A common question is, “What is a DIN rail?” A DIN rail is a metal track designed to hold electrical devices securely. It helps organize components inside control panels or equipment racks efficiently. When people ask what a DIN rail is, they refer to this special mounting system that allows you to quickly and easily install parts in a neat and orderly way.
DIN rails keep electrical systems tidy and efficient by enabling devices to snap into place without the need for extra brackets. Using DIN rails standardizes installations for everyone, allowing installers to save space and assemble systems faster without bulky boxes. Additionally, DIN rail mounting makes it easier to change or repair components later, benefiting anyone who works with these electrical systems.
Key Takeaways
- DIN rails are metal bars that hold electrical devices in place. They help keep control panels tidy and organized. Standard sizes and shapes let devices from many brands fit the same rail. This saves time and money when installing or fixing things. There are three main types of DIN rails. These are Top Hat, C-Section, and G-Section.
- Each type is made for different weights and uses. DIN rails make it simple to add, remove, or upgrade parts. You do not need to drill or rewire. This helps systems grow and stay safe. Factories, energy companies, and transportation use DIN rails a lot. They save space, make things safer, and help repairs go faster.
What Is a DIN Rail
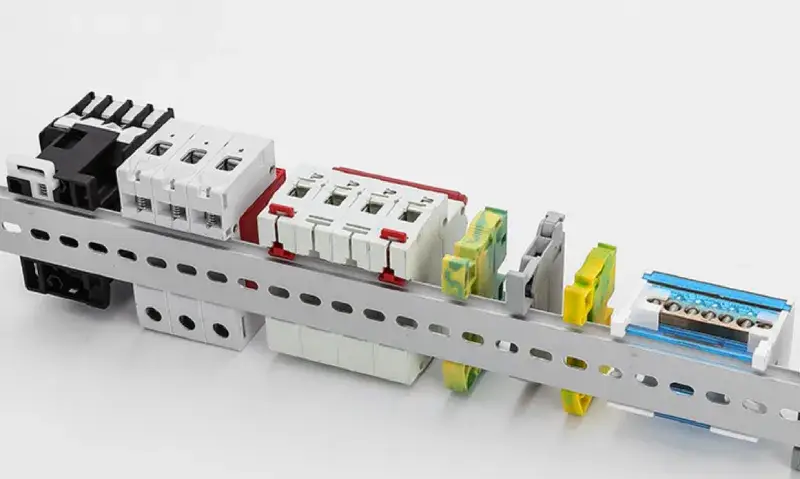
DIN Rail Meaning
People often ask, “what is a din rail” in factories and electrical work. The din rail meaning is a metal strip that holds electrical devices in place. Din rails help organize things inside boxes or panels. People use din rails to put circuit breakers, relays, and terminal blocks in a straight line. This keeps equipment safe and easy to reach. The word “din” comes from German rules that first described these rails. Now, din rails follow worldwide rules for size and shape. These rules make sure devices from different brands fit on the same rail. This helps with compatibility and standardisation.
A table below shows the most well-known standards for din rails:
| Standard / Norm | Description / Scope | Key Dimensions / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DIN 46277 series | Original German standards for din rails | Includes various rail types |
| EN 60715 | Current European standard for top hat rails | 35 mm wide, 7.5 mm and 15 mm depth |
| IEC 60715 | International standard for low-voltage switchgear | Same as EN 60715, international recognition |
| BS 5584 | British Standard for top hat rails | Similar to EN 50022 |
| AS 2756.1997 | Australian Standard for mounting rails | Low-voltage switchgear mounting rails |
These standards make sure din rails work the same everywhere. This makes it easier to install and fix things.
Main Function
The main job of a din rail is to hold electrical parts safely and neatly. Din rails are like the backbone inside control panels and racks. They support things like circuit breakers, surge arrestors, meters, and relays. Din rails do these jobs:
- Hold electrical equipment tightly.
- Let you add or remove devices quickly.
- Keep wires tidy and stop messes.
