Three-phase transformers are fundamental to power systems, but not all are created equal. They come in various types, each suited for different needs.
Exploring the distinct types of three-phase transformers reveals their unique benefits and specific applications across industries. Understanding these differences is crucial for efficient power distribution and system design.
What is Three Phase Transformer
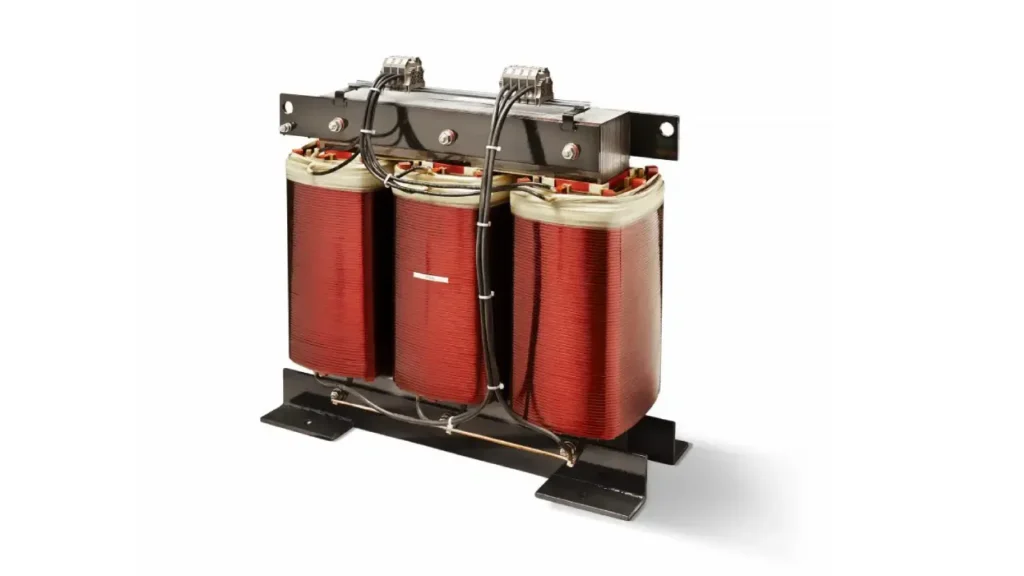

A three-phase transformer is an electrical device used to transfer electrical energy between three circuits simultaneously. Unlike a single-phase transformer, it handles three alternating voltages and currents that are offset in phase, typically by 120 degrees.
This makes them essential for efficiently stepping up or stepping down voltage in high-power applications such as electricity generation, transmission, distribution, and heavy industrial use, enabling the reliable operation of three-phase machinery and power systems.
Types of Three Phase Transformer
Exploring the different types of three-phase transformers is crucial for selecting the optimal unit for specific electrical needs. Each type possesses unique construction features and insulation methods, offering distinct benefits and lending themselves to particular applications across the power grid and various industries.
Three Phase Core Type Transformer
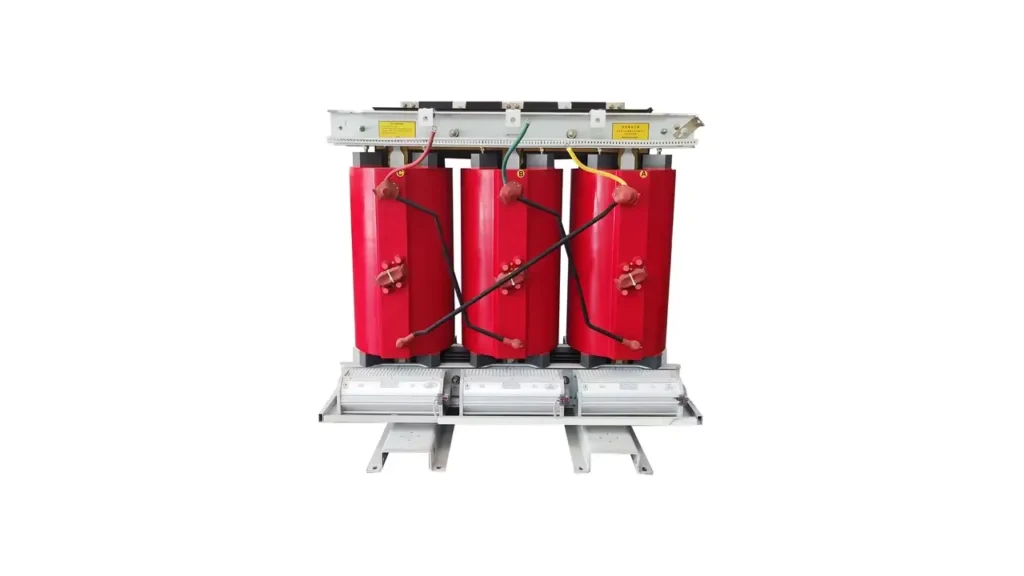

The three-phase core type transformer is characterized by a magnetic core featuring three limbs connected by upper and lower yokes. Each limb accommodates both the primary and secondary windings for one of the three phases. This arrangement allows the magnetic flux paths of the individual phases to share common sections of the core, providing an efficient magnetic circuit for voltage transformation.
