable, isolated power for control circuits. You save energy, reduce downtime, and extend the life of your equipment. With certifications and quality assurance, you get a transformer that meets global standards and delivers value for your business.
Note: Linkwell step down transformers combine reliability, safety, and customization, making them a smart choice for any industrial electrical cabinet.
Choosing the Right Transformer
Key Factors
When you pick a transformer for your project, you want to make sure it matches your needs. Start by checking the load size. If you expect your equipment to grow, choose a transformer that can handle future expansion. You should look at the type—single-phase or three-phase—based on your system. The voltage compatibility between the primary and secondary sides matters a lot. If you get this wrong, your devices might not work or could get damaged.
Here are some important things to keep in mind:
- Size the transformer for both current load and future growth.
- Decide if you need single-phase or three-phase.
- Match the primary and secondary voltage to your equipment.
- Choose the right cooling method. Air-cooled transformers work for small loads. Oil-cooled ones suit bigger jobs.
- Look for energy efficiency. Efficient step down transformers save money over time.
- Make sure the transformer meets safety standards. This helps prevent overheating and fire.
- Think about the environment. High temperature, humidity, or dust can affect performance.
- Manage noise and vibration, especially in quiet workspaces.
- Balance the upfront cost with long-term savings.
- Ask an engineer to check your calculations and compliance.
If you follow these tips, you’ll get a transformer that works well and lasts longer.
Application Scenarios
You’ll see step up transformers and step down transformers in many places. Step up transformers raise voltage and lower current. They help send power over long distances or adapt voltage for special equipment. Factories use them to power heavy machines. Renewable energy systems, like solar and wind, use step up transformers to connect low-voltage generation to the grid. Data centers and mining sites rely on them for stable, high-voltage supply.
Step down transformers do the opposite. They lower voltage and increase current, making power safe for your devices. You’ll find step down transformers in electrical cabinets, control panels, and telecom racks. These transformers protect sensitive equipment by matching the secondary voltage to what your devices need. Industrial plants use step down transformers to run motors, sensors, and automation lines. If you work with control cabinets, you need a transformer that can handle the primary voltage and deliver the right secondary voltage for your setup.
When you choose between step up transformers and step down transformers, think about your voltage needs, transmission distance, and load conditions. Always size the transformer for peak load. Document all connected equipment and add a buffer for unexpected growth. This way, your transformer will deliver reliable power and keep your system safe.
You’ve learned that a transformer changes voltage to fit your needs. Step down transformers lower high voltage to safe levels, while step up transformers do the opposite. Here’s a quick recap:
- Step down transformers have more primary windings and give you lower voltage for your equipment.
- Step up transformers have more secondary windings and boost voltage for long-distance power.
- Both types of transformer keep your system safe and efficient.
Choosing the right transformer matters. You want step down transformers in your cabinet to protect devices and save energy. Always check transformer ratings, cooling, and safety features. Step down transformers from Linkwell offer quality, reliability, and custom solutions for your industrial cabinet. You get peace of mind and long-lasting performance.
| Aspect | Step-Up Transformer | Step Down Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Transformation | Increases | Decreases |
| Winding Configuration | Secondary > Primary | Primary > Secondary |
| Typical Use | Transmission | Cabinets, Industry |
FAQ
What is the main job of a step down transformer in an electrical cabinet?
You use a step down transformer to lower high voltage to a safer level for your control circuits and devices. This keeps your equipment protected and running smoothly.
Can you customize a step down transformer for my cabinet?
Absolutely! You can request custom voltages, frequencies, and even special sizes. Linkwell offers tailored solutions so your transformer fits perfectly in your cabinet setup.
How do I know which transformer size I need?
Check the total power your devices use. Add a safety margin for future growth. If you’re unsure, ask your supplier or an engineer for help. Picking the right size prevents overloads.
Are Linkwell step down transformers safe for industrial use?
Yes, you can trust Linkwell transformers. They meet ISO 9001 and CE standards. Each unit goes through strict quality checks, so you get reliable and safe performance in your industrial cabinet.