- Make it easy to change or upgrade parts.
Din rails help with compatibility because their sizes are standard. Installers can use products from many brands. This saves time and money when setting up or fixing things. In control systems, din rails also make things safer. They keep devices secure and lower the chance of electrical problems.
Tip: Din rails let you add or move parts without drilling new holes or redoing wires. This makes it easy to grow or change your electrical setup.
Key Features
Din rails are special because of their strong build and design. These features make them popular for mounting in many jobs. Some key features are:
- Standardized Design: Din rails have set sizes, so parts fit and are easy to swap.
- Material Strength: Most din rails are made from steel with a zinc coat. This keeps them strong against heat and rust.
- Types of Din Rails: There are three main types—top hat, C-section, and G-section. Each type works for different weights and needs.
- Snap-On Mounting: Devices can snap or slide onto the rail. This makes setup fast and lowers mistakes.
- Space Efficiency: Din rails let you put devices close together, saving space.
- Safety and Reliability: Strong build, modular design, and airflow options protect parts and make systems work better.
A table below shows how din rail features help with safety and reliability:
| Design Feature | Safety and Reliability Benefit |
|---|---|
| Robust Construction | Protects parts from dust, water, and damage |
| Modular Design | Lets you arrange devices safely and flexibly |
| Ventilation Options | Stops overheating and keeps things safe |
| Easy Installation | Lowers mistakes and makes repairs faster |
| Standardisation and Compatibility | Makes sure all parts fit, no matter the brand |
Din rails are important in control panels and automation systems. Their modular and scalable design is good for setups that may grow or change. The snap-on feature and neat layout help with quick upgrades and fixing problems. Din rails keep systems safe, reliable, and simple to manage.
DIN Rail Types
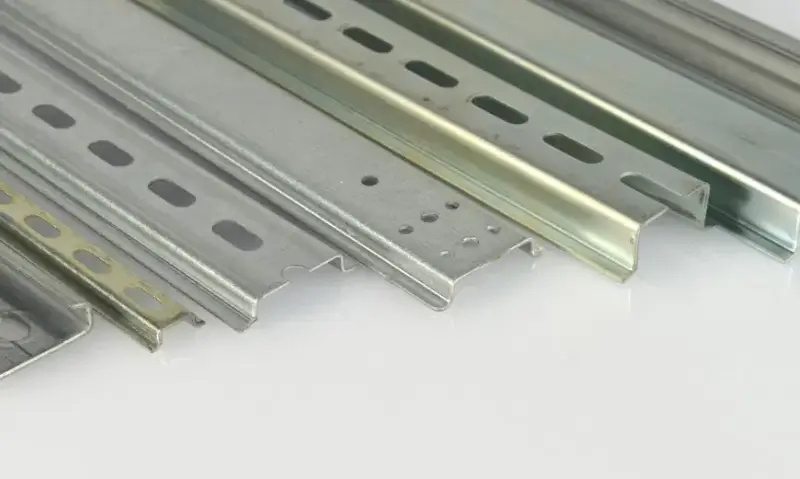
DIN rails come in different shapes and sizes. The main types are Top Hat, C-Section, and G-Section. Each type looks different and is used for special jobs. These DIN rails follow rules that help them fit with many brands.
| DIN Rail Type | Cross-Section Shape | Width (mm) | Depth/Height (mm) | Typical Use/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top Hat (TS35) | Hat-shaped (like a top hat) | 35 | 7.5 or 15 | Most common; standard mounting rail for many components |
| Mini Top Hat (TS15) | Smaller top hat shape | 15 | 5.5 | Used for compact components, space-saving |
| C Section | C-shaped | 32 | 20, 30, 40, 50 | Older type; preferred for heavier components like transformers |
| G Section | G-shaped profile | 32 | N/A | Heavy-duty components such as power supplies |
DIN, EN, and IEC set the rules for these rails. This makes them good for many jobs.
