You do not need to be a scientist to use a heat transfer calc. Anyone can get accurate answers with online calculators. Just pick the right heat transfer calc for your problem. There are calculators for conduction and convection, and you can see the options in this table:
| Type of Heat Transfer | Calculator Link |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Heat Transfer through Conduction Calculator |
| Convection | Heat Transfer through Convection Calculator |
| Radiation | N/A |
You should know if your heat transfer calc needs conduction, convection, or radiation. Always check your units before you start. Most calculators make every step clear, so you can follow along without stress. With the right heat transfer calc, you can solve problems fast and with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right heat transfer calculator based on your problem type: conduction, convection, or radiation.
- Gather accurate data and measurements before starting calculations to ensure reliable results.
- Check your units carefully to avoid common errors that can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Use user-friendly online calculators that provide clear instructions and support for beginners.
- Review your results and verify them against real-world data to ensure accuracy and confidence in your calculations.
Choose the right heat transfer calc

Compare online physics calculators
You have many options when it comes to online physics calculators. The first step is to know which type of heat transfer you need to solve. Some calculators focus on conduction, others on convection, and a few on radiation. If you work with more complex systems, like heat exchangers or heat pipes, you can find specialized calculators for those, too.
Here are some of the most popular online physics calculators you might use:
| Calculator Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Flow Calculator (HEAT/Calc) | A JavaScript-based tool for different heat transfer problems. |
| Heat Pipe Calculator | Helps you with heat pipe calculations for specific applications. |
When you compare online physics calculators, look for one that matches your problem. For example, if you want to calculate heat loss in a building, choose a calculator designed for that. If you need to check the performance of a heat pipe, use a calculator built for that purpose. There are many types of online physics calculators, so you can always find one that fits your needs.
Tip: Always check if the calculator supports the right heating method for your application. This helps you get accurate results and avoid mistakes.
User-friendly design and features
You want online physics calculators that make your job easy. The best calculators give you quick and accurate results. You just enter your data, and the calculator does the rest. Many calculators have a user-friendly interface, so you can see your results right away in a clear format.
Here are some features that make online physics calculators great for beginners:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Performance Curve | Shows how your system performs based on your input values. |
| Application-Specific Parameters | Lets you enter details like length, diameter, or heat load for more accurate results. |
| User Support | Offers help by email if you get stuck or have questions. |
Some calculators, like the Heat Loss Calculator from h2x Engineering, get high marks for being simple and easy to use. Users say these online physics calculators save time and reduce errors. You can even compare different designs, like fin configurations, to find the best option for your project.
When you pick from online physics calculators, remember to:
- Make sure the calculator matches your heat transfer type.
- Look for calculators with clear instructions and support.
- Choose calculators that help you optimize your design.
With the right online physics calculators, you can solve problems faster and with more confidence.
Prepare for heat transfer calculations
Before you start any heat transfer calculations, you need to get your facts straight. The more accurate your data, the better your results. You do not want to guess or use rough numbers. Instead, you want to collect real measurements and double-check your material details. This step sets you up for success and helps you avoid big mistakes later.
Collect data and measurements
You cannot do heat transfer calculations without the right data. Start by gathering all the measurements you need for your specific problem. For example, if you want to figure out how much heat escapes from a building, you need more than just the outside temperature. You need to know about the building itself and the environment around it.
Here is a handy checklist of what you might need:
- Heat transfer coefficient and heat capacity of the building
- Temperature readings inside and outside, taken every 5 minutes
- Wind speed data, measured hourly at 10 meters above the ground
- Building time constant, tracked over several nights
- Outside air temperature and relative humidity for ventilation heat loss
Tip: The accuracy of your input measurements makes a huge difference. If you use numbers that are off, your heat transfer calculations will be wrong. Even small errors in temperature or sensor placement can lead to big mistakes in your results.
When you collect your data, pay attention to where you place your sensors and how fast they respond. Good sensor placement helps you get the most reliable numbers. If you skip this step or rush through it, your heat transfer calculations might not match what happens in real life.