Benefits of the core type design include its relatively simpler construction compared to the shell type and its suitability for higher voltage applications. The winding structure around the core limbs facilitates effective insulation, making this type reliable for power transmission systems where higher voltages are prevalent and robust insulation is paramount for safety and performance.
Applications for three-phase core type transformers are widespread, particularly in utility-scale power systems. They are commonly used in transmission substations to step up generator voltage for long-distance transmission and in distribution substations to step down transmission voltage for local networks, forming a backbone of the electrical grid infrastructure.
Three Phase Dry Type Transformer
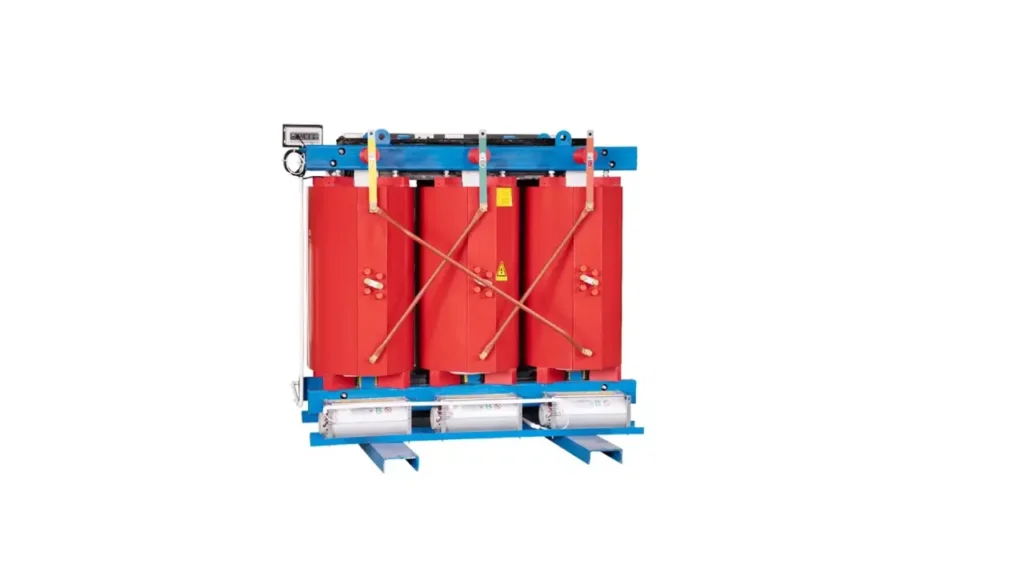

A three-phase dry type transformer utilizes solid insulation materials, such as resin or varnish, to insulate the windings and core, completely eliminating the need for liquid coolants like oil. Cooling is achieved through natural air convection or forced air circulation through ventilation ducts within the windings and core structure, making them environmentally friendly.
Key benefits include enhanced fire safety due to the absence of flammable oil, reduced environmental risk, and minimal maintenance requirements. These transformers do not require containment for oil leaks and are easier to install in indoor environments or locations where strict fire codes and environmental regulations are in place, offering peace of mind and lower operational costs.
Dry type transformers are widely applied in indoor substations within commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and industrial facilities where safety and environmental concerns are paramount. They are also used in applications like renewable energy integration and transportation systems where reliability and low maintenance are critical factors.