Top Hat
The Top Hat DIN rail is also called TS35. It is the most popular type. It has a “hat” shape and is 35 mm wide. People use it to hold many electrical parts. These include circuit breakers, relays, and terminal blocks. The Top Hat DIN rail is easy to use. You can snap devices onto it without tools. Many places use this rail because it is flexible and fits many needs.
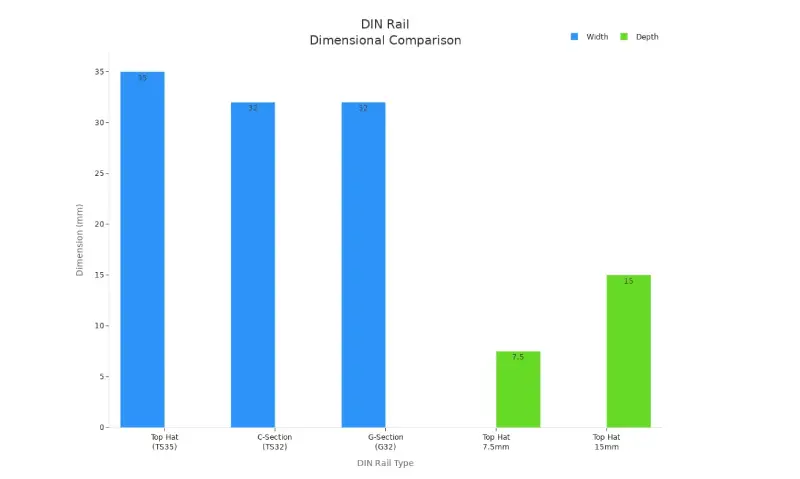
Note: Top Hat DIN rails come in two depths. The 7.5 mm size is for normal loads. The 15 mm size is for heavier parts.
C-Section
The C-Section DIN rail is also called TS32. It has a “C” shape and is 32 mm wide. It comes in different heights, like 20, 30, 40, or 50 mm. This type was used more in the past. Electricians pick C-Section rails for heavy things, like transformers. It gives strong support but is not as common now. Some old equipment still needs this rail because of its strength.
G-Section
The G-Section DIN rail has a “G” shape and is very strong. It is 32 mm wide and has a deep side. This shape makes it stable for heavy parts. People use G-Section rails for big power supplies and heavy relays. The strong steel keeps it from bending.
- G-Section DIN rails are extra strong and stable.
- The shape helps you install them the right way.
- They are best for heavy or important parts.
- Stainless steel or zinc coating keeps them from rusting.
DIN rails, especially G-Section, help keep systems safe. Their strong build and set sizes make them great for holding big electrical parts.
Applications of DIN Rails
Where DIN Rails Are Used
DIN rails are found in many places where safety is important. People often see DIN rails inside control panels and equipment racks. They are also in electrical enclosures and factory systems. DIN rails are used in places like factories and outdoor boxes.
These places can have dust, water, or big temperature changes. DIN rails help keep wires neat and save space. You can put them up and down or side to side. This makes it easy to fit more parts in small spaces. In control systems, DIN rails hold devices in place. This makes fixing or changing parts much easier.
Tip: DIN rails let you use space better in factories by giving you more ways to mount things.
Devices Mounted on DIN Rails
Many devices are made to fit on DIN rails. Some common ones are:
- Circuit breakers that stop too much electricity.
- Terminal blocks that help connect wires.
- Relays that let small signals control big circuits.
- Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for running machines.
- Motor controllers that control motors.
- Surge arrestors, switch disconnectors, and DIN rail meters.
- Transformers, automation controllers, actuators, and power supplies.
These devices often snap onto the DIN rail. This makes it fast to put them on or take them off. It helps workers fix things quickly. DIN rail terminal blocks help keep wires tidy in control systems.