Check units and material details
Now that you have your measurements, you need to make sure your units match. Mixing up units is one of the most common reasons for errors in heat transfer calculations. You might see different units for heat transfer rates, like Watts, kilocalories, or BTUs. If you do not keep them consistent, your answers will not make sense.
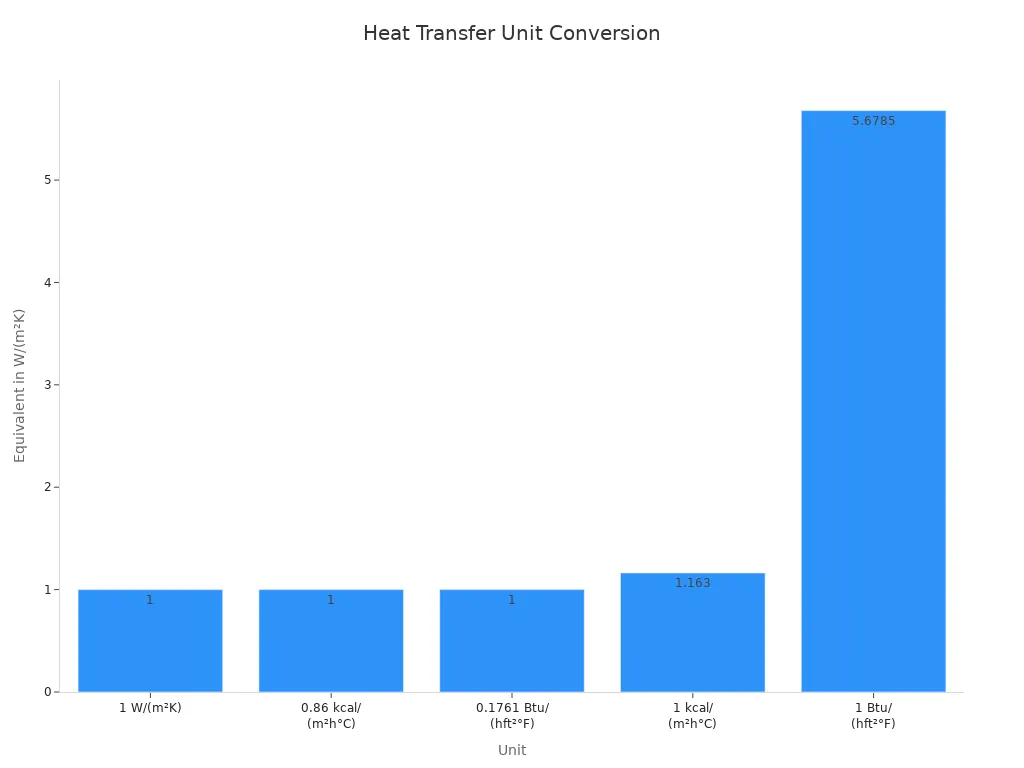
Here is a table to help you compare the most common units:
| Unit | Conversion to W/(m²K) |
|---|---|
| 1 W/(m²K) | 1 |
| 0.86 kcal/(m²h°C) | 1 W/(m²K) |
| 0.1761 Btu/(hft²°F) | 1 W/(m²K) |
| 1 kcal/(m²h°C) | 1.1630 W/(m²K) |
| 1 Btu/(hft²°F) | 5.6785 W/(m²K) |
You will often see the rate of heat transfer measured in Joules per second, which is the same as a Watt. This unit works for many situations, like conduction through walls or heat exchangers. Always check that every number you enter uses the same unit system. If you mix up grams and kilograms, or Celsius and Kelvin, your heat transfer calculations will not be correct.
Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Using grams instead of kilograms for mass
- Mixing Celsius and Kelvin for temperature
- Forgetting to convert BTUs to Watts
Note: Consistency in units is not just a good habit—it is essential for accurate heat transfer calculations.
