Electrical control panels and industrial automation rely heavily on organized and reliable wiring solutions. Among the most fundamental components for achieving this are terminal blocks, which provide secure connection points for wires. However, the sheer variety of terminal blocks can be overwhelming.
This guide will focus on a specific, incredibly popular, and efficient type: DIN rail terminal blocks. We’ll delve into what they are, their benefits, common types, and how they simplify complex wiring, making them an ultimate choice for modern electrical systems.
What are DIN Rail Terminal Blocks?
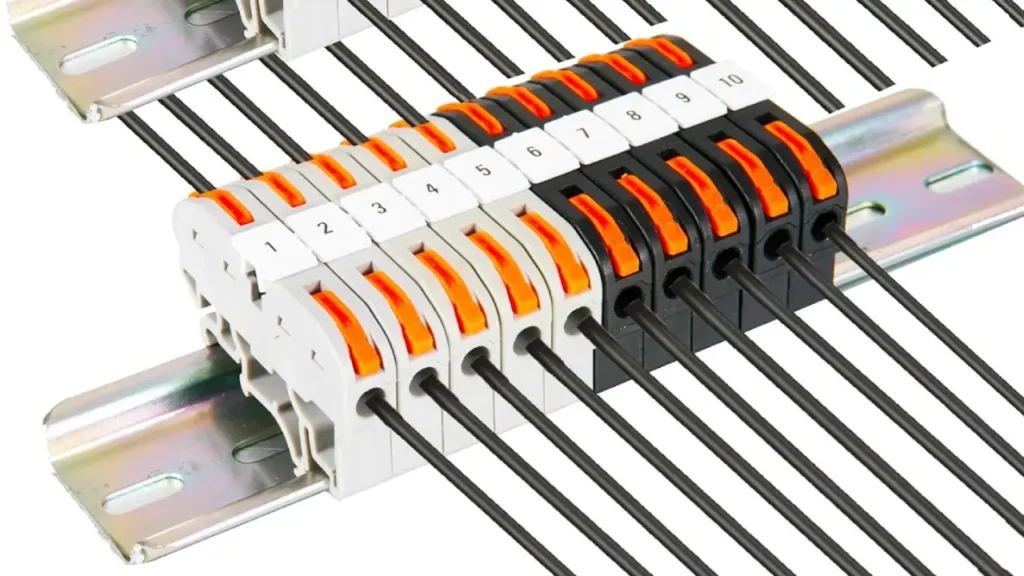

DIN rail terminal blocks are modular electrical connectors designed to terminate and connect wires within a circuit securely. Their defining feature is their compatibility with DIN rails, which are standardized metal rails used to mount electrical equipment inside control cabinets, panels, and other enclosures. This standardized mounting system allows for highly organized, space-efficient, and easily expandable wiring solutions.
How Do DIN Rail Terminal Blocks Work?
DIN rail terminal blocks are essential components in electrical and industrial control systems, primarily functioning to create secure and organized connections between wires. Their core principle involves providing an insulated housing, typically made of plastic, with a conductive metal part inside.
Wires are inserted into these blocks and then secured using various connection methods, such as screw clamps, spring clamps, or push-in mechanisms. This clamping action ensures a reliable electrical connection, preventing accidental disconnections, short circuits, and providing a clean, modular way to manage complex wiring.
The “DIN rail” aspect refers to a standardized metal mounting system, a long metal strip (often 35mm wide) onto which these terminal blocks clip. The DIN rail itself is a mechanical support and does not conduct electricity.
By mounting terminal blocks on a DIN rail, installers can create a neat and systematic arrangement of wiring connections within control cabinets, panels, and other equipment enclosures. This modularity allows for easy expansion, modification, and maintenance of electrical systems, making fault-finding and repairs much simpler compared to direct wire-to-wire connections.