Three Phase Shell Type Transformer
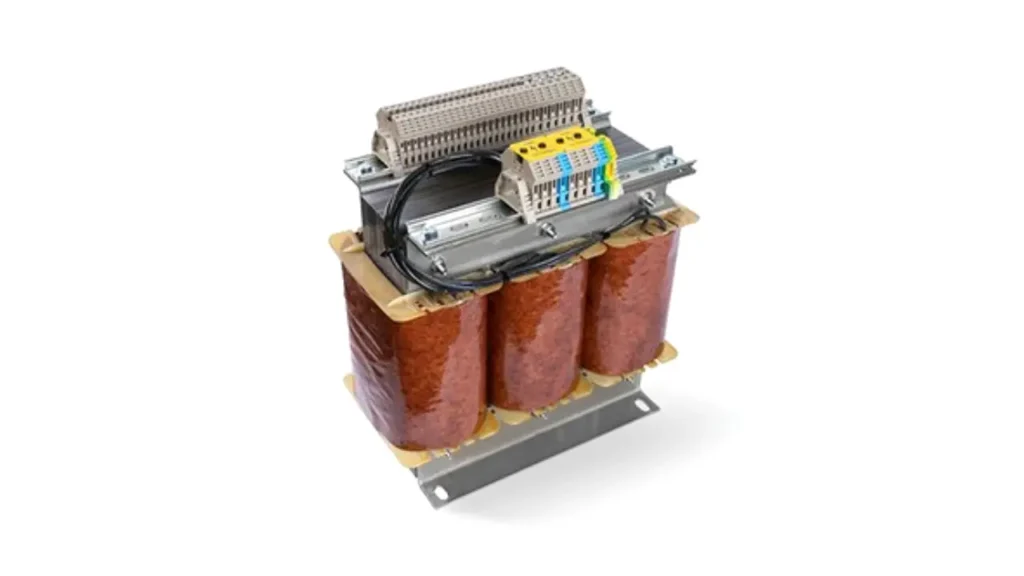

The three-phase shell type transformer features a magnetic core that effectively surrounds the windings, providing a protective “shell.” The primary and secondary windings for all three phases are typically placed on the central limb, with the core limbs extending around and enclosing the windings. This construction results in a more robust mechanical structure.
Benefits of the shell type include superior mechanical strength and excellent support for the windings, making them highly resistant to electromagnetic forces, especially during short circuits. The core’s large surface area also contributes to efficient heat dissipation, aiding in the cooling process and enhancing the transformer’s ability to handle thermal stress effectively.
Shell type transformers are frequently used in high-current, low-voltage applications and in systems where robustness and short-circuit withstand capability are critical. They are often found in industrial settings, welding applications, and specific types of power supplies where their durable construction and efficient cooling characteristics are highly advantageous.
Here is a comparison of common three-phase transformer types:
| Transformer Type | Construction Highlight | Insulation/Cooling Method | Key Benefit/Application Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Type | Windings on each of three limbs | Typically Oil-filled | High Voltage Applications, Power Transmission |
| Dry Type | No liquid coolant | Solid Insulation (Resin/Varnish), Air Cooled | Indoor Use, Fire Safety, Sensitive Locations |
| Shell Type | Core surrounds windings | Typically Oil-filled | High Current/Low Voltage, Robustness, Welding |
How to Choose the Best Three Phase Transformer
Selecting the best three-phase transformer starts with defining electrical needs: required kVA capacity, precise primary and secondary voltages, and the correct winding connection (Star/Delta) for your power system architecture and load requirements.
Consider the operating environment and safety needs to choose between dry-type or liquid-filled insulation. Evaluate cooling methods, size constraints, efficiency ratings, and compliance with relevant industry standards for reliable long-term performance tailored to your application.
Here’s how to choose the best three-phase transformer:
- Determine kVA Capacity and Voltage: Accurately assess the total power the transformer needs to supply, measured in kVA. Specify the exact primary voltage from the source and the required secondary voltage for your load to ensure proper voltage transformation for efficient operation.
- Select Winding Connection: Choose the appropriate primary and secondary winding configurations (Delta-Delta, Star-Delta, etc.). This decision impacts voltage/current relationships, grounding capabilities, and compatibility with your existing electrical system architecture and load type characteristics.
- Consider Insulation and Cooling: Decide between dry-type and liquid-filled transformers based on safety regulations and maintenance preferences. Evaluate the cooling method (natural air, fans, oil) required to effectively dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring thermal stability.
- Assess Environment and Safety: Analyze the installation location’s environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, and potential hazards. Select a transformer type and enclosure that meets necessary safety standards and can withstand the specific environmental stresses for reliable, safe performance.
- Evaluate Efficiency and Compliance: Compare efficiency ratings to minimize energy losses over the transformer’s lifespan. Check physical size constraints and ensure the transformer complies with relevant industry standards and certifications for quality, safety, and guaranteed performance tailored to your specific application needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the diverse types of three-phase transformers, such as core type, shell type, and dry type, is fundamental to appreciating their role in electrical systems. A guide on this topic would delve into the unique construction and characteristics of each, highlighting how these variations meet different operational demands.
These transformers offer key benefits like high efficiency and reliability, essential for handling large power loads. Their ability to manage significant electrical energy makes them vital for widespread applications in power distribution and heavy industry.
In conclusion, grasping the nuances of three-phase transformer types and their benefits is crucial for projects. Selecting the appropriate transformer ensures system performance. For your needs, get wholesale three phase transformers from Linkwell Electrics, a trusted source for these components.