Next, look at your material details. The properties of the materials you use, like thermal conductivity, can change your results a lot. Some materials let heat flow easily, while others block it. You need to know these numbers before you start.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of how well a material conducts or insulates against heat flow. |
| Importance in Selection | Helps you pick the right material for your project. |
| Example Application | Heat exchangers need good conductors; furnace linings need insulators. |
- Thermal conductivity affects how fast heat moves through a material.
- It also influences how much a material expands or contracts when the temperature changes.
- If you pick the wrong material, you might end up with cracks or even structural failure.
You can find reliable material property data from research studies and technical reports. Here are a few examples:
| Material | Properties Investigated | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Hempcrete | Thermal properties in fire | Complex heat and mass transfer; conductivity and specific heat measured. |
| Recycled Plastic (RESIN8) | Fire resistance | Different thermal parameters; tested in furnaces. |
| Crumb Rubber | Heat transfer modeling | Constant parameters predicted temperature changes well. |
So, before you jump into your heat transfer calculations, take time to gather your measurements, check your units, and look up the right material properties. This careful prep work will save you headaches and give you results you can trust.
Calculate heat transfer step-by-step
You might feel a little nervous when you first use online physics calculators, but you can relax. These tools guide you through each part of the process. If you follow a step-by-step method to calculate heat transfer, you will get results you can trust. Let’s break it down so you can see how easy it is.
Enter data in the calculator
Start by gathering all your measurements and details. Online physics calculators work best when you give them accurate information. Here’s a step-by-step method to calculate heat transfer and make sure you do not miss anything:
- Choose certified calculators for your heat transfer calculations.
- Measure important variables at one-hour intervals using data loggers. You should track:
- True RMS Power
- Outdoor Air Temperature
- System Air Temperature
- Relative Humidity
- Collect at least six weeks of hourly data for both heating and cooling seasons.
- Use your data to calculate heat transfer for the measurement period, then estimate for the whole year.
- Calculate the humidity ratio using the right equations for your measured relative humidity and temperature.
When you enter your data, double-check each value. Online physics calculators need the right numbers to give you the right answers. If you use a CAD model, remove extra details that do not matter for heat transfer. Define your materials clearly and set the correct boundary conditions. Watch the areas that matter most and make sure your simulation results make sense.
Tip: The more careful you are with your data, the more accurate your heat transfer calculations will be.
Select calculation options
After you enter your data, you will see several options in most online physics calculators. These choices help you match the calculator to your real-world problem. Picking the right options is a big part of getting good results when you calculate heat transfer.
Here’s a table showing some common calculation options and what they mean for your project:
| Calculation Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Select media | Choose a medium for both sides from a drop-down list. |
| Boundary conditions | Set the input and output variables you want. |
| Flow type | Pick if the flow is countercurrent or co-current. This changes heat transfer efficiency. |
| Input temperature difference | Enter the temperature difference between the two fluids. This is key for heat transfer. |
| Volumetric flow rates | Add the flow rates for both fluids. This affects the heat exchanger’s capacity. |
| Size of heat transferring surface | Enter the area available for heat transfer. Bigger areas mean more heat can move. |
| Heat transfer coefficient | Type in the efficiency of heat transfer. This number changes how well your system works. |
| Logarithmic temperature difference | Use this for simple flow forms. It helps when temperature changes along the path. |
Online physics calculators often let you switch between these options. You can try different settings to see how your results change. If you are not sure which option to pick, look for calculators with clear instructions or built-in help.
Note: Always match your calculation options to your real system. This helps you calculate heat transfer with more confidence.
Run and review results
Now you are ready for the final step. Hit the “calculate” button and let the online physics calculators do the work. You will see your results in just a few seconds. Take a close look at the numbers, especially the heat transfer rate and temperature changes.
You should always check if your results make sense. Here are some ways you can verify the accuracy of your heat transfer calculations:
| Verification Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Comparison with Experimental Data | Compare your results with real-world experiments. |
| Use of Multiple Calculation Tools | Try other online physics calculators and see if the answers match. |
| Thermal Testing of Prototypes | Test your design in real conditions to see if it works as expected. |
If your results look strange, go back and check your data and calculation options. Sometimes a small mistake in temperature or flow rate can change everything. Online physics calculators make it easy to try again and fix errors.