DIN Rail Terminal Block Types
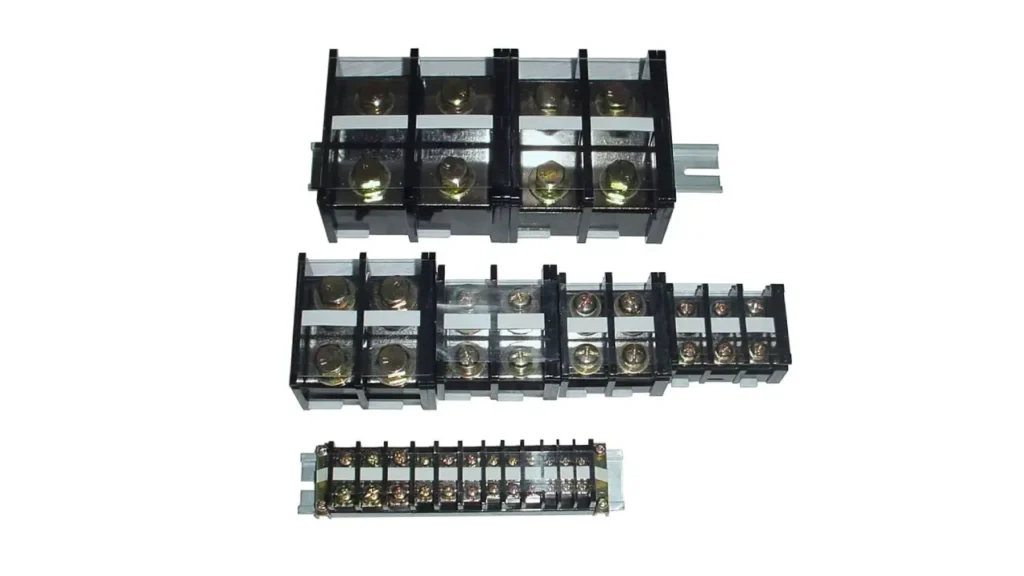

DIN rail terminal blocks are incredibly versatile, offering a wide array of specialized terminal block types to meet the diverse demands of electrical and electronic systems. Each type is designed with specific functionalities to optimize circuit performance, safety, and organization.
Feed-Through Terminal Blocks
These are the most basic and common type of DIN rail terminal block, designed for simple wire-to-wire connections. They provide a continuous electrical path, allowing current to “feed through” the block from one wire to another. They are typically used for connecting two conductors within a circuit, serving as a reliable junction point to extend or consolidate wiring.
Ground Terminal Blocks (PE Blocks)
Also known as Earth terminal blocks, these are specifically designed for protective earthing applications. They feature a direct, low-resistance connection to the DIN rail itself, effectively grounding the circuit. These blocks are easily identifiable by their green and yellow housing and are essential for safety, ensuring that any fault currents are safely discharged to the earth.
Fuse Terminal Blocks
Fuse terminal blocks integrate a fuse holder directly into the terminal block design, providing overcurrent protection within the terminal assembly. This allows for convenient and space-saving circuit protection. Many models include LED indicators to visually signal a blown fuse, simplifying troubleshooting and maintenance in applications safeguarding sensitive equipment.
Disconnect Terminal Blocks
These blocks allow for easy and safe disconnection of individual circuits without having to remove wires or use specialized tools. They typically feature a lever, knife-edge, or plug-in mechanism that can be opened to isolate a circuit for testing, maintenance, or troubleshooting, making them invaluable for quick circuit isolation.
Multi-Level Terminal Blocks
Multi-level terminal blocks, such as double-level or triple-level blocks, are designed to save space by offering multiple independent connection levels within a single block’s footprint. This compact design is ideal for high-density wiring applications, allowing for more complex wiring configurations in a smaller physical space, often seen in control panels.
Sensor/Actuator Terminal Blocks
These specialized terminal blocks are designed to simplify wiring for sensors and actuators by integrating multiple potential levels (e.g., positive, negative, and signal) into a single compact unit. They often feature narrow profiles and can include LED indicators for signal status, making them ideal for high-density I/O wiring in automation systems.
How to Use Din Rail Terminal Blocks?
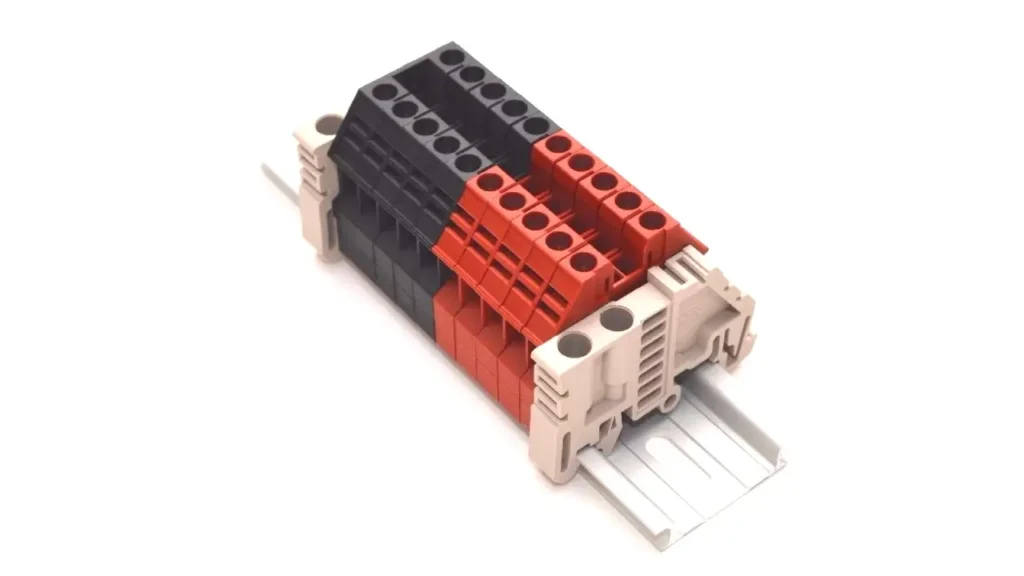
DIN rail terminal blocks are essential components in electrical systems, offering a standardized and efficient way to organize wiring. Understanding their installation, operation, and maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Step 1: Preparation and Safety
Before beginning any work with DIN rail terminal blocks, it is absolutely paramount to ensure that all power to the circuit is completely disconnected and locked out. This critical safety measure prevents accidental energization and mitigates the risk of electrical shock or damage to equipment during the installation or maintenance process. Always verify de-energization with a suitable voltage tester.