Industries
Many industries use DIN rails to keep equipment organized. Factories, energy companies, trains, phone networks, and car makers all use DIN rails. Plants and power companies use DIN rail terminal blocks to keep things safe and neat. The chart below shows how much each industry uses DIN rails:
| Industry Sector | Approximate Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | 40 |
| Energy and Utilities | 30 |
| Transportation (Rail) | 15 |
| Automotive and Telecom | 10 |
DIN rails help these industries by saving space and making things easy to fix. They keep parts safe and help workers do their jobs faster. DIN rails are important for safety and getting work done in many fields.
Installation and Materials
Installation Basics
To install a DIN rail, you follow simple steps. First, the technician gets all the tools and parts. These include the DIN rail, terminal blocks, wires, and a screwdriver. Sometimes, they also need crimping tools. The technician puts the DIN rail inside the box. Screws or clips hold the rail tight. The rail must be flat and face the right way.
Next, the technician snaps terminal blocks onto the rail. Each block lines up with the edge. The technician strips the wire ends to remove the cover. Sometimes, they add wire ferrules for better connections. The wires go into the terminal blocks. The technician tightens the screws or clamps. They gently pull each wire to check it is tight. The technician labels the blocks to help with repairs. End brackets stop the blocks from moving. The technician always turns off the power before starting.
Tip: Using the right tools, like a drill and measuring tape, helps make the job safe and quick. This also saves time when installing.
Material Options
DIN rails are made from different materials. The most common are:
- Steel, which is strong and lasts a long time.
- Aluminum, which is light and does not rust easily.
- Stainless steel, which is good for wet or tough places.
- Copper, which is used for special electrical jobs.
The table below shows how these materials compare:
| Material | Durability | Corrosion Resistance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High, robust in harsh conditions | Excellent, best for moisture and chemicals | Longest-lasting, ideal for tough settings |
| Steel | Strong mechanical strength | Moderate, needs protective coating | Cost-effective, good for most uses |
| Aluminum | Lower strength | Good, natural oxide layer | Lightweight, best for light loads |
Safety
DIN rails help keep electrical systems safe. They hold circuit breakers, relays, and terminal blocks steady. This stops things from coming loose or breaking. DIN rails keep wires neat and in order. This helps air move and keeps things from getting too hot.
DIN rails also hold safety devices like circuit breakers. These protect against too much electricity or short circuits. You can snap parts on or off without moving other parts. This makes fixing and upgrading easier. DIN rails follow rules like IEC 60715 to make sure they are safe and work well in many places.
DIN rails are very important in modern automation. They help keep electrical systems neat and working well. Their standard design lets people install them fast. It is also easy to fix or check things when needed. Many industries use DIN rails because they hold many types of devices. This makes it easier to find and fix problems.
- DIN rails help save space and stop long delays.
- You can upgrade or change parts easily because they are modular.
- The standard size makes sure everything fits and stays safe.
If you are starting a new electrical or factory project, DIN rails make setup simple and help things work better.
FAQ
What devices can be mounted on a DIN rail?
Electricians can mount circuit breakers, relays, terminal blocks, power supplies, and controllers on a DIN rail. These devices snap onto the rail for easy installation and removal.
Why do control panels use DIN rails?
Control panels use DIN rails to keep electrical parts organized and secure. This system saves space, helps with airflow, and makes repairs or upgrades faster.
Are DIN rails safe for outdoor use?
DIN rails made from stainless steel or aluminum resist rust and moisture. These materials work well in outdoor or harsh environments, keeping electrical systems safe.
How do you remove a device from a DIN rail?
A worker can remove a device by releasing its mounting clip or latch. Most devices slide or snap off the rail without special tools.
Can you reuse a DIN rail?
Yes, a DIN rail can be reused if it stays straight and free from damage. Workers often move rails to new panels or systems when needed.
Conclusion
DIN rails play a vital role in organizing and securing electrical components across control panels and automation systems. Their standardized design, space-saving structure, and easy snap-on mounting make them essential for efficient system setups. Whether used in factories, utilities, or transport, DIN rails reduce downtime and enhance safety.
For scalable, future-ready electrical installations, DIN rails are the smart choice trusted by professionals worldwide. Invest in reliability and system growth with DIN rail solutions.