Callout: Do not be afraid to run your calculations more than once. The best way to learn is by testing different scenarios and seeing how the results change.
When you use a step-by-step method to calculate heat transfer, you build your skills and confidence. Online physics calculators help you solve problems quickly and accurately. You can use them for school projects, work tasks, or even home improvement ideas. The more you practice, the easier it gets to calculate heat transfer and trust your results.
Interpret results and avoid mistakes
Read output values and units
When you use online physics calculators, you will see different output values. These numbers tell you how much heat moves through your system. The most common outputs include the heat transfer coefficient and the overall U-value. The U-value shows how well your setup moves heat from one side to the other. A higher U-value means heat moves faster, which can help you finish jobs quicker.
Here’s a quick table to help you understand what you see:
| Fluid | Convective heat transfer coefficient (h) |
|---|---|
| Water | about 1000 W/(m²°C) [176 Btu/(hr-ft²°F)] |
| Hot Water | 1000 – 6000 W/(m²°C) [176 – 1057 Btu/(hr-ft²°F)] |
| Steam | 6000 – 15000 W/(m²°C) [1057 – 2641 Btu/(hr-ft²°F)] |
You will also notice units like W m-2 K-1. This unit means how much heat passes through a square meter for each degree of temperature difference. If you see calories or Btu, assume they use the International Table standard unless told otherwise.
Common errors in heat transfer calc
You can avoid many mistakes by knowing what to watch for. Some of the most common mistakes when calculating heat transfer come from mixing up temperature units or guessing the wrong specific heat. Sometimes, people forget that specific heat can change with temperature. Other errors happen when you ignore heat loss to the environment or think everything heats up instantly.
Here are some common mistakes when calculating heat transfer:
- Misestimating specific heat capacity
- Assuming constant specific heat
- Ignoring heat loss to the environment
- Not checking if your sample is the same all over
- Thinking temperature changes happen right away
Tip: Always double-check your numbers and make sure your temperature readings match the units in your online physics calculators.
Tips for accuracy and double-checking
You want your results to be right the first time. Here are some expert tips to improve accuracy and help with troubleshooting your calculations:
- Measure everything carefully. Even small errors in temperature can cause big errors in your results.
- Check your instruments. Some tools cannot catch tiny temperature changes, so know their limits.
- Use Wilson plots to see how temperature difference and heat flow relate, but read them with care.
- Remember, heat transfer coefficients can be tricky, especially with small temperature differences.
- Use guides and tutorials from online physics calculators to make sure you follow every step.
If you run into trouble, try troubleshooting your calculations by comparing your results with another calculator or real-world data. These tips and expert tips to improve accuracy will help you avoid errors and get the most from online physics calculators. Keep practicing, and you will spot mistakes before they cause problems. 😊
You can master heat transfer calculations with just a few clicks. Start by picking a user-friendly calculator, enter your measurements, and review your results. These tools offer fast computations and make the application of online physics calculators in education simple for everyone. Check out the table below to see how easy it is to input your data and get answers:
| Input Parameters | Output Parameters |
|---|---|
| Length, width, conductivity | Thermal resistance for your project |
| Via height, plating thickness | Total resistance for all vias |
You will notice the benefits of using online physics calculators right away. They save time, support interactive learning, and help you gain enhanced understanding. Give one a try and watch your confidence grow!
FAQ
How do I know which type of heat transfer calculator to use?
You need to look at your problem. If you see heat moving through a solid, use conduction. If air or liquid moves heat, pick convection. For heat from sunlight or fire, choose radiation.
Can I use these calculators for any material?
Most calculators let you pick common materials. If you have a special material, check if you can enter custom values for things like thermal conductivity. Always double-check your numbers.
What if my units do not match?
Tip: Always convert your measurements before you start. Use the unit conversion table in this blog. If you mix units, your answer will not make sense.
Do I need to be good at math to use these calculators?
No, you do not! The calculator does the math for you. You just enter your numbers and read the results. If you get stuck, look for help or guides on the calculator page.