Step 2: Mounting the DIN Rail
The first physical step involves securely mounting the DIN rail itself within your enclosure or control panel. DIN rails typically come in standard lengths and can be cut to fit. Ensure the rail is firmly attached to a stable surface using appropriate screws or mounting hardware, providing a robust foundation for the terminal blocks and other components.
Step 3: Attaching the Terminal Blocks
Once the DIN rail is in place, individual terminal blocks are simply snapped onto the rail. Most DIN rail terminal blocks feature a spring-loaded or clip mechanism on their base that allows them to be easily pressed down onto the rail until they securely click into place. This modular design enables quick assembly and rearrangement of blocks as needed.
Step 4: Connecting the Wires
With the terminal blocks mounted, wires can now be connected. Depending on the type of terminal block (e.g., screw clamp, spring clamp, push-in), wires are inserted into the appropriate opening and then secured. For screw clamps, the wire is inserted and the screw tightened to create a secure connection. For spring or push-in types, the wire is simply inserted or a lever/button is pressed to open the clamp.
Step 5: Accessories and Customization
DIN rail systems offer a wide array of accessories to enhance functionality and organization. End covers are used to insulate the open end of a block, while end stops prevent blocks from sliding on the rail. Jumpers or bridges are used to connect multiple blocks electrically, and marking tags provide clear identification for each terminal, simplifying future troubleshooting and modifications.
Step 6: Testing and Verification
After all connections are made and accessories are in place, a thorough testing phase is crucial. Use a multimeter or continuity tester to verify all connections are secure and correct, checking for proper continuity and ensuring there are no short circuits. This final step confirms the integrity of the wiring before the system is energized, preventing potential issues.
How to Remove DIN Rail Terminal Blocks?
Removing DIN rail terminal blocks, while seemingly straightforward, requires a systematic approach to ensure safety and prevent damage to both the blocks and the wiring. Proper technique is essential for maintaining the integrity of your electrical system.
Step 1: Safety First – De-energize the Circuit
Before attempting to remove any DIN rail terminal block, the absolute first and most critical step is to completely de-energize the circuit. Locate the corresponding circuit breaker or power source and switch it off. Apply lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental re-energization. Always use a voltage tester to confirm that the circuit is dead before proceeding to touch any wiring or components.
Step 2: Disconnect All Wires
Once the circuit is confirmed to be de-energized, carefully disconnect all wires from the terminal block you intend to remove. For screw-type terminals, loosen the screw until the wire can be safely pulled out. For spring-clamp or push-in types, use the appropriate tool (screwdriver or release button) to release the clamping mechanism and extract the wire. Ensure no stray strands are left behind.
Step 3: Remove Accessories (if applicable)
If the terminal block is part of a larger assembly and is connected to adjacent blocks by jumpers, bridges, or marking tags, these accessories should be carefully removed first. Jumpers usually slide out or unclip, while marking tags can often be slid off or gently pried away. This step ensures clear access to the individual block and prevents damage to connected components.
Step 4: Release the Mounting Mechanism
Most DIN rail terminal blocks have a locking mechanism, often a spring-loaded foot or a latch, at their base that secures them to the DIN rail. To release the block, use a small flat-head screwdriver or a specialized release tool. Insert the tool into the designated slot on the side or bottom of the block and gently pry or twist to disengage the locking mechanism from the DIN rail.
Step 5: Slide and Lift Off the Rail
Once the locking mechanism is disengaged, the terminal block can typically be slid along the DIN rail. If it’s an end block, you can often just lift it straight off once released. If it’s in the middle of a row, you may need to slide it to an open section of the rail or temporarily move adjacent blocks to create space before lifting it clear of the DIN rail.
Conclusion
DIN rail terminal blocks are indispensable for modern electrical systems, offering a standardized, modular, and highly organized solution for wire termination. Their ease of installation, expandability, and ability to house various functionalities (like fusing or grounding) make them a cornerstone of efficient control panels and electrical enclosures.
The modular design ensures flexibility, allowing for easy expansion or modification of circuits without extensive re-wiring, which significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs. This adaptability, coupled with their robust construction, ensures long-term reliability in diverse industrial and commercial environments.
For a comprehensive range of high-quality wholesale terminal blocks, including versatile DIN rail options, contact us today.




